GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Allosteric Modulators
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Immuno Cell Type Associations
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 413 | 5q32 | ADRB2 | adrenoceptor beta 2 | 91 |
| Mouse | 7 | 418 | 18 35.1 cM | Adrb2 | adrenergic receptor, beta 2 | 4 |
| Rat | 7 | 418 | 18q12.1 | Adrb2 | adrenoceptor beta 2 | 60 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| ADRB2R | ADRBR | B2AR | beta-2 adrenoreceptor | beta-2 adrenergic receptor | beta 2-AR | Gpcr7 | Adrb-2 | adrenoceptor beta 2, surface | adrenergic receptor |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | adrb2_human (Hs), adrb2_mouse (Mm), adrb2_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P07550 (Hs), P18762 (Mm), P10608 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL210 (Hs), CHEMBL3707 (Mm), CHEMBL3754 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P07550 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000169252 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000045730 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000019217 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 154 (Hs), 11555 (Mm), 24176 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000169252 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:154 (Hs), mmu:11555 (Mm), rno:24176 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 109690 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P07550 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000024 (Hs), NM_007420 (Mm), NM_012492 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000015 (Hs), NP_031446 (Mm), NP_036624 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
1862 (in complex with (-)-adrenaline) 1879 (in complex with alprenolol) 80268 (in complex with carazolol) 1873 (in complex with ICI 118551) 1888 (in complex with timolol) |
| UniProtKB | P07550 (Hs), P18762 (Mm), P10608 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | ADRB2 (Hs) |
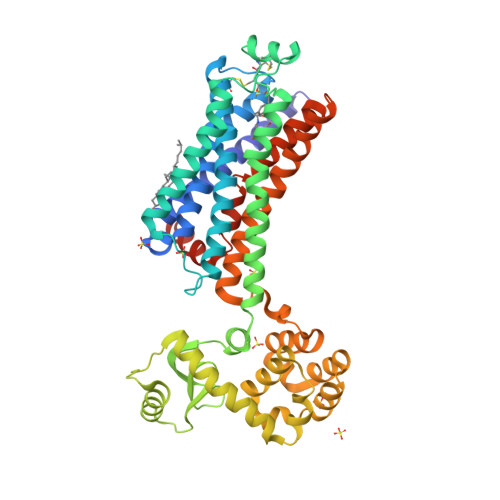
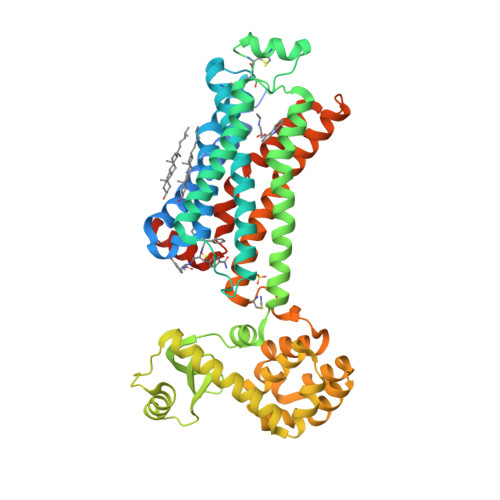
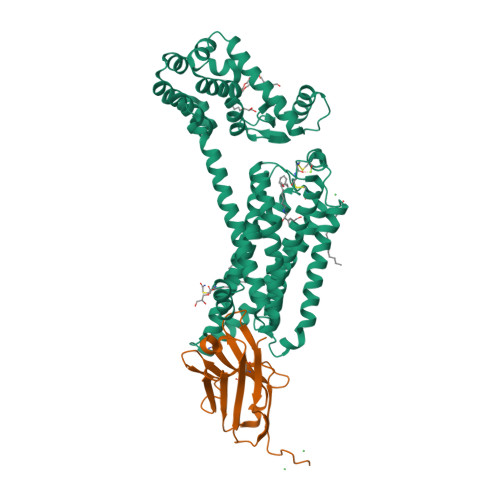
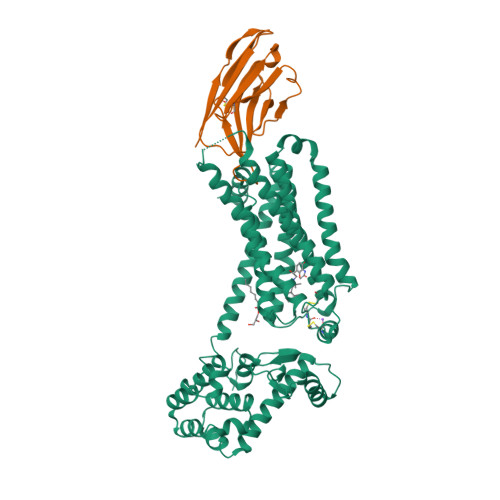
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
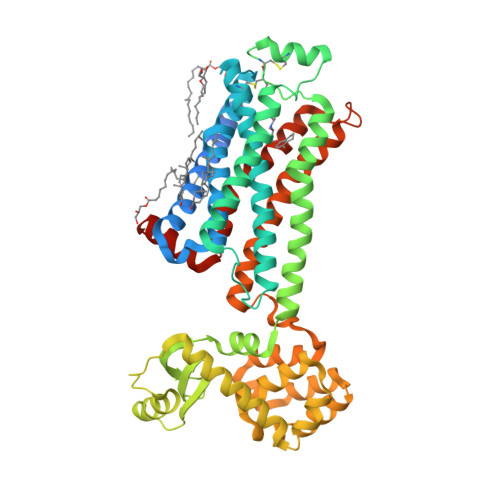
|
|
||||||||||||
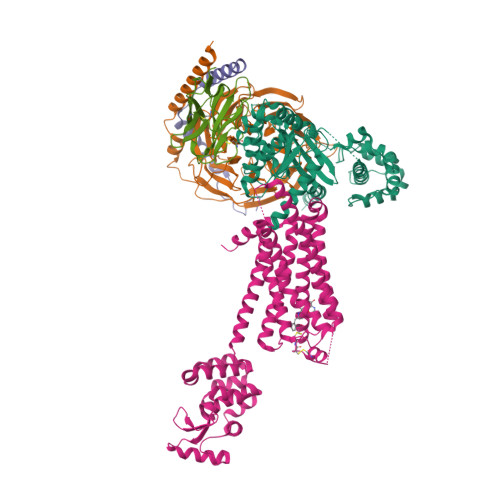
|
|
||||||||||||
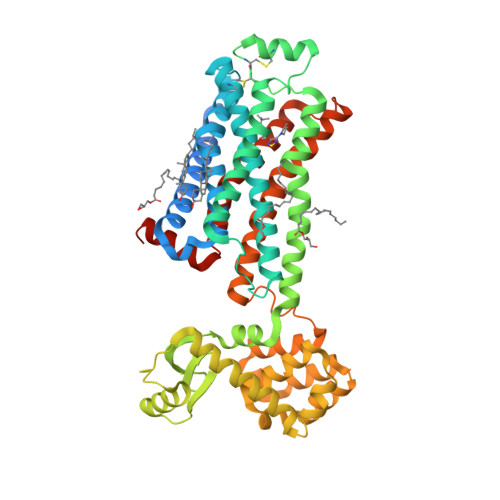
|
|
||||||||||||
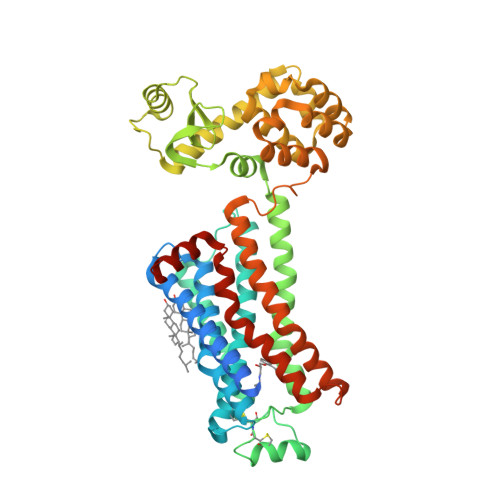
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| (-)-adrenaline |
| (-)-noradrenaline |
| Zn2+ |
| Comments: Adrenaline exhibits greater potency than noradrenaline |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands (Human) |
| (-)-adrenaline > (-)-noradrenaline |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Although [138] states that salbutamol was tested, in fact R-(-)salbutamol (levosalbutamol) was tested. pKi values are from binding studies and pEC50 from functional studies (usually cAMP generation) which give a better idea of relative experimental or clinical potency. Salbutamol, terbutaline and fenoterol are examples of short acting β agonists (SABAs), salmeterol and formoterol are long acting β agonists (LABAs) and indacaterol, olodaterol abediterol and vilanterol are ultra long acting β agonists (ultra-LABAs) [26]. BRL37344 and BRL35135 are classified as β3-AR selective agonists (rodent selective) but have significant actions at β2-AR [118]. Clenbuterol is included on the World Anti-Doping Authority's list of banned substances due to its popularity as a drug used by bodybuilders and for weight loss. Clinical uses: β2-AR agonists are widely used in asthma and COPD. Adrenaline is used as a bolus injection in cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis and as an intravenous infusion for shock. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The approved drug propranolol is categorised as a non-selective β-adrenoceptor antagonist but is slightly selective for β2-AR and has very low affinity for β3-AR. Propranolol also behaves as a biased agonist in several studies- an inverse agonist decreasing cAMP whilst stimulating β-arrestin and gene transcription [11,16]. Carvedilol is a non-selective β-AR and α1-AR antagonist used to treat cardiac failure. Carvedilol has been suggested to be a β-arrestin biased agonist [161] but this characteristic has been challenged [23] with evidence supporting low efficacy activation of Gs coupled β2-adrenoceptors as the explanation. Several 'cardioselective' or β1-AR selective antagonists such as atenolol and metoprolol have appreciable affinity for β2-AR. Several antagonists may display partial agonist activity at β2-AR including pindolol, carazolol, bucindolol, nebivolol and carvedilol [14] in assays where there is significant receptor reserve or receptor over-expression. ICI118551 is the most selective β2-AR antagonist currently available but is only used in in vitro studies where it displays ~300 fold selectivity vs. the other 8 adrenoceptor subtypes. Although often described as a β3-AR selective antagonist, SR59230A has little selectivity and is a high affinity antagonist at β2-AR [115]. The main action of propafenone is to block voltage gated Na+ channels (see the Voltage-gated sodium channels family in the Ion Channels section of this website for further details) but is also a weak β-adrenoceptor antagonist. Some cell systems (e.g. HEK cells) commonly used to study the pharmacology of β-AR subtypes express functionally active β2-AR populations. Clinical uses: not directly used, but effects of several β-AR antagonists used clinically (see β1-AR) are also likely to occur through β2-AR (e.g. migraine, portal hypertension, anxiety, glaucoma, thyrotoxicosis, infantile haemangioma). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific allosteric modulator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zn2+ appears to have both positive and negative effects on agonist affinity. At low concentrations it appears to enhance agonist affinity and agonist-stimulated cAMP accumulation. At high concentrations Zn2+ inhibits agonist binding but slows antagonist dissociation [143-144]. Cmpd-6 is a positive allosteric modulator of the pharmacological activity of carvedilol at the β2-AR [121]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| β2-ARs are expressed on innate and adaptive immune cells of humans and rodents, and are reported to have an immuno-modulating effect [48]. There is a large literature on the role of autoantibodies to β2-AR associated with a variety of disease processes [31,37,75,78,160]. |
| Cell Type Associations | ||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gs family | |
| Comments: Stimulation of adenylate cyclase (AC) causes the conversion of ATP into cAMP. This activates protein kinase A, which in turn phosphorylates several substrates, for example L-type Ca2+ channels. In skeletal muscle cAMP signalling is associated with mTORC2 activation that promotes GLUT4 translocation and increased glucose uptake. | |
| References: 100,135,140,159 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family | Guanylate cyclase stimulation |
| Comments: Adenylyl cyclase inhibition reduces the conversion of ATP to cAMP. Stimulation of guanylyl cyclase (GC) causes an increase in cGMP levels, and subsequent activation of protein kinase G. | |
| References: 100,162 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
| General Comments |
| For a review on the β-adrenoceptor polymorphisms see reference [98]. |
References
1. Abraham G, Kneuer C, Ehrhardt C, Honscha W, Ungemach FR. (2004) Expression of functional beta2-adrenergic receptors in the lung epithelial cell lines 16HBE14o(-), Calu-3 and A549. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1691 (2-3): 169-79. [PMID:15110997]
2. Ahn S, Kahsai AW, Pani B, Wang QT, Zhao S, Wall AL, Strachan RT, Staus DP, Wingler LM, Sun LD et al.. (2017) Allosteric "beta-blocker" isolated from a DNA-encoded small molecule library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 114 (7): 1708-1713. [PMID:28130548]
3. Alikhani V, Beer D, Bentley D, Bruce I, Cuenoud BM, Fairhurst RA, Gedeck P, Haberthuer S, Hayden C, Janus D et al.. (2004) Long-chain formoterol analogues: an investigation into the effect of increasing amino-substituent chain length on the beta2-adrenoceptor activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 14 (18): 4705-10. [PMID:15324892]
4. Allen JM, Baetge EE, Abrass IB, Palmiter RD. (1988) Isoproterenol response following transfection of the mouse beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene into Y1 cells. EMBO J, 7 (1): 133-8. [PMID:2834198]
5. André C, Erraji L, Gaston J, Grimber G, Briand P, Guillet JG. (1996) Transgenic mice carrying the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene with its own promoter overexpress beta 2-adrenergic receptors in liver. Eur J Biochem, 241 (2): 417-24. [PMID:8917438]
6. Angers S, Salahpour A, Joly E, Hilairet S, Chelsky D, Dennis M, Bouvier M. (2000) Detection of beta 2-adrenergic receptor dimerization in living cells using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 97 (7): 3684-9. [PMID:10725388]
7. Aparici M, Gómez-Angelats M, Vilella D, Otal R, Carcasona C, Viñals M, Ramos I, Gavaldà A, De Alba J, Gras J et al.. (2012) Pharmacological characterization of abediterol, a novel inhaled β(2)-adrenoceptor agonist with long duration of action and a favorable safety profile in preclinical models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 342 (2): 497-509. [PMID:22588259]
8. Araujo LP, Maricato JT, Guereschi MG, Takenaka MC, Nascimento VM, de Melo FM, Quintana FJ, Brum PC, Basso AS. (2019) The Sympathetic Nervous System Mitigates CNS Autoimmunity via β2-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling in Immune Cells. Cell Rep, 28 (12): 3120-3130.e5. [PMID:31533035]
9. Aristotelous T, Ahn S, Shukla AK, Gawron S, Sassano MF, Kahsai AW, Wingler LM, Zhu X, Tripathi-Shukla P, Huang XP et al.. (2013) Discovery of β2 Adrenergic Receptor Ligands Using Biosensor Fragment Screening of Tagged Wild-Type Receptor. ACS Med Chem Lett, 4 (10): 1005-1010. [PMID:24454993]
10. Auerbach SS, DrugMatrix® and ToxFX® Coordinator National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program: Dept of Health and Human Services. Accessed on 02/05/2014. Modified on 02/05/2014. DrugMatrix, https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/drugmatrix/index.html
11. Azzi M, Charest PG, Angers S, Rousseau G, Kohout T, Bouvier M, Piñeyro G. (2003) Beta-arrestin-mediated activation of MAPK by inverse agonists reveals distinct active conformations for G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (20): 11406-11. [PMID:13679574]
12. Baerwald C, Graefe C, Muhl C, Von Wichert P, Krause A. (1992) Beta 2-adrenergic receptors on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with rheumatic diseases. Eur J Clin Invest, 22 Suppl 1: 42-6. [PMID:1333966]
13. Baker JG. (2005) The selectivity of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists at the human beta1, beta2 and beta3 adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol, 144 (3): 317-22. [PMID:15655528]
14. Baker JG. (2010) The selectivity of beta-adrenoceptor agonists at human beta1-, beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol, 160 (5): 1048-61. [PMID:20590599]
15. Baker JG, Hall IP, Hill SJ. (2002) Pharmacological characterization of CGP 12177 at the human beta(2)-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol, 137 (3): 400-8. [PMID:12237261]
16. Baker JG, Hall IP, Hill SJ. (2003) Agonist and inverse agonist actions of beta-blockers at the human beta 2-adrenoceptor provide evidence for agonist-directed signaling. Mol Pharmacol, 64 (6): 1357-69. [PMID:14645666]
17. Baker JG, Hall IP, Hill SJ. (2003) Influence of agonist efficacy and receptor phosphorylation on antagonist affinity measurements: differences between second messenger and reporter gene responses. Mol Pharmacol, 64 (3): 679-88. [PMID:12920204]
18. Baker JG, Proudman RG, Hill SJ. (2015) Salmeterol's extreme β2 selectivity is due to residues in both extracellular loops and transmembrane domains. Mol Pharmacol, 87 (1): 103-20. [PMID:25324048]
19. Barki-Harrington L, Luttrell LM, Rockman HA. (2003) Dual inhibition of beta-adrenergic and angiotensin II receptors by a single antagonist: a functional role for receptor-receptor interaction in vivo. Circulation, 108 (13): 1611-8. [PMID:12963634]
20. Basarrate S, Monzel AS, Smith JLM, Marsland AL, Trumpff C, Picard M. (2024) Glucocorticoid and Adrenergic Receptor Distribution Across Human Organs and Tissues: A Map for Stress Transduction. Psychosom Med, 86 (2): 89-98. [PMID:38193786]
21. Battram C, Charlton SJ, Cuenoud B, Dowling MR, Fairhurst RA, Farr D, Fozard JR, Leighton-Davies JR, Lewis CA, McEvoy L et al.. (2006) In vitro and in vivo pharmacological characterization of 5-[(R)-2-(5,6-diethyl-indan-2-ylamino)-1-hydroxy-ethyl]-8-hydroxy-1H-quinolin-2-one (indacaterol), a novel inhaled beta(2) adrenoceptor agonist with a 24-h duration of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 317 (2): 762-70. [PMID:16434564]
22. Beattie D, Beer D, Bradley ME, Bruce I, Charlton SJ, Cuenoud BM, Fairhurst RA, Farr D, Fozard JR, Janus D et al.. (2012) An investigation into the structure-activity relationships associated with the systematic modification of the β(2)-adrenoceptor agonist indacaterol. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22 (19): 6280-5. [PMID:22932315]
23. Benkel T, Zimmermann M, Zeiner J, Bravo S, Merten N, Lim VJY, Matthees ESF, Drube J, Miess-Tanneberg E, Malan D et al.. (2022) How Carvedilol activates β2-adrenoceptors. Nat Commun, 13 (1): 7109. [PMID:36402762]
24. Bernstein D, Fajardo G, Zhao M, Urashima T, Powers J, Berry G, Kobilka BK. (2005) Differential cardioprotective/cardiotoxic effects mediated by beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 289 (6): H2441-9. [PMID:16040722]
25. Berthouze M, Ayoub M, Russo O, Rivail L, Sicsic S, Fischmeister R, Berque-Bestel I, Jockers R, Lezoualc'h F. (2005) Constitutive dimerization of human serotonin 5-HT4 receptors in living cells. FEBS Lett, 579 (14): 2973-80. [PMID:15896782]
26. Billington CK, Penn RB, Hall IP. (2017) β2 Agonists. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 237: 23-40. [PMID:27878470]
27. Blake K, Lima J. (2015) Pharmacogenomics of long-acting β2-agonists. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 11 (11): 1733-51. [PMID:26235677]
28. Bokoch MP, Zou Y, Rasmussen SG, Liu CW, Nygaard R, Rosenbaum DM, Fung JJ, Choi HJ, Thian FS, Kobilka TS et al.. (2010) Ligand-specific regulation of the extracellular surface of a G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature, 463 (7277): 108-12. [PMID:20054398]
29. Bouyssou T, Casarosa P, Naline E, Pestel S, Konetzki I, Devillier P, Schnapp A. (2010) Pharmacological characterization of olodaterol, a novel inhaled beta2-adrenoceptor agonist exerting a 24-hour-long duration of action in preclinical models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 334 (1): 53-62. [PMID:20371707]
30. Breit A, Lagacé M, Bouvier M. (2004) Hetero-oligomerization between beta2- and beta3-adrenergic receptors generates a beta-adrenergic signaling unit with distinct functional properties. J Biol Chem, 279 (27): 28756-65. [PMID:15123695]
31. Brisinda D, Sorbo AR, Venuti A, Ruggieri MP, Manna R, Fenici P, Wallukat G, Hoebeke J, Frustaci A, Fenici R. (2012) Anti-β-adrenoceptors autoimmunity causing 'idiopathic' arrhythmias and cardiomyopathy. Circ J, 76 (6): 1345-53. [PMID:22447021]
32. Brown DA, Dunn PM. (1983) Depolarization of rat isolated superior cervical ganglia mediated by beta 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol, 79 (2): 429-39. [PMID:6140042]
33. Burgess C, Ayson M, Rajasingham S, Crane J, Della Cioppa G, Till MD. (1998) The extrapulmonary effects of increasing doses of formoterol in patients with asthma. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 54 (2): 141-7. [PMID:9626918]
34. Buxton BF, Jones CR, Molenaar P, Summers RJ. (1987) Characterization and autoradiographic localization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in human cardiac tissues. Br J Pharmacol, 92 (2): 299-310. [PMID:2823947]
35. Callaerts-Vegh Z, Evans KL, Dudekula N, Cuba D, Knoll BJ, Callaerts PF, Giles H, Shardonofsky FR, Bond RA. (2004) Effects of acute and chronic administration of beta-adrenoceptor ligands on airway function in a murine model of asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101 (14): 4948-53. [PMID:15069206]
36. Candelore MR, Deng L, Tota L, Guan XM, Amend A, Liu Y, Newbold R, Cascieri MA, Weber AE. (1999) Potent and selective human beta(3)-adrenergic receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 290 (2): 649-55. [PMID:10411574]
37. Cao N, Chen H, Bai Y, Yang X, Xu W, Hao W, Zhou Y, Chai J, Wu Y, Wang Z et al.. (2018) β2-adrenergic receptor autoantibodies alleviated myocardial damage induced by β1-adrenergic receptor autoantibodies in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res, 114 (11): 1487-1498. [PMID:29746700]
38. Carzaniga L, Linney ID, Rizzi A, Delcanale M, Schmidt W, Knight CK, Pastore F, Miglietta D, Carnini C, Cesari N et al.. (2022) Discovery of Clinical Candidate CHF-6366: A Novel Super-soft Dual Pharmacology Muscarinic Antagonist and β2 Agonist (MABA) for the Inhaled Treatment of Respiratory Diseases. J Med Chem, 65 (15): 10233-10250. [PMID:35901125]
39. Chandrasekera PC, Wan TC, Gizewski ET, Auchampach JA, Lasley RD. (2013) Adenosine A1 receptors heterodimerize with β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors creating novel receptor complexes with altered G protein coupling and signaling. Cell Signal, 25 (4): 736-42. [PMID:23291003]
40. Cherezov V, Rosenbaum DM, Hanson MA, Rasmussen SG, Thian FS, Kobilka TS, Choi HJ, Kuhn P, Weis WI, Kobilka BK et al.. (2007) High-resolution crystal structure of an engineered human beta2-adrenergic G protein-coupled receptor. Science, 318 (5854): 1258-65. [PMID:17962520]
41. Chruscinski AJ, Rohrer DK, Schauble E, Desai KH, Bernstein D, Kobilka BK. (1999) Targeted disruption of the beta2 adrenergic receptor gene. J Biol Chem, 274 (24): 16694-700. [PMID:10358008]
42. Church JE, Trieu J, Sheorey R, Chee AY, Naim T, Baum DM, Ryall JG, Gregorevic P, Lynch GS. (2014) Functional β-adrenoceptors are important for early muscle regeneration in mice through effects on myoblast proliferation and differentiation. PLoS One, 9 (7): e101379. [PMID:25000590]
43. Cockcroft JR, Gazis AG, Cross DJ, Wheatley A, Dewar J, Hall IP, Noon JP. (2000) Beta(2)-adrenoceptor polymorphism determines vascular reactivity in humans. Hypertension, 36 (3): 371-5. [PMID:10988267]
44. Cros C, Brette F. (2013) Functional subcellular distribution of β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors in rat ventricular cardiac myocytes. Physiol Rep, 1 (3): e00038. [PMID:24303124]
45. Dang V, Medina B, Das D, Moghadam S, Martin KJ, Lin B, Naik P, Patel D, Nosheny R, Wesson Ashford J et al.. (2014) Formoterol, a long-acting β2 adrenergic agonist, improves cognitive function and promotes dendritic complexity in a mouse model of Down syndrome. Biol Psychiatry, 75 (3): 179-88. [PMID:23827853]
46. De Pascali F, Ippolito M, Wolfe E, Komolov KE, Hopfinger N, Lemenze D, Kim N, Armen RS, An SS, Scott CP et al.. (2022) β2 -Adrenoceptor agonist profiling reveals biased signalling phenotypes for the β2 -adrenoceptor with possible implications for the treatment of asthma. Br J Pharmacol, 179 (19): 4692-4708. [PMID:35732075]
47. Dehvari N, Sato M, Bokhari MH, Kalinovich A, Ham S, Gao J, Nguyen HTM, Whiting L, Mukaida S, Merlin J et al.. (2020) The metabolic effects of mirabegron are mediated primarily by β3 -adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 8 (5): e00643. [PMID:32813332]
48. Elenkov IJ, Wilder RL, Chrousos GP, Vizi ES. (2000) The sympathetic nerve--an integrative interface between two supersystems: the brain and the immune system. Pharmacol Rev, 52 (4): 595-638. [PMID:11121511]
49. Elnatan J, Molenaar P, Rosenfeldt FL, Summers RJ. (1994) Autoradiographic localization and quantitation of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in the human atrioventricular conducting system: a comparison of patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy and ischemic heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 26 (3): 313-23. [PMID:7913135]
50. Erdogan BR, Michel MC, Arioglu-Inan E. (2020) Expression and Signaling of β-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in the Diabetic Heart. Cells, 9 (12). [PMID:33256212]
51. Fernandes GW, Ueta CB, Fonseca TL, Gouveia CH, Lancellotti CL, Brum PC, Christoffolete MA, Bianco AC, Ribeiro MO. (2014) Inactivation of the adrenergic receptor β2 disrupts glucose homeostasis in mice. J Endocrinol, 221 (3): 381-90. [PMID:24868110]
52. Frazier EP, Michel-Reher MB, van Loenen P, Sand C, Schneider T, Peters SL, Michel MC. (2011) Lack of evidence that nebivolol is a β₃-adrenoceptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol, 654 (1): 86-91. [PMID:21172342]
53. Frey UH, Karlik J, Herbstreit F, Peters J. (2014) β2-Adrenoceptor gene variants affect vasopressor requirements in patients after thoracic epidural anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth, 112 (3): 477-84. [PMID:24366725]
54. Frielle T, Daniel KW, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. (1988) Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor subtype specificity studied with chimeric beta 1/beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 85 (24): 9494-8. [PMID:2849109]
55. Gálvez I, Martín-Cordero L, Hinchado MD, Álvarez-Barrientos A, Ortega E. (2019) Anti-inflammatory effect of β2 adrenergic stimulation on circulating monocytes with a pro-inflammatory state in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Brain Behav Immun, 80: 564-572. [PMID:31055173]
56. Galaz-Montoya M, Wright SJ, Rodriguez GJ, Lichtarge O, Wensel TG. (2017) β2-Adrenergic receptor activation mobilizes intracellular calcium via a non-canonical cAMP-independent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem, 292 (24): 9967-9974. [PMID:28442571]
57. Gao V, Suzuki A, Magistretti PJ, Lengacher S, Pollonini G, Steinman MQ, Alberini CM. (2016) Astrocytic β2-adrenergic receptors mediate hippocampal long-term memory consolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 113 (30): 8526-31. [PMID:27402767]
58. Garovic VD, Joyner MJ, Dietz NM, Boerwinkle E, Turner ST. (2003) Beta(2)-adrenergic receptor polymorphism and nitric oxide-dependent forearm blood flow responses to isoproterenol in humans. J Physiol (Lond.), 546 (Pt 2): 583-9. [PMID:12527744]
59. Giordani L, Cuzziol N, Del Pinto T, Sanchez M, Maccari S, Massimi A, Pietraforte D, Viora M. (2015) β2-Agonist clenbuterol hinders human monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells. Exp Cell Res, 339 (2): 163-73. [PMID:26524508]
60. Gocayne J, Robinson DA, FitzGerald MG, Chung FZ, Kerlavage AR, Lentes KU, Lai J, Wang CD, Fraser CM, Venter JC. (1987) Primary structure of rat cardiac beta-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors obtained by automated DNA sequence analysis: further evidence for a multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 84 (23): 8296-300. [PMID:2825184]
61. Grisanti LA, Gumpert AM, Traynham CJ, Gorsky JE, Repas AA, Gao E, Carter RL, Yu D, Calvert JW, García AP et al.. (2016) Leukocyte-Expressed β2-Adrenergic Receptors Are Essential for Survival After Acute Myocardial Injury. Circulation, 134 (2): 153-67. [PMID:27364164]
62. Guereschi MG, Araujo LP, Maricato JT, Takenaka MC, Nascimento VM, Vivanco BC, Reis VO, Keller AC, Brum PC, Basso AS. (2013) Beta2-adrenergic receptor signaling in CD4+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells enhances their suppressive function in a PKA-dependent manner. Eur J Immunol, 43 (4): 1001-12. [PMID:23436577]
63. Guhan AR, Cooper S, Oborne J, Lewis S, Bennett J, Tattersfield AE. (2000) Systemic effects of formoterol and salmeterol: a dose-response comparison in healthy subjects. Thorax, 55 (8): 650-6. [PMID:10899240]
64. Haack KK, Tougas MR, Jones KT, El-Dahr SS, Radhakrishna H, McCarty NA. (2010) A novel bioassay for detecting GPCR heterodimerization: transactivation of beta 2 adrenergic receptor by bradykinin receptor. J Biomol Screen, 15 (3): 251-60. [PMID:20150590]
65. Hague C, Uberti MA, Chen Z, Bush CF, Jones SV, Ressler KJ, Hall RA, Minneman KP. (2004) Olfactory receptor surface expression is driven by association with the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101 (37): 13672-6. [PMID:15347813]
66. Haley JM, Thackeray JT, Thorn SL, DaSilva JN. (2015) Cardiac β-Adrenoceptor Expression Is Reduced in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats as Type-2 Diabetes Progresses. PLoS One, 10 (5): e0127581. [PMID:25996498]
67. Hanson MA, Cherezov V, Griffith MT, Roth CB, Jaakola VP, Chien EY, Velasquez J, Kuhn P, Stevens RC. (2008) A specific cholesterol binding site is established by the 2.8 A structure of the human beta2-adrenergic receptor. Structure, 16 (6): 897-905. [PMID:18547522]
68. Havekes R, Canton DA, Park AJ, Huang T, Nie T, Day JP, Guercio LA, Grimes Q, Luczak V, Gelman IH et al.. (2012) Gravin orchestrates protein kinase A and β2-adrenergic receptor signaling critical for synaptic plasticity and memory. J Neurosci, 32 (50): 18137-49. [PMID:23238728]
69. Hebert TE, Moffett S, Morello JP, Loisel TP, Bichet DG, Barret C, Bouvier M. (1996) A peptide derived from a beta2-adrenergic receptor transmembrane domain inhibits both receptor dimerization and activation. J Biol Chem, 271 (27): 16384-92. [PMID:8663163]
70. Hervé J, Dubreil L, Tardif V, Terme M, Pogu S, Anegon I, Rozec B, Gauthier C, Bach JM, Blancou P. (2013) β2-Adrenoreceptor agonist inhibits antigen cross-presentation by dendritic cells. J Immunol, 190 (7): 3163-71. [PMID:23420884]
71. Heubach JF, Trebess I, Wettwer E, Himmel HM, Michel MC, Kaumann AJ, Koch WJ, Harding SE, Ravens U. (1999) L-type calcium current and contractility in ventricular myocytes from mice overexpressing the cardiac beta 2-adrenoceptor. Cardiovasc Res, 42 (1): 173-82. [PMID:10435008]
72. Hillman KL, Doze VA, Porter JE. (2005) Functional characterization of the beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes expressed by CA1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 314 (2): 561-7. [PMID:15908513]
73. Hoenke C, Bouyssou T, Tautermann CS, Rudolf K, Schnapp A, Konetzki I. (2009) Use of 5-hydroxy-4H-benzo[1,4]oxazin-3-ones as beta2-adrenoceptor agonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 19 (23): 6640-4. [PMID:19875286]
74. Hoffmann C, Leitz MR, Oberdorf-Maass S, Lohse MJ, Klotz KN. (2004) Comparative pharmacology of human beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes--characterization of stably transfected receptors in CHO cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 369 (2): 151-9. [PMID:14730417]
75. Hohberger B, Kunze R, Wallukat G, Kara K, Mardin CY, Lämmer R, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Hosari S, Horn F, Munoz L et al.. (2019) Autoantibodies Activating the β2-Adrenergic Receptor Characterize Patients With Primary and Secondary Glaucoma. Front Immunol, 10: 2112. [PMID:31632387]
76. Hoit BD, Suresh DP, Craft L, Walsh RA, Liggett SB. (2000) beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms at amino acid 16 differentially influence agonist-stimulated blood pressure and peripheral blood flow in normal individuals. Am Heart J, 139 (3): 537-42. [PMID:10689270]
77. Hostrup M, Onslev J. (2022) The beta2 -adrenergic receptor - a re-emerging target to combat obesity and induce leanness?. J Physiol, 600 (5): 1209-1227. [PMID:34676534]
78. Hou DY, Xu L, Zhang ZY, Xu XR, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu JM, Wang H, Chen J, Zhang L. (2020) Clinical value of detecting autoantibodies against β1-, β2,- and α1-adrenergic receptors in carvedilol treatment of patients with heart failure. J Geriatr Cardiol, 17 (6): 305-312. [PMID:32670360]
79. Hudson BD, Hébert TE, Kelly ME. (2010) Physical and functional interaction between CB1 cannabinoid receptors and beta2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol, 160 (3): 627-42. [PMID:20590567]
80. Ingebrigtsen TS, Vestbo J, Rode L, Marott JL, Lange P, Nordestgaard BG. (2019) β2-Adrenergic genotypes and risk of severe exacerbations in COPD: a prospective cohort study. Thorax, 74 (10): 934-940. [PMID:31481635]
81. Ippolito M, De Pascali F, Inoue A, Benovic JL. (2022) Phenylalanine 193 in Extracellular Loop 2 of the β 2-Adrenergic Receptor Coordinates β-Arrestin Interaction. Mol Pharmacol, 101 (2): 87-94. [PMID:34853152]
82. Isogaya M, Sugimoto Y, Tanimura R, Tanaka R, Kikkawa H, Nagao T, Kurose H. (1999) Binding pockets of the beta(1)- and beta(2)-adrenergic receptors for subtype-selective agonists. Mol Pharmacol, 56 (5): 875-85. [PMID:10531390]
83. Izeboud CA, Vermeulen RM, Zwart A, Voss HP, van Miert AS, Witkamp RF. (2000) Stereoselectivity at the beta2-adrenoceptor on macrophages is a major determinant of the anti-inflammatory effects of beta2-agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 362 (2): 184-9. [PMID:10961382]
84. January B, Seibold A, Whaley B, Hipkin RW, Lin D, Schonbrunn A, Barber R, Clark RB. (1997) beta2-adrenergic receptor desensitization, internalization, and phosphorylation in response to full and partial agonists. J Biol Chem, 272 (38): 23871-9. [PMID:9295336]
85. Jensen CJ, Demol F, Bauwens R, Kooijman R, Massie A, Villers A, Ris L, De Keyser J. (2016) Astrocytic β2 Adrenergic Receptor Gene Deletion Affects Memory in Aged Mice. PLoS One, 11 (10): e0164721. [PMID:27776147]
86. Johnstone EKM, See HB, Abhayawardana RS, Song A, Rosengren KJ, Hill SJ, Pfleger KDG. (2021) Investigation of Receptor Heteromers Using NanoBRET Ligand Binding. Int J Mol Sci, 22 (3). [PMID:33499147]
87. Joiner ML, Lisé MF, Yuen EY, Kam AY, Zhang M, Hall DD, Malik ZA, Qian H, Chen Y, Ulrich JD et al.. (2010) Assembly of a beta2-adrenergic receptor--GluR1 signalling complex for localized cAMP signalling. EMBO J, 29 (2): 482-95. [PMID:19942860]
88. Jordan BA, Trapaidze N, Gomes I, Nivarthi R, Devi LA. (2001) Oligomerization of opioid receptors with beta 2-adrenergic receptors: a role in trafficking and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98 (1): 343-8. [PMID:11134510]
89. Kamiar A, Yousefi K, Dunkley JC, Webster KA, Shehadeh LA. (2021) β2-Adrenergic receptor agonism as a therapeutic strategy for kidney disease. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 320 (5): R575-R587. [PMID:33565369]
90. Kern C, Meyer T, Droux S, Schollmeyer D, Miculka C. (2009) Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of beta2-adrenergic agonist enantiomers: zilpaterol. J Med Chem, 52 (6): 1773-7. [PMID:19245211]
91. Kobilka BK, Dixon RA, Frielle T, Dohlman HG, Bolanowski MA, Sigal IS, Yang-Feng TL, Francke U, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. (1987) cDNA for the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor: a protein with multiple membrane-spanning domains and encoded by a gene whose chromosomal location is shared with that of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 84 (1): 46-50. [PMID:3025863]
92. Krushinski Jr JH, Schaus JM, Thompson DC, Calligaro DO, Nelson DL, Luecke SH, Wainscott DB, Wong DT. (2007) Indoloxypropanolamine analogues as 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 17 (20): 5600-4. [PMID:17804228]
93. Kuravi S, Lan TH, Barik A, Lambert NA. (2010) Third-party bioluminescence resonance energy transfer indicates constitutive association of membrane proteins: application to class a g-protein-coupled receptors and g-proteins. Biophys J, 98 (10): 2391-9. [PMID:20483349]
94. Lakhlani PP, Amenta F, Napoleone P, Felici L, Eikenburg DC. (1994) Pharmacological characterization and anatomical localization of prejunctional beta-adrenoceptors in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol, 111: 1296-1308. [PMID:8032617]
95. LaRocca TJ, Schwarzkopf M, Altman P, Zhang S, Gupta A, Gomes I, Alvin Z, Champion HC, Haddad G, Hajjar RJ et al.. (2010) β2-Adrenergic receptor signaling in the cardiac myocyte is modulated by interactions with CXCR4. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 56 (5): 548-59. [PMID:20729750]
96. Lavoie C, Hébert TE. (2003) Pharmacological characterization of putative beta1-beta2-adrenergic receptor heterodimers. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 81 (2): 186-95. [PMID:12710533]
97. Lavoie C, Mercier JF, Salahpour A, Umapathy D, Breit A, Villeneuve LR, Zhu WZ, Xiao RP, Lakatta EG, Bouvier M et al.. (2002) Beta 1/beta 2-adrenergic receptor heterodimerization regulates beta 2-adrenergic receptor internalization and ERK signaling efficacy. J Biol Chem, 277 (38): 35402-10. [PMID:12140284]
98. Leineweber K, Büscher R, Bruck H, Brodde OE. (2004) Beta-adrenoceptor polymorphisms. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 369 (1): 1-22. [PMID:14647973]
99. Lewis RJ, Chachi L, Newby C, Amrani Y, Bradding P. (2016) Bidirectional Counterregulation of Human Lung Mast Cell and Airway Smooth Muscle β2 Adrenoceptors. J Immunol, 196 (1): 55-63. [PMID:26608913]
100. Li F, De Godoy M, Rattan S. (2004) Role of adenylate and guanylate cyclases in beta1-, beta2-, and beta3-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation of internal anal sphincter smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 308 (3): 1111-20. [PMID:14711933]
101. Liapakis G, Chan WC, Papadokostaki M, Javitch JA. (2004) Synergistic contributions of the functional groups of epinephrine to its affinity and efficacy at the beta2 adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 65 (5): 1181-90. [PMID:15102946]
102. Lima JJ. (2014) Do genetic polymorphisms alter patient response to inhaled bronchodilators?. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol, 10 (9): 1231-40. [PMID:25102170]
103. Littmann T, Göttle M, Reinartz MT, Kälble S, Wainer IW, Ozawa T, Seifert R. (2015) Recruitment of β-arrestin 1 and 2 to the β2-adrenoceptor: analysis of 65 ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 355 (2): 183-90. [PMID:26306764]
104. Liu X, Ahn S, Kahsai AW, Meng KC, Latorraca NR, Pani B, Venkatakrishnan AJ, Masoudi A, Weis WI, Dror RO et al.. (2017) Mechanism of intracellular allosteric β2AR antagonist revealed by X-ray crystal structure. Nature, 548 (7668): 480-484. [PMID:28813418]
105. Liu X, Kaindl J, Korczynska M, Stößel A, Dengler D, Stanek M, Hübner H, Clark MJ, Mahoney J, Matt RA et al.. (2020) An allosteric modulator binds to a conformational hub in the β2 adrenergic receptor. Nat Chem Biol, 16 (7): 749-755. [PMID:32483378]
106. Liu Y, Liang X, Ren WW, Li BM. (2014) Expression of β1- and β2-adrenoceptors in different subtypes of interneurons in the medial prefrontal cortex of mice. Neuroscience, 257: 149-57. [PMID:24215978]
107. Liu YL, Nwosu UC, Rice PJ. (1998) Relaxation of isolated human myometrial muscle by beta2-adrenergic receptors but not beta1-adrenergic receptors. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 179 (4): 895-8. [PMID:9790366]
108. Louis SN, Nero TL, Iakovidis D, Jackman GP, Louis WJ. (1999) LK 204-545, a highly selective beta1-adrenoceptor antagonist at human beta-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 367 (2-3): 431-5. [PMID:10079020]
109. Masureel M, Zou Y, Picard LP, van der Westhuizen E, Mahoney JP, Rodrigues JPGLM, Mildorf TJ, Dror RO, Shaw DE, Bouvier M et al.. (2018) Structural insights into binding specificity, efficacy and bias of a β2AR partial agonist. Nat Chem Biol, 14 (11): 1059-1066. [PMID:30327561]
110. Maudsley S, Pierce KL, Zamah AM, Miller WE, Ahn S, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ, Luttrell LM. (2000) The beta(2)-adrenergic receptor mediates extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation via assembly of a multi-receptor complex with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem, 275 (13): 9572-80. [PMID:10734107]
111. McGraw DW, Forbes SL, Kramer LA, Witte DP, Fortner CN, Paul RJ, Liggett SB. (1999) Transgenic overexpression of beta(2)-adrenergic receptors in airway smooth muscle alters myocyte function and ablates bronchial hyperreactivity. J Biol Chem, 274 (45): 32241-7. [PMID:10542262]
112. McGraw DW, Mihlbachler KA, Schwarb MR, Rahman FF, Small KM, Almoosa KF, Liggett SB. (2006) Airway smooth muscle prostaglandin-EP1 receptors directly modulate beta2-adrenergic receptors within a unique heterodimeric complex. J Clin Invest, 116 (5): 1400-9. [PMID:16670773]
113. McVey M, Ramsay D, Kellett E, Rees S, Wilson S, Pope AJ, Milligan G. (2001) Monitoring receptor oligomerization using time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. The human delta -opioid receptor displays constitutive oligomerization at the cell surface, which is not regulated by receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem, 276 (17): 14092-9. [PMID:11278447]
114. Mercier JF, Salahpour A, Angers S, Breit A, Bouvier M. (2002) Quantitative assessment of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor homo- and heterodimerization by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem, 277 (47): 44925-31. [PMID:12244098]
115. Michel MC, Seifert R. (2015) Selectivity of pharmacological tools: implications for use in cell physiology. A review in the theme: Cell signaling: proteins, pathways and mechanisms. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol, 308 (7): C505-20. [PMID:25631871]
116. Minneman KP, Hegstrand LR, Molinoff PB. (1979) The pharmacological specificity of beta-1 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors in rat heart and lung in vitro. Mol Pharmacol, 16 (1): 21-33. [PMID:39243]
117. Molenaar P, Savarimuthu SM, Sarsero D, Chen L, Semmler AB, Carle A, Yang I, Bartel S, Vetter D, Beyerdörfer I et al.. (2007) (-)-Adrenaline elicits positive inotropic, lusitropic, and biochemical effects through beta2 -adrenoceptors in human atrial myocardium from nonfailing and failing hearts, consistent with Gs coupling but not with Gi coupling. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 375 (1): 11-28. [PMID:17295024]
118. Mukaida S, Sato M, Öberg AI, Dehvari N, Olsen JM, Kocan M, Halls ML, Merlin J, Sandström AL, Csikasz RI et al.. (2019) BRL37344 stimulates GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle via β2-adrenoceptors without causing classical receptor desensitization. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 316 (5): R666-R677. [PMID:30892909]
119. Nakai A, Hayano Y, Furuta F, Noda M, Suzuki K. (2014) Control of lymphocyte egress from lymph nodes through β2-adrenergic receptors. J Exp Med, 211 (13): 2583-98. [PMID:25422496]
120. Nevzorova J, Evans BA, Bengtsson T, Summers RJ. (2006) Multiple signalling pathways involved in beta2-adrenoceptor-mediated glucose uptake in rat skeletal muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol, 147 (4): 446-54. [PMID:16415914]
121. Pani B, Ahn S, Rambarat PK, Vege S, Kahsai AW, Liu A, Valan BN, Staus DP, Costa T, Lefkowitz RJ. (2021) Unique Positive Cooperativity Between the β-Arrestin-Biased β-Blocker Carvedilol and a Small Molecule Positive Allosteric Modulator of the β2-Adrenergic Receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 100 (5): 513-525. [PMID:34580163]
122. Potter DE. (1981) Adrenergic pharmacology of aqueous humor dynamics. Pharmacol Rev, 33 (3): 133-53. [PMID:7323134]
123. Procopiou PA, Barrett VJ, Bevan NJ, Biggadike K, Box PC, Butchers PR, Coe DM, Conroy R, Emmons A, Ford AJ et al.. (2010) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of long-acting beta2 adrenergic receptor agonists incorporating metabolic inactivation: an antedrug approach. J Med Chem, 53 (11): 4522-30. [PMID:20462258]
124. Puri R, Liew GY, Nicholls SJ, Nelson AJ, Leong DP, Carbone A, Copus B, Wong DT, Beltrame JF, Worthley SG et al.. (2012) Coronary β2-adrenoreceptors mediate endothelium-dependent vasoreactivity in humans: novel insights from an in vivo intravascular ultrasound study. Eur Heart J, 33 (4): 495-504. [PMID:21951627]
125. Pönicke K, Heinroth-Hoffmann I, Brodde OE. (2003) Role of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in hypertrophic and apoptotic effects of noradrenaline and adrenaline in adult rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 367 (6): 592-9. [PMID:12750877]
126. Rasmussen SG, Choi HJ, Rosenbaum DM, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Edwards PC, Burghammer M, Ratnala VR, Sanishvili R, Fischetti RF et al.. (2007) Crystal structure of the human beta2 adrenergic G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature, 450 (7168): 383-7. [PMID:17952055]
127. Rasmussen SG, DeVree BT, Zou Y, Kruse AC, Chung KY, Kobilka TS, Thian FS, Chae PS, Pardon E, Calinski D et al.. (2011) Crystal structure of the β2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature, 477 (7366): 549-55. [PMID:21772288]
128. Ring AM, Manglik A, Kruse AC, Enos MD, Weis WI, Garcia KC, Kobilka BK. (2013) Adrenaline-activated structure of β2-adrenoceptor stabilized by an engineered nanobody. Nature, 502 (7472): 575-579. [PMID:24056936]
129. Rohrer DK, Chruscinski A, Schauble EH, Bernstein D, Kobilka BK. (1999) Cardiovascular and metabolic alterations in mice lacking both beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem, 274 (24): 16701-8. [PMID:10358009]
130. Rosenbaum DM, Zhang C, Lyons JA, Holl R, Aragao D, Arlow DH, Rasmussen SG, Choi HJ, Devree BT, Sunahara RK et al.. (2011) Structure and function of an irreversible agonist-β(2) adrenoceptor complex. Nature, 469 (7329): 236-40. [PMID:21228876]
131. Sabio M, Jones K, Topiol S. (2008) Use of the X-ray structure of the beta2-adrenergic receptor for drug discovery. Part 2: Identification of active compounds. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 18 (20): 5391-5. [PMID:18829308]
132. Sato M, Dehvari N, Oberg AI, Dallner OS, Sandström AL, Olsen JM, Csikasz RI, Summers RJ, Hutchinson DS, Bengtsson T. (2014) Improving type 2 diabetes through a distinct adrenergic signaling pathway involving mTORC2 that mediates glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Diabetes, 63 (12): 4115-29. [PMID:25008179]
133. Sato T, Baker J, Warne T, Brown GA, Leslie AG, Congreve M, Tate CG. (2015) Pharmacological Analysis and Structure Determination of 7-Methylcyanopindolol-Bound β1-Adrenergic Receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 88 (6): 1024-34. [PMID:26385885]
134. Sato Y, Kurose H, Isogaya M, Nagao T. (1996) Molecular characterization of pharmacological properties of T-0509 for beta-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 315 (3): 363-7. [PMID:8982677]
135. Seifert R, Lee TW, Lam VT, Kobilka BK. (1998) Reconstitution of beta2-adrenoceptor-GTP-binding-protein interaction in Sf9 cells--high coupling efficiency in a beta2-adrenoceptor-G(s alpha) fusion protein. Eur J Biochem, 255 (2): 369-82. [PMID:9716378]
136. Sharif NA, Xu SX, Crider JY, McLaughlin M, Davis TL. (2001) Levobetaxolol (Betaxon) and other beta-adrenergic antagonists: preclinical pharmacology, IOP-lowering activity and sites of action in human eyes. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther, 17 (4): 305-17. [PMID:11572462]
137. Song Y, Xu C, Liu J, Li Y, Wang H, Shan D, Wainer IW, Hu X, Zhang Y, Woo AY et al.. (2021) Heterodimerization With 5-HT2BR Is Indispensable for β2AR-Mediated Cardioprotection. Circ Res, 128 (2): 262-277. [PMID:33208036]
138. Soriano-Ursúa MA, McNaught-Flores DA, Nieto-Alamilla G, Segura-Cabrera A, Correa-Basurto J, Arias-Montaño JA, Trujillo-Ferrara JG. (2012) Cell-based and in-silico studies on the high intrinsic activity of two boron-containing salbutamol derivatives at the human β₂-adrenoceptor. Bioorg Med Chem, 20 (2): 933-41. [PMID:22182578]
139. Soriano-Ursúa MA, Valencia-Hernández I, Arellano-Mendoza MG, Correa-Basurto J, Trujillo-Ferrara JG. (2009) Synthesis, pharmacological and in silico evaluation of 1-(4-di-hydroxy-3,5-dioxa-4-borabicyclo[4.4.0]deca-7,9,11-trien-9-yl)-2-(tert-butylamino)ethanol, a compound designed to act as a beta2 adrenoceptor agonist. Eur J Med Chem, 44 (7): 2840-6. [PMID:19168263]
140. Stiles GL, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. (1984) Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiol Rev, 64 (2): 661-743. [PMID:6143332]
141. Summers RJ, Molnaar P, Russell F, Elnatan J, Jones CR, Buxton BF, Chang V, Hambley J. (1989) Coexistence and localization of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in the human heart. Eur Heart J, 10 Suppl B: 11-21. [PMID:2553407]
142. Susec M, Sencanski M, Glisic S, Veljkovic N, Pedersen C, Drinovec L, Stojan J, Nøhr J, Vrecl M. (2019) Functional characterization of β2-adrenergic and insulin receptor heteromers. Neuropharmacology, 152: 78-89. [PMID:30707913]
143. Swaminath G, Lee TW, Kobilka B. (2003) Identification of an allosteric binding site for Zn2+ on the beta2 adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem, 278 (1): 352-6. [PMID:12409304]
144. Swaminath G, Steenhuis J, Kobilka B, Lee TW. (2002) Allosteric modulation of beta2-adrenergic receptor by Zn(2+). Mol Pharmacol, 61 (1): 65-72. [PMID:11752207]
145. Sykes DA, Charlton SJ. (2012) Slow receptor dissociation is not a key factor in the duration of action of inhaled long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol, 165 (8): 2672-83. [PMID:21883146]
146. Takasu T, Ukai M, Sato S, Matsui T, Nagase I, Maruyama T, Sasamata M, Miyata K, Uchida H, Yamaguchi O. (2007) Effect of (R)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4'-{2-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]ethyl} acetanilide (YM178), a novel selective beta3-adrenoceptor agonist, on bladder function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 321 (2): 642-7. [PMID:17293563]
147. Tanner MA, Maitz CA, Grisanti LA. (2021) Immune cell β2-adrenergic receptors contribute to the development of heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 321 (4): H633-H649. [PMID:34415184]
148. Thomsen M, Nordestgaard BG, Sethi AA, Tybjærg-Hansen A, Dahl M. (2012) β2-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms, asthma and COPD: two large population-based studies. Eur Respir J, 39 (3): 558-66. [PMID:22075484]
149. Tsuchihashi H, Nakashima Y, Kinami J, Nagatomo T. (1990) Characteristics of 125I-iodocyanopindolol binding to beta-adrenergic and serotonin-1B receptors of rat brain: selectivity of beta-adrenergic agents. Jpn J Pharmacol, 52 (2): 195-200. [PMID:1968985]
150. Turki J, Lorenz JN, Green SA, Donnelly ET, Jacinto M, Liggett SB. (1996) Myocardial signaling defects and impaired cardiac function of a human beta 2-adrenergic receptor polymorphism expressed in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 93 (19): 10483-8. [PMID:8816827]
151. Turki J, Pak J, Green SA, Martin RJ, Liggett SB. (1995) Genetic polymorphisms of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor in nocturnal and nonnocturnal asthma. Evidence that Gly16 correlates with the nocturnal phenotype. J Clin Invest, 95 (4): 1635-41. [PMID:7706471]
152. Uberti MA, Hague C, Oller H, Minneman KP, Hall RA. (2005) Heterodimerization with beta2-adrenergic receptors promotes surface expression and functional activity of alpha1D-adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 313 (1): 16-23. [PMID:15615865]
153. Uehling DE, Shearer BG, Donaldson KH, Chao EY, Deaton DN, Adkison KK, Brown KK, Cariello NF, Faison WL, Lancaster ME et al.. (2006) Biarylaniline phenethanolamines as potent and selective beta3 adrenergic receptor agonists. J Med Chem, 49 (9): 2758-71. [PMID:16640337]
154. Vargas Pelaez AF, Gao Z, Ahmad TA, Leuenberger UA, Proctor DN, Maman SR, Muller MD. (2016) Effect of adrenergic agonists on coronary blood flow: a laboratory study in healthy volunteers. Physiol Rep, 4 (10). [PMID:27225628]
155. Vedel L, Bräuner-Osborne H, Mathiesen JM. (2015) A cAMP Biosensor-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for Identification of Gs-Coupled GPCR Ligands and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors. J Biomol Screen, 20 (7): 849-57. [PMID:25851033]
156. Wacker D, Fenalti G, Brown MA, Katritch V, Abagyan R, Cherezov V, Stevens RC. (2010) Conserved binding mode of human beta2 adrenergic receptor inverse agonists and antagonist revealed by X-ray crystallography. J Am Chem Soc, 132 (33): 11443-5. [PMID:20669948]
157. Weichert D, Kruse AC, Manglik A, Hiller C, Zhang C, Hübner H, Kobilka BK, Gmeiner P. (2014) Covalent agonists for studying G protein-coupled receptor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111 (29): 10744-8. [PMID:25006259]
158. Wendell SG, Fan H, Zhang C. (2020) G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Asthma Therapy: Pharmacology and Drug Action. Pharmacol Rev, 72 (1): 1-49. [PMID:31767622]
159. Wenzel-Seifert K, Liu HY, Seifert R. (2002) Similarities and differences in the coupling of human beta1- and beta2-adrenoceptors to Gs(alpha) splice variants. Biochem Pharmacol, 64 (1): 9-20. [PMID:12106601]
160. Werner C, Müller N, Müller UA. (2019) Agonistic autoantibodies against B2-adrenergic receptors correlating with macrovascular disease in longstanding diabetes type 2. Acta Diabetol, 56 (6): 659-665. [PMID:30770998]
161. Wisler JW, DeWire SM, Whalen EJ, Violin JD, Drake MT, Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ. (2007) A unique mechanism of beta-blocker action: carvedilol stimulates beta-arrestin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 104 (42): 16657-62. [PMID:17925438]
162. Woo AY, Song Y, Xiao RP, Zhu W. (2015) Biased β2-adrenoceptor signalling in heart failure: pathophysiology and drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol, 172 (23): 5444-56. [PMID:25298054]
163. Wrzal PK, Devost D, Pétrin D, Goupil E, Iorio-Morin C, Laporte SA, Zingg HH, Hébert TE. (2012) Allosteric interactions between the oxytocin receptor and the β2-adrenergic receptor in the modulation of ERK1/2 activation are mediated by heterodimerization. Cell Signal, 24 (1): 342-50. [PMID:21963428]
164. Wrzal PK, Goupil E, Laporte SA, Hébert TE, Zingg HH. (2012) Functional interactions between the oxytocin receptor and the β2-adrenergic receptor: implications for ERK1/2 activation in human myometrial cells. Cell Signal, 24 (1): 333-41. [PMID:21964067]
165. Yatani A, Tajima Y, Green SA. (1999) Coupling of beta-adrenergic receptors to cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels: preferential coupling of the beta1 versus beta2 receptor subtype and evidence for PKA-independent activation of the channel. Cell Signal, 11 (5): 337-42. [PMID:10376806]
166. Zhu WZ, Chakir K, Zhang S, Yang D, Lavoie C, Bouvier M, Hébert TE, Lakatta EG, Cheng H, Xiao RP. (2005) Heterodimerization of beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptor subtypes optimizes beta-adrenergic modulation of cardiac contractility. Circ Res, 97 (3): 244-51. [PMID:16002745]
167. Zuurhout MJ, Vijverberg SJ, Raaijmakers JA, Koenderman L, Postma DS, Koppelman GH, Maitland-van der Zee AH. (2013) Arg16 ADRB2 genotype increases the risk of asthma exacerbation in children with a reported use of long-acting β2-agonists: results of the PACMAN cohort. Pharmacogenomics, 14 (16): 1965-71. [PMID:24279851]














