GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: INCB-028050 | INCB028050 | LY-3009104 | LY3009104 | Olumiant®
baricitinib is an approved drug (EMA (2017), FDA (2018))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
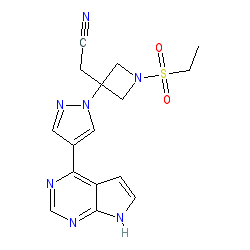
Comment: Baricitinib is a JAK1 and 2 selective inhibitor. The compound is orally bioavailable.
SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: The powerful anti-inflammatory activity of baricitinib (and potentially other approved JAK inhibitors such as fedratinib, and ruxolitinib) was suggested as potential therapeutic option to combat the immunopathological effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with severe COVID-19. A number of small-medium sized clinical studies have examined the effect of short-term baricitinib (or other JAK inhibitors) treatment in hospitalised patients with confirmed COVID-19. Such short term use of this drug during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection (7-14 days) is not anticipated to cause serious side-effects. In March 2022, data reported from the largest of the baricitinib studies (part of the University of Oxford-led RECOVERY trial) indicated that it provided clinical benefit in hospitalised COVID-19 patients, including in those already receiving other standard care immunomodulatory treatments (e.g. dexamethasone, tocilizumab) or the antiviral drug remdesivir. This made baricitinib the 4th effective COVID-19 therapy to be identified by the RECOVERY trial. Through the application of proprietary artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms baricitinib was predicted to possess antiviral activity in addition to its known anti-inflammatory efficacy [1,9-10]. Antiviral activity is predicted to arise from inhibition of the numb-associated kinase (NAK) AAK1 which is an important regulator of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Inhibition of AAK1 would likely reduce the ability of viruses to infect lung cells, and is being proposed as a pharmacological mechanism that warrants further investigation as a treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bioactivity Comments |
| Preclinical studies of baricitinib have shown it to be effective in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis [3]. A single patient with alopecia areata (AA) with comorbid CANDLE syndrome (a immunoproteasome-related disorder with a prominent interferon (IFN) signature, a disease feature shared with AA), recruited to a clinical trial testing baricitinib as a treatment for their CANDLE syndrome (NCT01724580) experienced significant hair regrowth [5]. Mechanistic assessment in a mouse AA model, confirmed that clinical improvement correlated with baricitinib-induced resolution of the IFN signature. Other JAK inhibitors such as tofacitinib and ruxolitinib have also been reported to promote hair regrowth in AA in early stage trials [6,8,13]. |
| Selectivity at enzymes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||