GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: INCB-028050 | INCB028050 | LY-3009104 | LY3009104 | Olumiant®
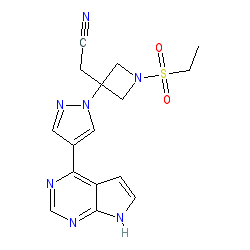
baricitinib is an approved drug (EMA (2017), FDA (2018))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Baricitinib is a JAK1 and 2 selective inhibitor. The compound is orally bioavailable.
SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: The powerful anti-inflammatory activity of baricitinib (and potentially other approved JAK inhibitors such as fedratinib, and ruxolitinib) was suggested as potential therapeutic option to combat the immunopathological effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with severe COVID-19. A number of small-medium sized clinical studies have examined the effect of short-term baricitinib (or other JAK inhibitors) treatment in hospitalised patients with confirmed COVID-19. Such short term use of this drug during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection (7-14 days) is not anticipated to cause serious side-effects. In March 2022, data reported from the largest of the baricitinib studies (part of the University of Oxford-led RECOVERY trial) indicated that it provided clinical benefit in hospitalised COVID-19 patients, including in those already receiving other standard care immunomodulatory treatments (e.g. dexamethasone, tocilizumab) or the antiviral drug remdesivir. This made baricitinib the 4th effective COVID-19 therapy to be identified by the RECOVERY trial. Through the application of proprietary artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms baricitinib was predicted to possess antiviral activity in addition to its known anti-inflammatory efficacy [1,9-10]. Antiviral activity is predicted to arise from inhibition of the numb-associated kinase (NAK) AAK1 which is an important regulator of clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Inhibition of AAK1 would likely reduce the ability of viruses to infect lung cells, and is being proposed as a pharmacological mechanism that warrants further investigation as a treatment for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| The EMA granted baricitinib marketing authorisation in February 2017, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This approval covered doses of either 2 or 4 mg. Phase 3 trial results reporting significant clinical improvement in patients who's symptoms had failed to respond to other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) were published in [4]. These are the results of the RA-BEACON study NCT01721044. FDA approval, as a once daily treatment for moderately-to-severely active RA, in patients with an inadequate response to one or more tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor therapies, was granted in June 2018, but only for the 2 mg dose. In both jurisdictions, baricitinib can be used as monotherapy, or in combination with methotrexate or other non-biologic DMARDs. Use of baricitinib in combination with other JAK inhibitors, biologic DMARDs, or with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine and cyclosporin A is not recommended. Baricitinib was approved by the FDA as the first systemic, once-daily therapy for severe alopecia areata in June 2022. SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: In November 2020, the FDA granted the combination of baricitinib + remdesivir emergency use authorisation (EUA) as a treatment option for hospitalised COVID-19 patients, based on data from the ACTT-2 study (NCT04401579). Most recently (late 2023), baricitinib has been shown to preserve β-cell function in patients with new-onset Type 1 diabetes [12]. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT01721044 | A Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Study | Phase 3 Interventional | Eli Lilly and Company | ||
| NCT04401579 | Adaptive COVID-19 Treatment Trial 2 (ACTT-2) | Phase 3 Interventional | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) | The combination of baricitinib plus |
|
| NCT03899259 | A Study of Baricitinib (LY3009104) in Adults With Severe or Very Severe Alopecia Areata | Phase 3 Interventional | Eli Lilly and Company | This is also known as the BRAVE-AA2 study | 7 |
| NCT03570749 | A Study of Baricitinib (LY3009104) in Participants With Severe or Very Severe Alopecia Areata | Phase 2/Phase 3 Interventional | Eli Lilly and Company | This is also known as the BRAVE-AA1 study. In this study and the BRAVE-AA2 study, oral baricitinib was superior to placebo in promoting hair regrowth in patients with severe alopecia areata. | 7 |
| NCT04774224 | Baricitinib in New-onset Type 1 Diabetes | Phase 2 Interventional | St Vincent's Institute of Medical Research | 11 | |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com European Medicines Agency (EMA) |