GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Activators
- Gating Inhibitors
- Channel Blockers
- Tissue Distribution
- Physiological Functions
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Gene Expression and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 2 | 1 | 423 | 21q22.13 | KCNJ6 | potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 6 | 10,50 |
| Mouse | 2 | 1 | 425 | 16 55.44 cM | Kcnj6 | potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 6 | 33,60 |
| Rat | 2 | 1 | 425 | 11q11 | Kcnj6 | potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 6 | 54 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | P48051 (Hs), P48542 (Mm), P48550 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 2.60.40.1400 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL2406895 (Hs), CHEMBL4680029 (Mm) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000157542 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000043301 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000001658 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 3763 (Hs), 16522 (Mm), 25743 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000157542 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:3763 (Hs), mmu:16522 (Mm), rno:25743 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600877 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P48051 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_002240 (Hs), NM_001025585 (Mm), NM_010606 (Mm), NM_001025584 (Mm), NM_001025590 (Mm), NM_013192 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_002231 (Hs), NP_001020755 (Mm), NP_034736 (Mm), NP_001020756 (Mm), NP_001020761 (Mm), NP_037324 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P48051 (Hs), P48542 (Mm), P48550 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | KCNJ6 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
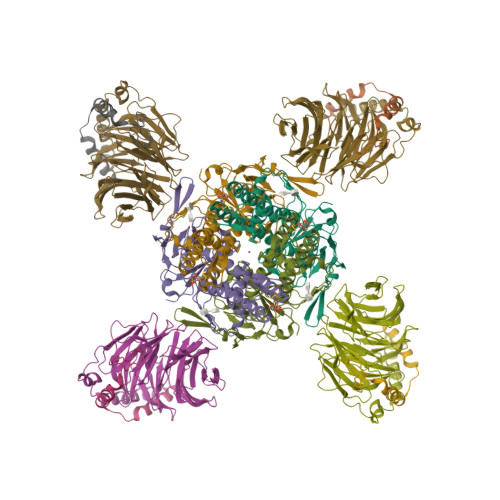
|
|
||||||||||||
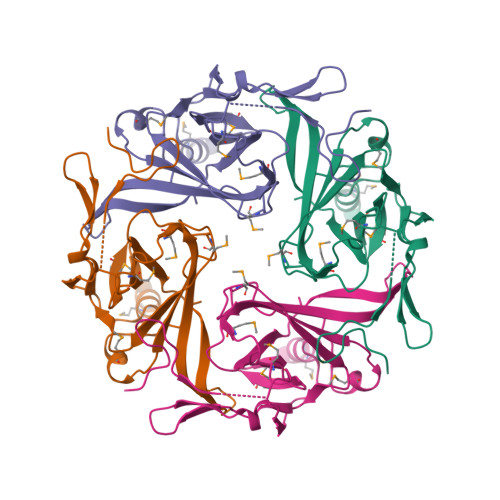
|
|
||||||||||||
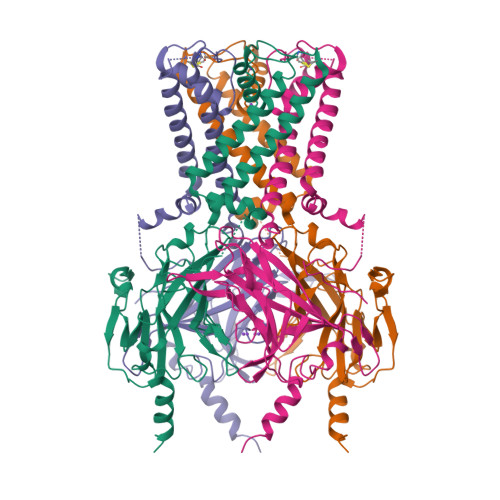
|
|
||||||||||||
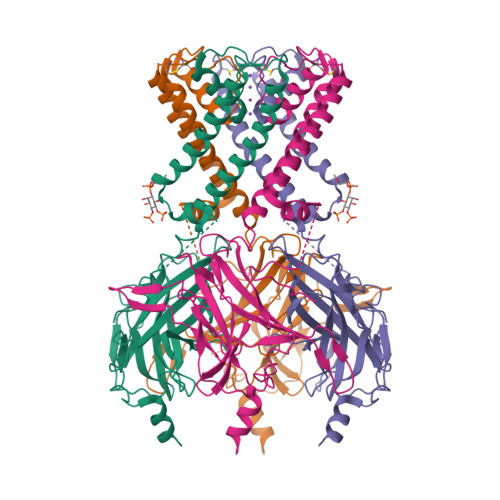
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated Protein Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The main functional assemblies in the brain are Kir3.1/3.2, Kir3.1/3.3 and Kir3.2/3.3 [2,9,12,26,28,32,34,36,42,55]. Kir3.2c contains PDZ binding motif that binds PDZ domain of SNX27 [37]. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Functional Characteristics  |
|
| G protein-activated inward-rectifier current | |
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
| Ion Selectivity and Conductance Comments | ||||||
| Kir3.2 forms functional heteromers with Kir3.3 (31pS, [18]). |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kir3.2 is also activated by Gβγ subunits [26]. The studies of the action of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, Na+ and ethanol were performed using Kir3.1/3.2 heteromers or Kir3.2 heterotetramers. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gating inhibitors 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific gating inhibitor tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The following references encompass data regarding the Kir3.1/3.2 heteromer: [23-24,29,57,61,63]. Kir3.2 is also inhibited by Gαi subunits[47]. RGS (regulators of G-protein signalling) proteins accelerate GTP hydrolysis of Gαsubunits, so that they increase the amount of GDP-bound Gα subunits, thus reducing the numbers of Gα-free Gβγ subunits [8,49]. Gα subunits bind to Kir3.2 [5,47]. ER forward export motif identified in Kir3.2 [39]. SNX27 regulates trafficking of Kir3.2c and Kir3.3 channels [37]. Data for verapamil and dizocilpine is derived from experiments using weaver mouse Kir3.2. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The following references encompass data regarding the Kir3.1/3.2 heteromer: [25] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Physiological Functions Comments | ||||||||
|
||||||||
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology Comments |
| In the weaver mouse the natural missense mutation at molecular location G156S in Kir3.2 permits Na+, as well as K+, ions to pass through the channel and reduces its sensitivity to Gβγ [27,44,52]. The weaver mouse experiences spontaneous tonic-clonic seizures [1,46,51]. |
Gene Expression and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| Biologically Significant Variant Comments | ||||||||||||||
| Distribution of Kir3.2 is related to isoform expression. At least seven exons contribute to producing at least four splice variants [15,56,60]. In the brain some Kir3.2 isoforms exist as complexes, not only with Kir3.1, but also with Kir3.3 [18,55] and Kir 3.4 [34]. |
References
1. Adelbrecht C, Murer MG, Lauritzen I, Lesage F, Ladzunski M, Agid Y, Raisman-Vozari R. (1997) An immunocytochemical study of a G-protein-gated inward rectifier K+ channel (GIRK2) in the weaver mouse mesencephalon. Neuroreport, 8 (4): 969-74. [PMID:9141074]
2. Aguado C, Colón J, Ciruela F, Schlaudraff F, Cabañero MJ, Perry C, Watanabe M, Liss B, Wickman K, Luján R. (2008) Cell type-specific subunit composition of G protein-gated potassium channels in the cerebellum. J Neurochem, 105 (2): 497-511. [PMID:18088366]
3. Arora D, Hearing M, Haluk DM, Mirkovic K, Fajardo-Serrano A, Wessendorf MW, Watanabe M, Luján R, Wickman K. (2011) Acute cocaine exposure weakens GABA(B) receptor-dependent G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ signaling in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci, 31 (34): 12251-7. [PMID:21865468]
4. Aryal P, Dvir H, Choe S, Slesinger PA. (2009) A discrete alcohol pocket involved in GIRK channel activation. Nat Neurosci, 12 (8): 988-95. [PMID:19561601]
5. Clancy SM, Fowler CE, Finley M, Suen KF, Arrabit C, Berton F, Kosaza T, Casey PJ, Slesinger PA. (2005) Pertussis-toxin-sensitive Galpha subunits selectively bind to C-terminal domain of neuronal GIRK channels: evidence for a heterotrimeric G-protein-channel complex. Mol Cell Neurosci, 28 (2): 375-89. [PMID:15691717]
6. Cruz HG, Berton F, Sollini M, Blanchet C, Pravetoni M, Wickman K, Lüscher C. (2008) Absence and rescue of morphine withdrawal in GIRK/Kir3 knock-out mice. J Neurosci, 28 (15): 4069-77. [PMID:18400906]
7. Cruz HG, Ivanova T, Lunn ML, Stoffel M, Slesinger PA, Lüscher C. (2004) Bi-directional effects of GABA(B) receptor agonists on the mesolimbic dopamine system. Nat Neurosci, 7 (2): 153-9. [PMID:14745451]
8. Doupnik CA, Davidson N, Lester HA, Kofuji P. (1997) RGS proteins reconstitute the rapid gating kinetics of gbetagamma-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (19): 10461-6. [PMID:9294233]
9. Fernández-Alacid L, Aguado C, Ciruela F, Martín R, Colón J, Cabañero MJ, Gassmann M, Watanabe M, Shigemoto R, Wickman K et al.. (2009) Subcellular compartment-specific molecular diversity of pre- and post-synaptic GABA-activated GIRK channels in Purkinje cells. J Neurochem, 110 (4): 1363-76. [PMID:19558451]
10. Ferrer J, Nichols CG, Makhina EN, Salkoff L, Bernstein J, Gerhard D, Wasson J, Ramanadham S, Permutt A. (1995) Pancreatic islet cells express a family of inwardly rectifying K+ channel subunits which interact to form G-protein-activated channels. J Biol Chem, 270 (44): 26086-91. [PMID:7592809]
11. Fowler CE, Aryal P, Suen KF, Slesinger PA. (2007) Evidence for association of GABA(B) receptors with Kir3 channels and regulators of G protein signalling (RGS4) proteins. J Physiol (Lond.), 580 (Pt 1): 51-65. [PMID:17185339]
12. Hearing M, Kotecki L, Marron Fernandez de Velasco E, Fajardo-Serrano A, Chung HJ, Luján R, Wickman K. (2013) Repeated cocaine weakens GABA(B)-Girk signaling in layer 5/6 pyramidal neurons in the prelimbic cortex. Neuron, 80 (1): 159-70. [PMID:24094109]
13. Ho IH, Murrell-Lagnado RD. (1999) Molecular determinants for sodium-dependent activation of G protein-gated K+ channels. J Biol Chem, 274 (13): 8639-48. [PMID:10085101]
14. Huang CL, Feng S, Hilgemann DW. (1998) Direct activation of inward rectifier potassium channels by PIP2 and its stabilization by Gbetagamma. Nature, 391 (6669): 803-6. [PMID:9486652]
15. Inanobe A, Horio Y, Fujita A, Tanemoto M, Hibino H, Inageda K, Kurachi Y. (1999) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel splicing variant of the Kir3.2 subunit predominantly expressed in mouse testis. J Physiol (Lond.), 521 Pt 1: 19-30. [PMID:10562331]
16. Inanobe A, Yoshimoto Y, Horio Y, Morishige KI, Hibino H, Matsumoto S, Tokunaga Y, Maeda T, Hata Y, Takai Y et al.. (1999) Characterization of G-protein-gated K+ channels composed of Kir3.2 subunits in dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. J Neurosci, 19 (3): 1006-17. [PMID:9920664]
17. Isomoto S, Kondo C, Takahashi N, Matsumoto S, Yamada M, Takumi T, Horio Y, Kurachi Y. (1996) A novel ubiquitously distributed isoform of GIRK2 (GIRK2B) enhances GIRK1 expression of the G-protein-gated K+ current in Xenopus oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 218 (1): 286-91. [PMID:8573147]
18. Jelacic TM, Kennedy ME, Wickman K, Clapham DE. (2000) Functional and biochemical evidence for G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK) channels composed of GIRK2 and GIRK3. J Biol Chem, 275 (46): 36211-6. [PMID:10956667]
19. Karschin C, Dissmann E, Stühmer W, Karschin A. (1996) IRK(1-3) and GIRK(1-4) inwardly rectifying K+ channel mRNAs are differentially expressed in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci, 16 (11): 3559-70. [PMID:8642402]
20. Karschin C, Karschin A. (1997) Ontogeny of gene expression of Kir channel subunits in the rat. Mol Cell Neurosci, 10 (3-4): 131-48. [PMID:9532576]
21. Kobayashi T, Ikeda K, Ichikawa T, Abe S, Togashi S, Kumanishi T. (1995) Molecular cloning of a mouse G-protein-activated K+ channel (mGIRK1) and distinct distributions of three GIRK (GIRK1, 2 and 3) mRNAs in mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 208 (3): 1166-73. [PMID:7702616]
22. Kobayashi T, Ikeda K, Kojima H, Niki H, Yano R, Yoshioka T, Kumanishi T. (1999) Ethanol opens G-protein-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Nat Neurosci, 2 (12): 1091-7. [PMID:10570486]
23. Kobayashi T, Ikeda K, Kumanishi T. (2000) Inhibition by various antipsychotic drugs of the G-protein-activated inwardly rectifying K(+) (GIRK) channels expressed in xenopus oocytes. Br J Pharmacol, 129 (8): 1716-22. [PMID:10780978]
24. Kobayashi T, Washiyama K, Ikeda K. (2003) Inhibition of G protein-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels by fluoxetine (Prozac). Br J Pharmacol, 138 (6): 1119-28. [PMID:12684268]
25. Kobayashi T, Washiyama K, Ikeda K. (2004) Inhibition of G protein-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels by various antidepressant drugs. Neuropsychopharmacology, 29 (10): 1841-51. [PMID:15150531]
26. Kofuji P, Davidson N, Lester HA. (1995) Evidence that neuronal G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels are activated by G beta gamma subunits and function as heteromultimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (14): 6542-6. [PMID:7604029]
27. Kofuji P, Hofer M, Millen KJ, Millonig JH, Davidson N, Lester HA, Hatten ME. (1996) Functional analysis of the weaver mutant GIRK2 K+ channel and rescue of weaver granule cells. Neuron, 16 (5): 941-52. [PMID:8630252]
28. Koyrakh L, Luján R, Colón J, Karschin C, Kurachi Y, Karschin A, Wickman K. (2005) Molecular and cellular diversity of neuronal G-protein-gated potassium channels. J Neurosci, 25 (49): 11468-78. [PMID:16339040]
29. Kuzhikandathil EV, Oxford GS. (2002) Classic D1 dopamine receptor antagonist R-(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine hydrochloride (SCH23390) directly inhibits G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Mol Pharmacol, 62 (1): 119-26. [PMID:12065762]
30. Labouèbe G, Lomazzi M, Cruz HG, Creton C, Luján R, Li M, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Watanabe M, Wickman K et al.. (2007) RGS2 modulates coupling between GABAB receptors and GIRK channels in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area. Nat Neurosci, 10 (12): 1559-68. [PMID:17965710]
31. Lalive AL, Munoz MB, Bellone C, Slesinger PA, Lüscher C, Tan KR. (2014) Firing modes of dopamine neurons drive bidirectional GIRK channel plasticity. J Neurosci, 34 (15): 5107-14. [PMID:24719090]
32. Leaney JL. (2003) Contribution of Kir3.1, Kir3.2A and Kir3.2C subunits to native G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci, 18 (8): 2110-8. [PMID:14622172]
33. Lesage F, Duprat F, Fink M, Guillemare E, Coppola T, Lazdunski M, Hugnot JP. (1994) Cloning provides evidence for a family of inward rectifier and G-protein coupled K+ channels in the brain. FEBS Lett, 353 (1): 37-42. [PMID:7926018]
34. Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Duprat F, Heurteaux C, Fosset M, Romey G, Barhanin J, Lazdunski M. (1995) Molecular properties of neuronal G-protein-activated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. J Biol Chem, 270 (48): 28660-7. [PMID:7499385]
35. Lewohl JM, Wilson WR, Mayfield RD, Brozowski SJ, Morrisett RA, Harris RA. (1999) G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels are targets of alcohol action. Nat Neurosci, 2 (12): 1084-90. [PMID:10570485]
36. Liao YJ, Jan YN, Jan LY. (1996) Heteromultimerization of G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channel proteins GIRK1 and GIRK2 and their altered expression in weaver brain. J Neurosci, 16 (22): 7137-50. [PMID:8929423]
37. Lunn ML, Nassirpour R, Arrabit C, Tan J, McLeod I, Arias CM, Sawchenko PE, Yates 3rd JR, Slesinger PA. (2007) A unique sorting nexin regulates trafficking of potassium channels via a PDZ domain interaction. Nat Neurosci, 10 (10): 1249-59. [PMID:17828261]
38. Lüscher C, Jan LY, Stoffel M, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA. (1997) G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ channels (GIRKs) mediate postsynaptic but not presynaptic transmitter actions in hippocampal neurons. Neuron, 19 (3): 687-95. [PMID:9331358]
39. Ma D, Zerangue N, Raab-Graham K, Fried SR, Jan YN, Jan LY. (2002) Diverse trafficking patterns due to multiple traffic motifs in G protein-activated inwardly rectifying potassium channels from brain and heart. Neuron, 33 (5): 715-29. [PMID:11879649]
40. Morgan AD, Carroll ME, Loth AK, Stoffel M, Wickman K. (2003) Decreased cocaine self-administration in Kir3 potassium channel subunit knockout mice. Neuropsychopharmacology, 28 (5): 932-8. [PMID:12637950]
41. Morishige K, Inanobe A, Yoshimoto Y, Kurachi H, Murata Y, Tokunaga Y, Maeda T, Maruyama Y, Kurachi Y. (1999) Secretagogue-induced exocytosis recruits G protein-gated K+ channels to plasma membrane in endocrine cells. J Biol Chem, 274 (12): 7969-74. [PMID:10075694]
42. Munoz MB, Slesinger PA. (2014) Sorting nexin 27 regulation of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K⁺ channels attenuates in vivo cocaine response. Neuron, 82 (3): 659-69. [PMID:24811384]
43. Murer G, Adelbrecht C, Lauritzen I, Lesage F, Lazdunski M, Agid Y, Raisman-Vozari R. (1997) An immunocytochemical study on the distribution of two G-protein-gated inward rectifier potassium channels (GIRK2 and GIRK4) in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience, 80 (2): 345-57. [PMID:9284339]
44. Navarro B, Kennedy ME, Velimirovíc B, Bhat D, Peterson AS, Clapham DE. (1996) Nonselective and G betagamma-insensitive weaver K+ channels. Science, 272 (5270): 1950-3. [PMID:8658170]
45. Padgett CL, Lalive AL, Tan KR, Terunuma M, Munoz MB, Pangalos MN, Martínez-Hernández J, Watanabe M, Moss SJ, Luján R et al.. (2012) Methamphetamine-evoked depression of GABA(B) receptor signaling in GABA neurons of the VTA. Neuron, 73 (5): 978-89. [PMID:22405207]
46. Patil N, Cox DR, Bhat D, Faham M, Myers RM, Peterson AS. (1995) A potassium channel mutation in weaver mice implicates membrane excitability in granule cell differentiation. Nat Genet, 11 (2): 126-9. [PMID:7550338]
47. Peleg S, Varon D, Ivanina T, Dessauer CW, Dascal N. (2002) G(alpha)(i) controls the gating of the G protein-activated K(+) channel, GIRK. Neuron, 33 (1): 87-99. [PMID:11779482]
48. Pravetoni M, Wickman K. (2008) Behavioral characterization of mice lacking GIRK/Kir3 channel subunits. Genes Brain Behav, 7 (5): 523-31. [PMID:18194467]
49. Saitoh O, Kubo Y, Miyatani Y, Asano T, Nakata H. (1997) RGS8 accelerates G-protein-mediated modulation of K+ currents. Nature, 390 (6659): 525-9. [PMID:9394004]
50. Schoots O, Wilson JM, Ethier N, Bigras E, Hebert TE, Van Tol HH. (1999) Co-expression of human Kir3 subunits can yield channels with different functional properties. Cell Signal, 11 (12): 871-83. [PMID:10659995]
51. Signorini S, Liao YJ, Duncan SA, Jan LY, Stoffel M. (1997) Normal cerebellar development but susceptibility to seizures in mice lacking G protein-coupled, inwardly rectifying K+ channel GIRK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (3): 923-7. [PMID:9023358]
52. Slesinger PA, Patil N, Liao YJ, Jan YN, Jan LY, Cox DR. (1996) Functional effects of the mouse weaver mutation on G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Neuron, 16 (2): 321-31. [PMID:8789947]
53. Stoffel M, Tokuyama Y, Trabb JB, German MS, Tsaar ML, Jan LY, Polonsky KS, Bell GI. (1995) Cloning of rat KATP-2 channel and decreased expression in pancreatic islets of male Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 212 (3): 894-9. [PMID:7626127]
54. Suda S, Nibuya M, Suda H, Takamatsu K, Miyazaki T, Nomura S, Kawai N. (2002) Potassium channel mRNAs with AU-rich elements and brain-specific expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 291 (5): 1265-71. [PMID:11883954]
55. Torrecilla M, Marker CL, Cintora SC, Stoffel M, Williams JT, Wickman K. (2002) G-protein-gated potassium channels containing Kir3.2 and Kir3.3 subunits mediate the acute inhibitory effects of opioids on locus ceruleus neurons. J Neurosci, 22 (11): 4328-34. [PMID:12040038]
56. Wei J, Hodes ME, Piva R, Feng Y, Wang Y, Ghetti B, Dlouhy SR. (1998) Characterization of murine Girk2 transcript isoforms: structure and differential expression. Genomics, 51 (3): 379-90. [PMID:9721208]
57. Weigl LG, Schreibmayer W. (2001) G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channels are targets for volatile anesthetics. Mol Pharmacol, 60 (2): 282-9. [PMID:11455015]
58. Whorton MR, MacKinnon R. (2011) Crystal structure of the mammalian GIRK2 K+ channel and gating regulation by G proteins, PIP2, and sodium. Cell, 147 (1): 199-208. [PMID:21962516]
59. Whorton MR, MacKinnon R. (2013) X-ray structure of the mammalian GIRK2-βγ G-protein complex. Nature, 498 (7453): 190-7. [PMID:23739333]
60. Wickman K, Pu WT, Clapham DE. (2002) Structural characterization of the mouse Girk genes. Gene, 284 (1-2): 241-50. [PMID:11891065]
61. Yamakura T, Lewohl JM, Harris RA. (2001) Differential effects of general anesthetics on G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying and other potassium channels. Anesthesiology, 95 (1): 144-53. [PMID:11465552]
62. Yoshimoto Y, Fukuyama Y, Horio Y, Inanobe A, Gotoh M, Kurachi Y. (1999) Somatostatin induces hyperpolarization in pancreatic islet alpha cells by activating a G protein-gated K+ channel. FEBS Lett, 444 (2-3): 265-9. [PMID:10050772]
63. Zhou W, Arrabit C, Choe S, Slesinger PA. (2001) Mechanism underlying bupivacaine inhibition of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98 (11): 6482-7. [PMID:11353868]










