GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Voltage Dependence
- Rank order lists
- Activators
- Inhibitors
- Gating Inhibitors
- Antagonists
- Channel Blockers
- Allosteric Modulators
- Immunopharmacology Comments
- Immuno Cell Type Associations
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Gene Expression and Pathophysiology
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 6 | 1 | 839 | 17p13.2 | TRPV1 | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 | 26 |
| Mouse | 6 | 1 | 839 | 11 45.25 cM | Trpv1 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 1 | 18 |
| Rat | 6 | 1 | 838 | 10q24 | Trpv1 | transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily V, member 1 | 14 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| OTRPC1 | VR1 | osm-9-like TRP channel 1 | vanilloid receptor 1 | capsaicin receptor | transient receptor potential cation channel |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q8NER1 (Hs), Q704Y3 (Mm), O35433 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 1.25.40.20 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4794 (Hs), CHEMBL1781864 (Mm), CHEMBL5102 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000196689 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000005952 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000019486 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 7442 (Hs), 193034 (Mm), 83810 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000196689 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:7442 (Hs), mmu:193034 (Mm), rno:83810 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 602076 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q8NER1 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_018727 (Hs), NM_001001445 (Mm), NM_031982 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_061197 (Hs), NP_001001445 (Mm), NP_114188 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q8NER1 (Hs), Q704Y3 (Mm), O35433 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | TRPV1 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||

|
|
||||||||||||
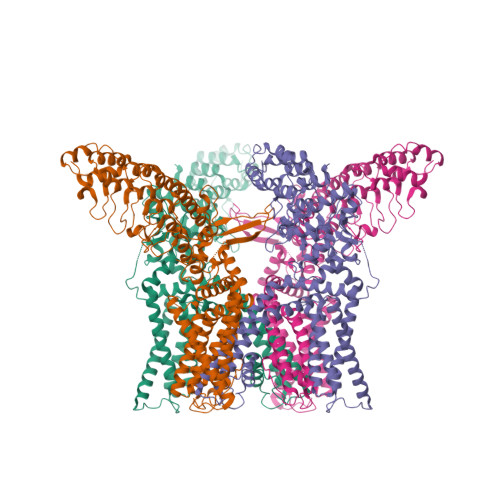
|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
Voltage Dependence  |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other chemical activators (Human) |
| NO-mediated cysteine S-nitrosylation |
| Physical activators (Human) |
| depolarization (V½ ~ 0 mV at 35°C), noxious heat (> 43°C at pH 7.4) |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRPV1 is also activated by heat, ethanol, protons and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate [7,14,57]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | ||
| Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate is also an inhibitor of channel gating [46]. |
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blocker Comments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Of the compounds listed above, there is good evidence to denote agatoxin 489 and ruthenium red as true channel blockers. The others should be considered antagonists. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| Several lines of evidence suggest that TRPV1 is implicated in some inflammatory processes [4,6,35,37,48]. TRPV1 is expressed on mouse T cells, mouse and human dendritic cells, mouse monocytes/macrophages, and human mast cells [44]. Pharmaceutical development is targeting TRPV1 antagonists as novel anti-inflammatory agents (e.g. the clinical candidate asivatrep). |
| Cell Type Associations | ||||||
|
||||||
|
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Expression and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
References
1. Ahern GP. (2003) Activation of TRPV1 by the satiety factor oleoylethanolamide. J Biol Chem, 278 (33): 30429-34. [PMID:12761211]
2. Ann J, Kim HS, Thorat SA, Kim H, Ha HJ, Choi K, Kim YH, Kim M, Hwang SW, Pearce LV et al.. (2020) Discovery of Nonpungent Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) Agonist as Strong Topical Analgesic. J Med Chem, 63 (1): 418-424. [PMID:31702924]
3. Appendino G, De Petrocellis L, Trevisani M, Minassi A, Daddario N, Moriello AS, Gazzieri D, Ligresti A, Campi B, Fontana G et al.. (2005) Development of the first ultra-potent "capsaicinoid" agonist at transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels and its therapeutic potential. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 312 (2): 561-70. [PMID:15356216]
4. Assas BM, Wakid MH, Zakai HA, Miyan JA, Pennock JL. (2016) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 expression and function in splenic dendritic cells: a potential role in immune homeostasis. Immunology, 147 (3): 292-304. [PMID:26643862]
5. Bertin S, Aoki-Nonaka Y, de Jong PR, Nohara LL, Xu H, Stanwood SR, Srikanth S, Lee J, To K, Abramson L et al.. (2014) The ion channel TRPV1 regulates the activation and proinflammatory properties of CD4⁺ T cells. Nat Immunol, 15 (11): 1055-1063. [PMID:25282159]
6. Bertin S, de Jong PR, Jefferies WA, Raz E. (2014) Novel immune function for the TRPV1 channel in T lymphocytes. Channels (Austin), 8 (6): 479-80. [PMID:25530461]
7. Bhave G, Hu HJ, Glauner KS, Zhu W, Wang H, Brasier DJ, Oxford GS, Gereau 4th RW. (2003) Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (21): 12480-5. [PMID:14523239]
8. Bianchi BR, El Kouhen R, Neelands TR, Lee CH, Gomtsyan A, Raja SN, Vaidyanathan SN, Surber B, McDonald HA, Surowy CS et al.. (2007) [3H]A-778317 [1-((R)-5-tert-butyl-indan-1-yl)-3-isoquinolin-5-yl-urea]: a novel, stereoselective, high-affinity antagonist is a useful radioligand for the human transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 323 (1): 285-93. [PMID:17660385]
9. Birder LA, Kanai AJ, de Groat WC, Kiss S, Nealen ML, Burke NE, Dineley KE, Watkins S, Reynolds IJ, Caterina MJ. (2001) Vanilloid receptor expression suggests a sensory role for urinary bladder epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 98 (23): 13396-401. [PMID:11606761]
10. Blum CA, Caldwell T, Zheng X, Bakthavatchalam R, Capitosti S, Brielmann H, De Lombaert S, Kershaw MT, Matson D, Krause JE et al.. (2010) Discovery of novel 6,6-heterocycles as transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV1) antagonists. J Med Chem, 53 (8): 3330-48. [PMID:20307063]
11. Bohlen CJ, Priel A, Zhou S, King D, Siemens J, Julius D. (2010) A bivalent tarantula toxin activates the capsaicin receptor, TRPV1, by targeting the outer pore domain. Cell, 141 (5): 834-45. [PMID:20510930]
12. Cao E, Liao M, Cheng Y, Julius D. (2013) TRPV1 structures in distinct conformations reveal activation mechanisms. Nature, 504 (7478): 113-8. [PMID:24305161]
13. Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB, Martin WJ, Trafton J, Petersen-Zeitz KR, Koltzenburg M, Basbaum AI, Julius D. (2000) Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science, 288 (5464): 306-13. [PMID:10764638]
14. Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D. (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 389 (6653): 816-24. [PMID:9349813]
15. Cavanaugh DJ, Chesler AT, Bráz JM, Shah NM, Julius D, Basbaum AI. (2011) Restriction of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 to the peptidergic subset of primary afferent neurons follows its developmental downregulation in nonpeptidergic neurons. J Neurosci, 31 (28): 10119-27. [PMID:21752988]
16. Cavanaugh DJ, Chesler AT, Jackson AC, Sigal YM, Yamanaka H, Grant R, O'Donnell D, Nicoll RA, Shah NM, Julius D et al.. (2011) Trpv1 reporter mice reveal highly restricted brain distribution and functional expression in arteriolar smooth muscle cells. J Neurosci, 31 (13): 5067-77. [PMID:21451044]
17. Chaudhari SS, Kadam AB, Khairatkar-Joshi N, Mukhopadhyay I, Karnik PV, Raghuram A, Rao SS, Vaiyapuri TS, Wale DP, Bhosale VM et al.. (2013) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel N-aryl-3,4-dihydro-1'H-spiro[chromene-2,4'-piperidine]-1'-carboxamides as TRPM8 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem, 21 (21): 6542-53. [PMID:24055075]
18. Correll CC, Phelps PT, Anthes JC, Umland S, Greenfeder S. (2004) Cloning and pharmacological characterization of mouse TRPV1. Neurosci Lett, 370 (1): 55-60. [PMID:15489017]
19. Davis JB, Gray J, Gunthorpe MJ, Hatcher JP, Davey PT, Overend P, Harries MH, Latcham J, Clapham C, Atkinson K et al.. (2000) Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature, 405 (6783): 183-7. [PMID:10821274]
20. El Kouhen R, Surowy CS, Bianchi BR, Neelands TR, McDonald HA, Niforatos W, Gomtsyan A, Lee CH, Honore P, Sullivan JP et al.. (2005) A-425619 [1-isoquinolin-5-yl-3-(4-trifluoromethyl-benzyl)-urea], a novel and selective transient receptor potential type V1 receptor antagonist, blocks channel activation by vanilloids, heat, and acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 314 (1): 400-9. [PMID:15837819]
21. Fernihough J, Gentry C, Bevan S, Winter J. (2005) Regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide and TRPV1 in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Neurosci Lett, 388 (2): 75-80. [PMID:16039054]
22. Gavva NR, Tamir R, Qu Y, Klionsky L, Zhang TJ, Immke D, Wang J, Zhu D, Vanderah TW, Porreca F et al.. (2005) AMG 9810 [(E)-3-(4-t-butylphenyl)-N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4] dioxin-6-yl)acrylamide], a novel vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) antagonist with antihyperalgesic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 313 (1): 474-84. [PMID:15615864]
23. Geppetti P, Trevisani M. (2004) Activation and sensitisation of the vanilloid receptor: role in gastrointestinal inflammation and function. Br J Pharmacol, 141 (8): 1313-20. [PMID:15051629]
24. Gunthorpe MJ, Hannan SL, Smart D, Jerman JC, Arpino S, Smith GD, Brough S, Wright J, Egerton J, Lappin SC et al.. (2007) Characterization of SB-705498, a potent and selective vanilloid receptor-1 (VR1/TRPV1) antagonist that inhibits the capsaicin-, acid-, and heat-mediated activation of the receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 321 (3): 1183-92. [PMID:17392405]
25. Gunthorpe MJ, Rami HK, Jerman JC, Smart D, Gill CH, Soffin EM, Luis Hannan S, Lappin SC, Egerton J, Smith GD et al.. (2004) Identification and characterisation of SB-366791, a potent and selective vanilloid receptor (VR1/TRPV1) antagonist. Neuropharmacology, 46 (1): 133-49. [PMID:14654105]
26. Hayes P, Meadows HJ, Gunthorpe MJ, Harries MH, Duckworth DM, Cairns W, Harrison DC, Clarke CE, Ellington K, Prinjha RK et al.. (2000) Cloning and functional expression of a human orthologue of rat vanilloid receptor-1. Pain, 88 (2): 205-15. [PMID:11050376]
27. Hu HZ, Gu Q, Wang C, Colton CK, Tang J, Kinoshita-Kawada M, Lee LY, Wood JD, Zhu MX. (2004) 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate is a common activator of TRPV1, TRPV2, and TRPV3. J Biol Chem, 279 (34): 35741-8. [PMID:15194687]
28. Hwang SW, Cho H, Kwak J, Lee SY, Kang CJ, Jung J, Cho S, Min KH, Suh YG, Kim D et al.. (2000) Direct activation of capsaicin receptors by products of lipoxygenases: endogenous capsaicin-like substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 97 (11): 6155-60. [PMID:10823958]
29. Jerman JC, Brough SJ, Prinjha R, Harries MH, Davis JB, Smart D. (2000) Characterization using FLIPR of rat vanilloid receptor (rVR1) pharmacology. Br J Pharmacol, 130 (4): 916-22. [PMID:10864900]
30. Kaszas K, Keller JM, Coddou C, Mishra SK, Hoon MA, Stojilkovic S, Jacobson KA, Iadarola MJ. (2012) Small molecule positive allosteric modulation of TRPV1 activation by vanilloids and acidic pH. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 340 (1): 152-60. [PMID:22005042]
31. Kim S-Y, Kim JK, Lee K-W, Woo BY, Shin SS, Moh J-H, Kim S-il, Jeong YS, Lim KM, Choi JK et al.. (2010) Compounds, isomer thereof, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof as vanilloid receptor antagonist; and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same. Patent number: US7858621. Assignee: Amorepacific Corporation. Priority date: 27/07/2006. Publication date: 28/12/2010.
32. Kitaguchi T, Swartz KJ. (2005) An inhibitor of TRPV1 channels isolated from funnel Web spider venom. Biochemistry, 44 (47): 15544-9. [PMID:16300403]
33. Liapi A, Wood JN. (2005) Extensive co-localization and heteromultimer formation of the vanilloid receptor-like protein TRPV2 and the capsaicin receptor TRPV1 in the adult rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Neurosci, 22 (4): 825-34. [PMID:16115206]
34. Liedtke WB, Heller S, Latorre R, Vargas G, Orta G, Brauchi S. (2007) Voltage and Temperature Gating of ThermoTRP Channels. Frontiers in Neuroscience,. [PMID:21204490]
35. Lowin T, Apitz M, Anders S, Straub RH. (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of N-acylethanolamines in rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells are mediated by TRPV1 and TRPA1 in a COX-2 dependent manner. Arthritis Res Ther, 17: 321. [PMID:26567045]
36. Macpherson LJ, Geierstanger BH, Viswanath V, Bandell M, Eid SR, Hwang S, Patapoutian A. (2005) The pungency of garlic: activation of TRPA1 and TRPV1 in response to allicin. Curr Biol, 15 (10): 929-34. [PMID:15916949]
37. Majhi RK, Sahoo SS, Yadav M, Pratheek BM, Chattopadhyay S, Goswami C. (2015) Functional expression of TRPV channels in T cells and their implications in immune regulation. FEBS J, 282 (14): 2661-81. [PMID:25903376]
38. Matta JA, Ahern GP. (2007) Voltage is a partial activator of rat thermosensitive TRP channels. J Physiol (Lond.), 585 (Pt 2): 469-82. [PMID:17932142]
39. McIntyre P, McLatchie LM, Chambers A, Phillips E, Clarke M, Savidge J, Toms C, Peacock M, Shah K, Winter J et al.. (2001) Pharmacological differences between the human and rat vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Br J Pharmacol, 132 (5): 1084-94. [PMID:11226139]
40. McNamara FN, Randall A, Gunthorpe MJ. (2005) Effects of piperine, the pungent component of black pepper, at the human vanilloid receptor (TRPV1). Br J Pharmacol, 144 (6): 781-90. [PMID:15685214]
41. Mishra SK, Tisel SM, Orestes P, Bhangoo SK, Hoon MA. (2011) TRPV1-lineage neurons are required for thermal sensation. EMBO J, 30 (3): 582-93. [PMID:21139565]
42. MRC. AZD1386 TRPV1 ion channel inhibitor. Accessed on 28/10/2014. Modified on 28/10/2014. MRC/AstraZeneca: Mechanisms of Disease Call, http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20120104105854/http://www.mrc.ac.uk/consumption/groups/public/documents/content/mrc008366.pdf
43. Numazaki M, Tominaga T, Takeuchi K, Murayama N, Toyooka H, Tominaga M. (2003) Structural determinant of TRPV1 desensitization interacts with calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (13): 8002-6. [PMID:12808128]
44. Parenti A, De Logu F, Geppetti P, Benemei S. (2016) What is the evidence for the role of TRP channels in inflammatory and immune cells?. Br J Pharmacol, 173 (6): 953-69. [PMID:26603538]
45. Parsons WH, Calvo RR, Cheung W, Lee YK, Patel S, Liu J, Youngman MA, Dax SL, Stone D, Qin N et al.. (2015) Benzo[d]imidazole Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 Antagonists for the Treatment of Pain: Discovery of trans-2-(2-{2-[2-(4-Trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-vinyl]-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl}-phenyl)-propan-2-ol (Mavatrep). J Med Chem, 58 (9): 3859-74. [PMID:25850459]
46. Prescott ED, Julius D. (2003) A modular PIP2 binding site as a determinant of capsaicin receptor sensitivity. Science, 300 (5623): 1284-8. [PMID:12764195]
47. Rutter AR, Ma QP, Leveridge M, Bonnert TP. (2005) Heteromerization and colocalization of TrpV1 and TrpV2 in mammalian cell lines and rat dorsal root ganglia. Neuroreport, 16 (16): 1735-9. [PMID:16237318]
48. Samivel R, Kim DW, Son HR, Rhee YH, Kim EH, Kim JH, Bae JS, Chung YJ, Chung PS, Raz E et al.. (2016) The role of TRPV1 in the CD4+ T cell-mediated inflammatory response of allergic rhinitis. Oncotarget, 7 (1): 148-60. [PMID:26700618]
49. Siemens J, Zhou S, Piskorowski R, Nikai T, Lumpkin EA, Basbaum AI, King D, Julius D. (2006) Spider toxins activate the capsaicin receptor to produce inflammatory pain. Nature, 444 (7116): 208-12. [PMID:17093448]
50. Smart D, Gunthorpe MJ, Jerman JC, Nasir S, Gray J, Muir AI, Chambers JK, Randall AD, Davis JB. (2000) The endogenous lipid anandamide is a full agonist at the human vanilloid receptor (hVR1). Br J Pharmacol, 129 (2): 227-30. [PMID:10694225]
51. Smart D, Jerman JC, Gunthorpe MJ, Brough SJ, Ranson J, Cairns W, Hayes PD, Randall AD, Davis JB. (2001) Characterisation using FLIPR of human vanilloid VR1 receptor pharmacology. Eur J Pharmacol, 417 (1-2): 51-8. [PMID:11301059]
52. Smith GD, Gunthorpe MJ, Kelsell RE, Hayes PD, Reilly P, Facer P, Wright JE, Jerman JC, Walhin JP, Ooi L et al.. (2002) TRPV3 is a temperature-sensitive vanilloid receptor-like protein. Nature, 418 (6894): 186-90. [PMID:12077606]
53. Stein AT, Ufret-Vincenty CA, Hua L, Santana LF, Gordon SE. (2006) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase binds to TRPV1 and mediates NGF-stimulated TRPV1 trafficking to the plasma membrane. J Gen Physiol, 128 (5): 509-22. [PMID:17074976]
54. Sugiura T, Bielefeldt K, Gebhart GF. (2007) Mouse colon sensory neurons detect extracellular acidosis via TRPV1. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol, 292 (5): C1768-74. [PMID:17251322]
55. Swanson DM, Dubin AE, Shah C, Nasser N, Chang L, Dax SL, Jetter M, Breitenbucher JG, Liu C, Mazur C et al.. (2005) Identification and biological evaluation of 4-(3-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl)piperazine-1-carboxylic acid (5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl)amide, a high affinity TRPV1 (VR1) vanilloid receptor antagonist. J Med Chem, 48 (6): 1857-72. [PMID:15771431]
56. Tominaga M, Caterina MJ, Malmberg AB, Rosen TA, Gilbert H, Skinner K, Raumann BE, Basbaum AI, Julius D. (1998) The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron, 21 (3): 531-43. [PMID:9768840]
57. Trevisani M, Smart D, Gunthorpe MJ, Tognetto M, Barbieri M, Campi B, Amadesi S, Gray J, Jerman JC, Brough SJ et al.. (2002) Ethanol elicits and potentiates nociceptor responses via the vanilloid receptor-1. Nat Neurosci, 5 (6): 546-51. [PMID:11992116]
58. Tympanidis P, Casula MA, Yiangou Y, Terenghi G, Dowd P, Anand P. (2004) Increased vanilloid receptor VR1 innervation in vulvodynia. Eur J Pain, 8 (2): 129-33. [PMID:14987622]
59. Vaeth M, Feske S. (2018) Ion channelopathies of the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol, 52: 39-50. [PMID:29635109]
60. Valenzano KJ, Grant ER, Wu G, Hachicha M, Schmid L, Tafesse L, Sun Q, Rotshteyn Y, Francis J, Limberis J et al.. (2003) N-(4-tertiarybutylphenyl)-4-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)tetrahydropyrazine -1(2H)-carbox-amide (BCTC), a novel, orally effective vanilloid receptor 1 antagonist with analgesic properties: I. in vitro characterization and pharmacokinetic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 306 (1): 377-86. [PMID:12721338]
61. Voets T, Droogmans G, Wissenbach U, Janssens A, Flockerzi V, Nilius B. (2004) The principle of temperature-dependent gating in cold- and heat-sensitive TRP channels. Nature, 430 (7001): 748-54. [PMID:15306801]
62. Voight EA, Gomtsyan AR, Daanen JF, Perner RJ, Schmidt RG, Bayburt EK, DiDomenico S, McDonald HA, Puttfarcken PS, Chen J et al.. (2014) Discovery of (R)-1-(7-chloro-2,2-bis(fluoromethyl)chroman-4-yl)-3-(3-methylisoquinolin-5-yl)urea (A-1165442): a temperature-neutral transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) antagonist with analgesic efficacy. J Med Chem, 57 (17): 7412-24. [PMID:25100568]
63. Wahl P, Foged C, Tullin S, Thomsen C. (2001) Iodo-resiniferatoxin, a new potent vanilloid receptor antagonist. Mol Pharmacol, 59 (1): 9-15. [PMID:11125018]
64. Wang HL, Katon J, Balan C, Bannon AW, Bernard C, Doherty EM, Dominguez C, Gavva NR, Gore V, Ma V et al.. (2007) Novel vanilloid receptor-1 antagonists: 3. The identification of a second-generation clinical candidate with improved physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. J Med Chem, 50 (15): 3528-39. [PMID:17585751]
65. Wang Y, Szabo T, Welter JD, Toth A, Tran R, Lee J, Kang SU, Suh YG, Blumberg PM, Lee J. (2002) High affinity antagonists of the vanilloid receptor. Mol Pharmacol, 62 (4): 947-56. [PMID:12237342]
66. Yang S, Yang F, Wei N, Hong J, Li B, Luo L, Rong M, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Zheng J, Wang K et al.. (2015) A pain-inducing centipede toxin targets the heat activation machinery of nociceptor TRPV1. Nat Commun, 6: 8297. [PMID:26420335]
67. Yiangou Y, Facer P, Dyer NH, Chan CL, Knowles C, Williams NS, Anand P. (2001) Vanilloid receptor 1 immunoreactivity in inflamed human bowel. Lancet, 357 (9265): 1338-9. [PMID:11343743]
68. Zhang H, Lin JJ, Xie YK, Song XZ, Sun JY, Zhang BL, Qi YK, Xu ZZ, Yang F. (2023) Structure-guided peptide engineering of a positive allosteric modulator targeting the outer pore of TRPV1 for long-lasting analgesia. Nat Commun, 14 (1): 4. [PMID:36596769]
69. Zhang X, Li L, McNaughton PA. (2008) Proinflammatory mediators modulate the heat-activated ion channel TRPV1 via the scaffolding protein AKAP79/150. Neuron, 59 (3): 450-61. [PMID:18701070]
70. Zygmunt PM, Petersson J, Andersson DA, Chuang H, Sørgård M, Di Marzo V, Julius D, Högestätt ED. (1999) Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature, 400 (6743): 452-7. [PMID:10440374]















