GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Biologically Significant Variants
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 350 | 4q35.2 | MTNR1A | melatonin receptor 1A | 64-65,76 |
| Mouse | 7 | 353 | 8 24.95 cM | Mtnr1a | melatonin receptor 1A | 68 |
| Rat | 3 | 156 | 16q11 | Mtnr1a | melatonin receptor 1A | 3 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| mel1a receptor | MelR |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | mtr1a_human (Hs), mtr1a_mouse (Mm) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P48039 (Hs), Q61184 (Mm), P49218 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1945 (Hs) |
| DrugBank Target | P48039 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000168412 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000054764 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000028744 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 4543 (Hs), 17773 (Mm), 114211 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000168412 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:4543 (Hs), mmu:17773 (Mm), rno:114211 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600665 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P48039 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_005958 (Hs), NM_008639 (Mm), NM_053676 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_005949 (Hs), NP_032665 (Mm), NP_446128 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P48039 (Hs), Q61184 (Mm), P49218 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | MTNR1A (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
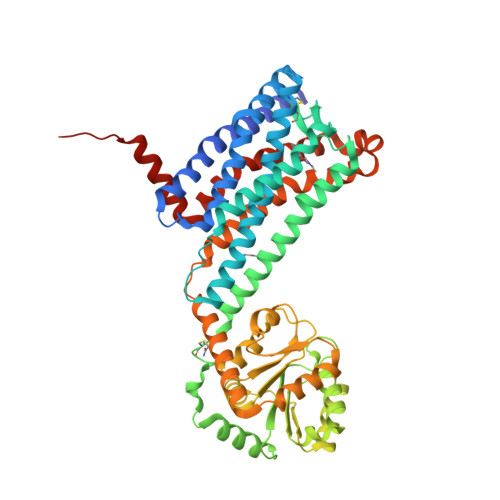
|
|
||||||||||||
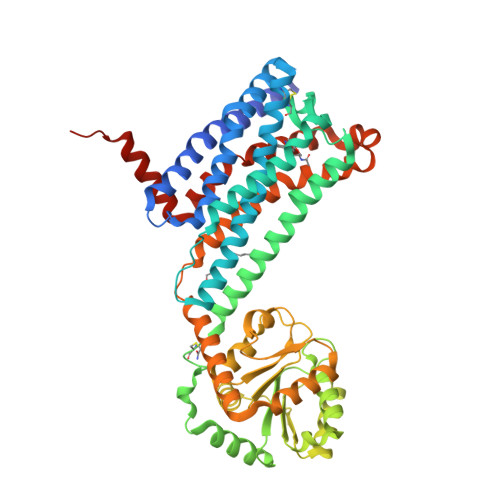
|
|
||||||||||||
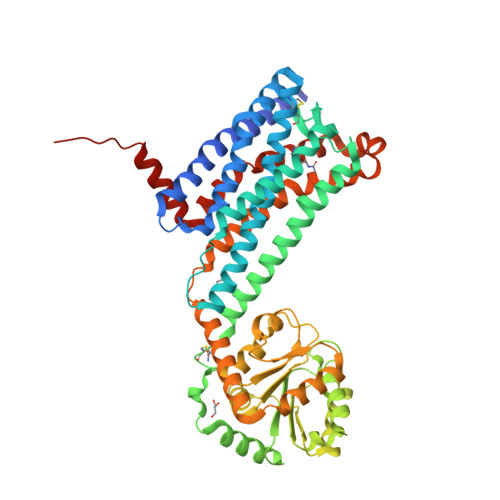
|
|
||||||||||||
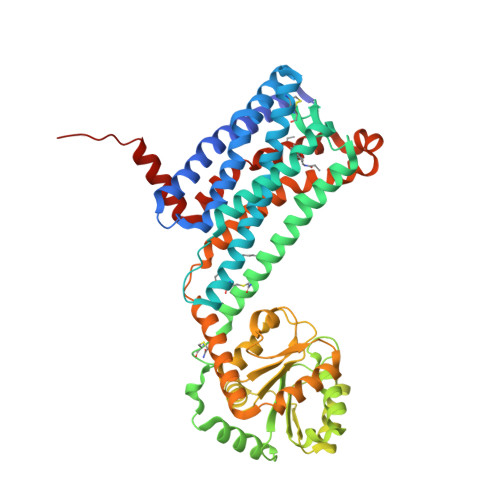
|
|
||||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| melatonin |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family | Adenylyl cyclase inhibition |
| References: 27,40,50,54,64 | |
Secondary Transduction Mechanisms  |
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gq/G11 family |
Phospholipase C stimulation Potassium channel Calcium channel |
| References: 27,50,54,69 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Tissue Distribution Comments | ||||||||
| For a review on melatonin receptor function see [22-23,25,27,85,93]. | ||||||||
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
| General Comments |
| The molecular pharmacology of ovine melatonin receptors has been shown to be different to human recombinant melatonin receptors [52]. |
References
1. Al-Ghoul WM, Herman MD, Dubocovich ML. (1998) Melatonin receptor subtype expression in human cerebellum. Neuroreport, 9 (18): 4063-8. [PMID:9926848]
2. AstraZeneca. AZD7325. Accessed on 11/09/2014. Modified on 11/09/2014. astrazeneca.com, http://openinnovation.astrazeneca.com/what-we-offer/compound/azd7325/
3. Audinot V, Bonnaud A, Grandcolas L, Rodriguez M, Nagel N, Galizzi JP, Balik A, Messager S, Hazlerigg DG, Barrett P et al.. (2008) Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of rat melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol, 75 (10): 2007-19. [PMID:18384758]
4. Audinot V, Mailliet F, Lahaye-Brasseur C, Bonnaud A, Le Gall A, Amossé C, Dromaint S, Rodriguez M, Nagel N, Galizzi JP et al.. (2003) New selective ligands of human cloned melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 367 (6): 553-61. [PMID:12764576]
5. Ayoub MA, Couturier C, Lucas-Meunier E, Angers S, Fossier P, Bouvier M, Jockers R. (2002) Monitoring of ligand-independent dimerization and ligand-induced conformational changes of melatonin receptors in living cells by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer. J Biol Chem, 277 (24): 21522-8. [PMID:11940583]
6. Ayoub MA, Levoye A, Delagrange P, Jockers R. (2004) Preferential formation of MT1/MT2 melatonin receptor heterodimers with distinct ligand interaction properties compared with MT2 homodimers. Mol Pharmacol, 66 (2): 312-21. [PMID:15266022]
7. Baba K, Pozdeyev N, Mazzoni F, Contreras-Alcantara S, Liu C, Kasamatsu M, Martinez-Merlos T, Strettoi E, Iuvone PM, Tosini G. (2009) Melatonin modulates visual function and cell viability in the mouse retina via the MT1 melatonin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106 (35): 15043-8. [PMID:19706469]
8. Benleulmi-Chaachoua A, Hegron A, Le Boulch M, Karamitri A, Wierzbicka M, Wong V, Stagljar I, Delagrange P, Ahmad R, Jockers R. (2018) Melatonin receptors limit dopamine reuptake by regulating dopamine transporter cell-surface exposure. Cell Mol Life Sci, 75 (23): 4357-4370. [PMID:30043140]
9. Beresford IJ, Browning C, Starkey SJ, Brown J, Foord SM, Coughlan J, North PC, Dubocovich ML, Hagan RM. (1998) GR196429: a nonindolic agonist at high-affinity melatonin receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 285 (3): 1239-45. [PMID:9618428]
10. Beresford IJ, Harvey FJ, Hall DA, Giles H. (1998) Pharmacological characterisation of melatonin mt1 receptor-mediated stimulation of [35S]-GTPgammaS binding. Biochem Pharmacol, 56 (9): 1167-74. [PMID:9802327]
11. Blask DE, Brainard GC, Dauchy RT, Hanifin JP, Davidson LK, Krause JA, Sauer LA, Rivera-Bermudez MA, Dubocovich ML, Jasser SA et al.. (2005) Melatonin-depleted blood from premenopausal women exposed to light at night stimulates growth of human breast cancer xenografts in nude rats. Cancer Res, 65 (23): 11174-84. [PMID:16322268]
12. Blask DE, Dauchy RT, Sauer LA, Krause JA, Brainard GC. (2002) Light during darkness, melatonin suppression and cancer progression. Neuro Endocrinol Lett, 23 Suppl 2: 52-6. [PMID:12163849]
13. Browning C, Beresford I, Fraser N, Giles H. (2000) Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin mt(1) and MT(2) receptors. Br J Pharmacol, 129 (5): 877-86. [PMID:10696085]
14. Brydon L, Petit L, Delagrange P, Strosberg AD, Jockers R. (2001) Functional expression of MT2 (Mel1b) melatonin receptors in human PAZ6 adipocytes. Endocrinology, 142 (10): 4264-71. [PMID:11564683]
15. Carrillo-Vico A, García-Mauriño S, Calvo JR, Guerrero JM. (2003) Melatonin counteracts the inhibitory effect of PGE2 on IL-2 production in human lymphocytes via its mt1 membrane receptor. FASEB J, 17 (6): 755-7. [PMID:12594180]
16. Chaste P, Clement N, Botros HG, Guillaume JL, Konyukh M, Pagan C, Scheid I, Nygren G, Anckarsäter H, Rastam M et al.. (2011) Genetic variations of the melatonin pathway in patients with attention-deficit and hyperactivity disorders. J Pineal Res, 51 (4): 394-9. [PMID:21615493]
17. Chaste P, Clement N, Mercati O, Guillaume JL, Delorme R, Botros HG, Pagan C, Périvier S, Scheid I, Nygren G, Anckarsäter H, Rastam M, Ståhlberg O, Gillberg C, Serrano E, Lemière N, Launay JM, Mouren-Simeoni MC, Leboyer M, Gillberg C, Jockers R, Bourgeron T. (2010) Identification of pathway-biased and deleterious melatonin receptor mutants in autism spectrum disorders and in the general population. PLoS ONE, 5 (7): e11495. [PMID:20657642]
18. Doolen S, Krause DN, Dubocovich ML, Duckles SP. (1998) Melatonin mediates two distinct responses in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol, 345 (1): 67-9. [PMID:9593596]
19. Drew JE, Williams LM, Hannah LT, Barrett P, Abramovich DR. (1998) Melatonin receptors in the human fetal kidney: 2-[125I]iodomelatonin binding sites correlated with expression of Mel1a and Mel1b receptor genes. J Endocrinol, 156 (2): 261-7. [PMID:9518871]
20. Dubocovich ML. (1985) Characterization of a retinal melatonin receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 234 (2): 395-401. [PMID:2991499]
21. Dubocovich ML. (1988) Luzindole (N-0774): a novel melatonin receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 246 (3): 902-10. [PMID:2843633]
22. Dubocovich ML. (2007) Melatonin receptors: role on sleep and circadian rhythm regulation. Sleep Med, 8 Suppl 3: 34-42. [PMID:18032103]
23. Dubocovich ML, Delagrange P, Krause DN, Sugden D, Cardinali DP, Olcese J. (2010) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXV. Nomenclature, classification, and pharmacology of G protein-coupled melatonin receptors. Pharmacol Rev, 62 (3): 343-80. [PMID:20605968]
24. Dubocovich ML, Hudson RL, Sumaya IC, Masana MI, Manna E. (2005) Effect of MT1 melatonin receptor deletion on melatonin-mediated phase shift of circadian rhythms in the C57BL/6 mouse. J Pineal Res, 39 (2): 113-20. [PMID:16098087]
25. Dubocovich ML, Markowska M. (2005) Functional MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors in mammals. Endocrine, 27 (2): 101-10. [PMID:16217123]
26. Dubocovich ML, Masana MI, Iacob S, Sauri DM. (1997) Melatonin receptor antagonists that differentiate between the human Mel1a and Mel1b recombinant subtypes are used to assess the pharmacological profile of the rabbit retina ML1 presynaptic heteroreceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 355 (3): 365-75. [PMID:9089668]
27. Dubocovich ML, Rivera-Bermudez MA, Gerdin MJ, Masana MI. (2003) Molecular pharmacology, regulation and function of mammalian melatonin receptors. Front Biosci, 8: d1093-108. [PMID:12957828]
28. Dubocovich ML, Yun K, Al-Ghoul WM, Benloucif S, Masana MI. (1998) Selective MT2 melatonin receptor antagonists block melatonin-mediated phase advances of circadian rhythms. FASEB J, 12 (12): 1211-20. [PMID:9737724]
29. Ebisawa T, Kajimura N, Uchiyama M, Katoh M, Sekimoto M, Watanabe T, Ozeki Y, Ikeda M, Jodoi T, Sugishita M et al.. (1999) Alleic variants of human melatonin 1a receptor: function and prevalence in subjects with circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 262 (3): 832-7. [PMID:10471411]
30. Ekmekcioglu C, Haslmayer P, Philipp C, Mehrabi MR, Glogar HD, Grimm M, Leibetseder VJ, Thalhammer T, Marktl W. (2001) Expression of the MT1 melatonin receptor subtype in human coronary arteries. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 21 (1): 85-91. [PMID:11693175]
31. Ekmekcioglu C, Haslmayer P, Philipp C, Mehrabi MR, Glogar HD, Grimm M, Thalhammer T, Marktl W. (2001) 24h variation in the expression of the mt1 melatonin receptor subtype in coronary arteries derived from patients with coronary heart disease. Chronobiol Int, 18 (6): 973-85. [PMID:11777084]
32. Ettaoussi M, Sabaouni A, Rami M, Boutin JA, Delagrange P, Renard P, Spedding M, Caignard DH, Berthelot P, Yous S. (2012) Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of new series of naphthalenic analogues as melatoninergic (MT1/MT2) and serotoninergic 5-HT2C dual ligands (I). Eur J Med Chem, 49: 310-23. [PMID:22301214]
33. Faust R, Garratt PJ, Jones R, Yeh LK, Tsotinis A, Panoussopoulou M, Calogeropoulou T, Teh MT, Sugden D. (2000) Mapping the melatonin receptor. 6. Melatonin agonists and antagonists derived from 6H-isoindolo[2,1-a]indoles, 5,6-dihydroindolo[2,1-a]isoquinolines, and 6,7-dihydro-5H-benzo[c]azepino[2,1-a]indoles. J Med Chem, 43 (6): 1050-61. [PMID:10737738]
34. Gbahou F, Cecon E, Viault G, Gerbier R, Jean-Alphonse F, Karamitri A, Guillaumet G, Delagrange P, Friedlander RM, Vilardaga JP et al.. (2017) Design and validation of the first cell-impermeant melatonin receptor agonist. Br J Pharmacol, 174 (14): 2409-2421. [PMID:28493341]
35. Geary GG, Duckles SP, Krause DN. (1998) Effect of melatonin in the rat tail artery: role of K+ channels and endothelial factors. Br J Pharmacol, 123 (8): 1533-40. [PMID:9605558]
36. Geary GG, Krause DN, Duckles SP. (1997) Melatonin directly constricts rat cerebral arteries through modulation of potassium channels. Am J Physiol, 273 (3 Pt 2): H1530-6. [PMID:9321846]
37. Jilg A, Moek J, Weaver DR, Korf HW, Stehle JH, von Gall C. (2005) Rhythms in clock proteins in the mouse pars tuberalis depend on MT1 melatonin receptor signalling. Eur J Neurosci, 22 (11): 2845-54. [PMID:16324119]
38. Johnston JD, Messager S, Barrett P, Hazlerigg DG. (2003) Melatonin action in the pituitary: neuroendocrine synchronizer and developmental modulator?. J Neuroendocrinol, 15 (4): 405-8. [PMID:12622841]
39. Johnston JD, Messager S, Ebling FJ, Williams LM, Barrett P, Hazlerigg DG. (2003) Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone drives melatonin receptor down-regulation in the developing pituitary gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (5): 2831-5. [PMID:12598657]
40. Kato K, Hirai K, Nishiyama K, Uchikawa O, Fukatsu K, Ohkawa S, Kawamata Y, Hinuma S, Miyamoto M. (2005) Neurochemical properties of ramelteon (TAK-375), a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist. Neuropharmacology, 48 (2): 301-10. [PMID:15695169]
41. Kemp DM, Ubeda M, Habener JF. (2002) Identification and functional characterization of melatonin Mel 1a receptors in pancreatic beta cells: potential role in incretin-mediated cell function by sensitization of cAMP signaling. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 191 (2): 157-66. [PMID:12062899]
42. Koike T, Takai T, Hoashi Y, Nakayama M, Kosugi Y, Nakashima M, Yoshikubo S, Hirai K, Uchikawa O. (2011) Synthesis of a novel series of tricyclic dihydrofuran derivatives: discovery of 8,9-dihydrofuro[3,2-c]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridines as melatonin receptor (MT1/MT2) ligands. J Med Chem, 54 (12): 4207-18. [PMID:21568291]
43. Krause DN, Barrios VE, Duckles SP. (1995) Melatonin receptors mediate potentiation of contractile responses to adrenergic nerve stimulation in rat caudal artery. Eur J Pharmacol, 276 (3): 207-13. [PMID:7601206]
44. Lardone PJ, Rubio A, Cerrillo I, Gómez-Corvera A, Carrillo-Vico A, Sanchez-Hidalgo M, Guerrero JM, Fernandez-Riejos P, Sanchez-Margalet V, Molinero P. (2010) Blocking of melatonin synthesis and MT(1) receptor impairs the activation of Jurkat T cells. Cell Mol Life Sci, 67 (18): 3163-72. [PMID:20440532]
45. Legros C, Brasseur C, Delagrange P, Ducrot P, Nosjean O, Boutin JA. (2016) Alternative Radioligands for Investigating the Molecular Pharmacology of Melatonin Receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 356 (3): 681-92. [PMID:26759496]
46. Legros C, Matthey U, Grelak T, Pedragona-Moreau S, Hassler W, Yous S, Thomas E, Suzenet F, Folleas B, Lefoulon F et al.. (2013) New Radioligands for Describing the Molecular Pharmacology of MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors. Int J Mol Sci, 14 (5): 8948-62. [PMID:23698757]
47. Levoye A, Dam J, Ayoub MA, Guillaume JL, Couturier C, Delagrange P, Jockers R. (2006) The orphan GPR50 receptor specifically inhibits MT1 melatonin receptor function through heterodimerization. EMBO J, 25 (13): 3012-23. [PMID:16778767]
48. Liu C, Weaver DR, Jin X, Shearman LP, Pieschl RL, Gribkoff VK, Reppert SM. (1997) Molecular dissection of two distinct actions of melatonin on the suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Neuron, 19 (1): 91-102. [PMID:9247266]
49. Lucini V, Pannacci M, Scaglione F, Fraschini F, Rivara S, Mor M, Bordi F, Plazzi PV, Spadoni G, Bedini A et al.. (2004) Tricyclic alkylamides as melatonin receptor ligands with antagonist or inverse agonist activity. J Med Chem, 47 (17): 4202-12. [PMID:15293992]
50. MacKenzie RS, Melan MA, Passey DK, Witt-Enderby PA. (2002) Dual coupling of MT(1) and MT(2) melatonin receptors to cyclic AMP and phosphoinositide signal transduction cascades and their regulation following melatonin exposure. Biochem Pharmacol, 63 (4): 587-95. [PMID:11992626]
51. Mahle CD, Goggins GD, Agarwal P, Ryan E, Watson AJ. (1997) Melatonin modulates vascular smooth muscle tone. J Biol Rhythms, 12 (6): 690-6. [PMID:9406046]
52. Mailliet F, Audinot V, Malpaux B, Bonnaud A, Delagrange P, Migaud M, Barrett P, Viaud-Massuard MC, Lesieur D, Lefoulon F et al.. (2004) Molecular pharmacology of the ovine melatonin receptor: comparison with recombinant human MT1 and MT2 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol, 67 (4): 667-77. [PMID:14757166]
53. Masana MI, Doolen S, Ersahin C, Al-Ghoul WM, Duckles SP, Dubocovich ML, Krause DN. (2002) MT(2) melatonin receptors are present and functional in rat caudal artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 302: 1295-1302. [PMID:12183692]
54. Masana MI, Dubocovich ML. (2001) Melatonin receptor signaling: finding the path through the dark. Sci STKE, 2001 (107): pe39. [PMID:11698691]
55. Mazzucchelli C, Pannacci M, Nonno R, Lucini V, Fraschini F, Stankov BM. (1996) The melatonin receptor in the human brain: cloning experiments and distribution studies. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 39 (1-2): 117-26. [PMID:8804720]
56. Morellato L, Lefas-Le Gall M, Langlois M, Caignard DH, Renard P, Delagrange P, Mathé-Allainmat M. (2013) Synthesis of new N-(arylcyclopropyl)acetamides and N-(arylvinyl)acetamides as conformationally-restricted ligands for melatonin receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 23 (2): 430-4. [PMID:23265885]
57. Mulchahey JJ, Goldwater DR, Zemlan FP. (2004) A single blind, placebo controlled, across groups dose escalation study of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the melatonin analog beta-methyl-6-chloromelatonin. Life Sci, 75 (15): 1843-56. [PMID:15302228]
58. Mésangeau C, Pérès B, Descamps-François C, Chavatte P, Audinot V, Coumailleau S, Boutin JA, Delagrange P, Bennejean C, Renard P et al.. (2010) Design, synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of novel naphthalenic derivatives as selective MT(1) melatoninergic ligands. Bioorg Med Chem, 18 (10): 3426-36. [PMID:20444610]
59. Naji L, Carrillo-Vico A, Guerrero JM, Calvo JR. (2004) Expression of membrane and nuclear melatonin receptors in mouse peripheral organs. Life Sci, 74: 2227-2236. [PMID:14987948]
60. Niles LP, Wang J, Shen L, Lobb DK, Younglai EV. (1999) Melatonin receptor mRNA expression in human granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 156 (1-2): 107-10. [PMID:10612428]
61. Nonno R, Lucini V, Spadoni G, Pannacci M, Croce A, Esposti D, Balsamini C, Tarzia G, Fraschini F, Stankov BM. (2000) A new melatonin receptor ligand with mt1-agonist and MT2-antagonist properties. J Pineal Res, 29 (4): 234-40. [PMID:11068946]
62. Rajaratnam SM, Polymeropoulos MH, Fisher DM, Roth T, Scott C, Birznieks G, Klerman EB. (2009) Melatonin agonist tasimelteon (VEC-162) for transient insomnia after sleep-time shift: two randomised controlled multicentre trials. Lancet, 373 (9662): 482-91. [PMID:19054552]
63. Ram PT, Dai J, Yuan L, Dong C, Kiefer TL, Lai L, Hill SM. (2002) Involvement of the mt1 melatonin receptor in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett, 179 (2): 141-50. [PMID:11888668]
64. Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Ebisawa T. (1994) Cloning and characterization of a mammalian melatonin receptor that mediates reproductive and circadian responses. Neuron, 13 (5): 1177-85. [PMID:7946354]
65. Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Godson C. (1996) Melatonin receptors step into the light: cloning and classification of subtypes. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 17 (3): 100-2. [PMID:8936344]
66. Rivara S, Lodola A, Mor M, Bedini A, Spadoni G, Lucini V, Pannacci M, Fraschini F, Scaglione F, Sanchez RO et al.. (2007) N-(substituted-anilinoethyl)amides: design, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of a new class of melatonin receptor ligands. J Med Chem, 50 (26): 6618-26. [PMID:18052314]
67. Rivara S, Pala D, Lodola A, Mor M, Lucini V, Dugnani S, Scaglione F, Bedini A, Lucarini S, Tarzia G et al.. (2012) MT1-selective melatonin receptor ligands: synthesis, pharmacological evaluation, and molecular dynamics investigation of N-{[(3-O-substituted)anilino]alkyl}amides. ChemMedChem, 7 (11): 1954-64. [PMID:22927210]
68. Roca AL, Godson C, Weaver DR, Reppert SM. (1996) Structure, characterization, and expression of the gene encoding the mouse Mel1a melatonin receptor. Endocrinology, 137 (8): 3469-77. [PMID:8754776]
69. Roka F, Brydon L, Waldhoer M, Strosberg AD, Freissmuth M, Jockers R, Nanoff C. (1999) Tight association of the human Mel(1a)-melatonin receptor and G(i): precoupling and constitutive activity. Mol Pharmacol, 56 (5): 1014-24. [PMID:10531408]
70. Sallinen P, Saarela S, Ilves M, Vakkuri O, Leppäluoto J. (2005) The expression of MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptor mRNA in several rat tissues. Life Sci, 76 (10): 1123-34. [PMID:15620576]
71. Savaskan E, Olivieri G, Brydon L, Jockers R, Kräuchi K, Wirz-Justice A, Müller-Spahn F. (2001) Cerebrovascular melatonin MT1-receptor alterations in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett, 308 (1): 9-12. [PMID:11445273]
72. Savaskan E, Wirz-Justice A, Olivieri G, Pache M, Kräuchi K, Brydon L, Jockers R, Müller-Spahn F, Meyer P. (2002) Distribution of melatonin MT1 receptor immunoreactivity in human retina. J Histochem Cytochem, 50 (4): 519-26. [PMID:11897804]
73. Scher J, Wankiewicz E, Brown GM, Fujieda H. (2002) MT(1) melatonin receptor in the human retina: expression and localization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 43 (3): 889-97. [PMID:11867612]
74. Scher J, Wankiewicz E, Brown GM, Fujieda H. (2003) AII amacrine cells express the MT1 melatonin receptor in human and macaque retina. Exp Eye Res, 77 (3): 375-82. [PMID:12907170]
75. Sengupta A, Baba K, Mazzoni F, Pozdeyev NV, Strettoi E, Iuvone PM, Tosini G. (2011) Localization of melatonin receptor 1 in mouse retina and its role in the circadian regulation of the electroretinogram and dopamine levels. PLoS ONE, 6 (9): e24483. [PMID:21915336]
76. Slaugenhaupt SA, Roca AL, Liebert CB, Altherr MR, Gusella JF, Reppert SM. (1995) Mapping of the gene for the Mel1a-melatonin receptor to human chromosome 4 (MTNR1A) and mouse chromosome 8 (Mtnr1a). Genomics, 27 (2): 355-7. [PMID:7558006]
77. Soares Jr JM, Masana MI, Erşahin C, Dubocovich ML. (2003) Functional melatonin receptors in rat ovaries at various stages of the estrous cycle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 306 (2): 694-702. [PMID:12721330]
78. Spadoni G, Bedini A, Diamantini G, Tarzia G, Rivara S, Lorenzi S, Lodola A, Mor M, Lucini V, Pannacci M et al.. (2007) Synthesis, enantiomeric resolution, and structure-activity relationship study of a series of 10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]cycloheptene MT2 receptor antagonists. ChemMedChem, 2 (12): 1741-9. [PMID:17907131]
79. Spadoni G, Bedini A, Furiassi L, Mari M, Mor M, Scalvini L, Lodola A, Ghidini A, Lucini V, Dugnani S et al.. (2018) Identification of Bivalent Ligands with Melatonin Receptor Agonist and Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH) Inhibitory Activity That Exhibit Ocular Hypotensive Effect in the Rabbit. J Med Chem, 61 (17): 7902-7916. [PMID:30126274]
80. Stauch B, Johansson LC, McCorvy JD, Patel N, Han GW, Huang XP, Gati C, Batyuk A, Slocum ST, Ishchenko A et al.. (2019) Structural basis of ligand recognition at the human MT1 melatonin receptor. Nature, 569 (7755): 284-288. [PMID:31019306]
81. Stein RM, Kang HJ, McCorvy JD, Glatfelter GC, Jones AJ, Che T, Slocum S, Huang XP, Savych O, Moroz YS et al.. (2020) Virtual discovery of melatonin receptor ligands to modulate circadian rhythms. Nature, 579 (7800): 609-614. [PMID:32040955]
82. Teh MT, Sugden D. (1999) The putative melatonin receptor antagonist GR128107 is a partial agonist on Xenopus laevis melanophores. Br J Pharmacol, 126 (5): 1237-45. [PMID:10205014]
83. Ting KN, Blaylock NA, Sugden D, Delagrange P, Scalbert E, Wilson VG. (1999) Molecular and pharmacological evidence for MT1 melatonin receptor subtype in the tail artery of juvenile Wistar rats. Br J Pharmacol, 127: 987-995. [PMID:10433507]
84. Ting KN, Dunn WR, Davies DJ, Sugden D, Delagrange P, Guardiola-Lemaître B, Scalbert E, Wilson VG. (1997) Studies on the vasoconstrictor action of melatonin and putative melatonin receptor ligands in the tail artery of juvenile Wistar rats. Br J Pharmacol, 122 (7): 1299-306. [PMID:9421275]
85. Tosini G, Owino S, Guillaume JL, Jockers R. (2014) Understanding melatonin receptor pharmacology: latest insights from mouse models, and their relevance to human disease. Bioessays, 36 (8): 778-87. [PMID:24903552]
86. Valenti S, Thellung S, Florio T, Giusti M, Schettini G, Giordano G. (1999) A novel mechanism for the melatonin inhibition of testosterone secretion by rat Leydig cells: reduction of GnRH-induced increase in cytosolic Ca2+. J Mol Endocrinol, 23 (3): 299-306. [PMID:10601975]
87. Vanecek J. (1998) Cellular mechanisms of melatonin action. Physiol Rev, 78 (3): 687-721. [PMID:9674691]
88. von Gall C, Garabette ML, Kell CA, Frenzel S, Dehghani F, Schumm-Draeger PM, Weaver DR, Korf HW, Hastings MH, Stehle JH. (2002) Rhythmic gene expression in pituitary depends on heterologous sensitization by the neurohormone melatonin. Nat Neurosci, 5: 234-238. [PMID:11836530]
89. Weaver DR, Reppert SM. (1996) The Mel1a melatonin receptor gene is expressed in human suprachiasmatic nuclei. Neuroreport, 8 (1): 109-12. [PMID:9051762]
90. Weil ZM, Hotchkiss AK, Gatien ML, Pieke-Dahl S, Nelson RJ. (2006) Melatonin receptor (MT1) knockout mice display depression-like behaviors and deficits in sensorimotor gating. Brain Res Bull, 68 (6): 425-9. [PMID:16459197]
91. Witt-Enderby PA, Dubocovich ML. (1996) Characterization and regulation of the human ML1A melatonin receptor stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Pharmacol, 50 (1): 166-74. [PMID:8700109]
92. Yasuo S, Yoshimura T, Ebihara S, Korf HW. (2009) Melatonin transmits photoperiodic signals through the MT1 melatonin receptor. J Neurosci, 29 (9): 2885-9. [PMID:19261884]
93. Zlotos DP, Jockers R, Cecon E, Rivara S, Witt-Enderby PA. (2014) MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors: ligands, models, oligomers, and therapeutic potential. J Med Chem, 57 (8): 3161-85. [PMID:24228714]














