GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
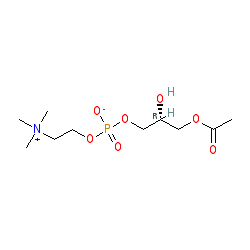
Abbreviated name: LPC
Compound class:
Metabolite
Comment: The structure shown here is a representative example of the lysophosphatidylcholine class of compounds. The R group terminal linked to the ester (shown here as a methyl group) is a fatty acid chain of varying length. For examples of lysophospatidylcholine compounds with specified chain lengths see oleoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine and 1-palmitoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Clair T, Aoki J, Koh E, Bandle RW, Nam SW, Ptaszynska MM, Mills GB, Schiffmann E, Liotta LA, Stracke ML. (2003)
Autotaxin hydrolyzes sphingosylphosphorylcholine to produce the regulator of migration, sphingosine-1-phosphate. Cancer Res, 63 (17): 5446-53. [PMID:14500380] |
|
2. Davenport AP, Alexander SP, Sharman JL, Pawson AJ, Benson HE, Monaghan AE, Liew WC, Mpamhanga CP, Bonner TI, Neubig RR et al.. (2013)
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXVIII. G protein-coupled receptor list: recommendations for new pairings with cognate ligands. Pharmacol Rev, 65 (3): 967-86. [PMID:23686350] |
|
3. Kabarowski JH, Zhu K, Le LQ, Witte ON, Xu Y. (2001)
Lysophosphatidylcholine as a ligand for the immunoregulatory receptor G2A. Science, 293 (5530): 702-5. [PMID:11474113] |
|
4. Lesage F, Terrenoire C, Romey G, Lazdunski M. (2000)
Human TREK2, a 2P domain mechano-sensitive K+ channel with multiple regulations by polyunsaturated fatty acids, lysophospholipids, and Gs, Gi, and Gq protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem, 275 (37): 28398-405. [PMID:10880510] |
|
5. Marra S, Ferru-Clément R, Breuil V, Delaunay A, Christin M, Friend V, Sebille S, Cognard C, Ferreira T, Roux C et al.. (2016)
Non-acidic activation of pain-related Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 3 by lipids. EMBO J, 35 (4): 414-28. [PMID:26772186] |
|
6. Mihara H, Boudaka A, Shibasaki K, Yamanaka A, Sugiyama T, Tominaga M. (2010)
Involvement of TRPV2 activation in intestinal movement through nitric oxide production in mice. J Neurosci, 30 (49): 16536-44. [PMID:21147993] |
|
7. Monet M, Gkika D, Lehen'kyi V, Pourtier A, Vanden Abeele F, Bidaux G, Juvin V, Rassendren F, Humez S, Prevarsakaya N. (2009)
Lysophospholipids stimulate prostate cancer cell migration via TRPV2 channel activation. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1793 (3): 528-39. [PMID:19321128] |
|
8. No authors listed. (2005)
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine are ligands for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR4. (Retraction). J Biol Chem, 280 (52): 43280. [PMID:16498716] |
|
9. Seuwen K, Ludwig MG, Wolf RM. (2006)
Receptors for protons or lipid messengers or both?. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 26 (5-6): 599-610. [PMID:17118800] |
|
10. Tobo A, Tobo M, Nakakura T, Ebara M, Tomura H, Mogi C, Im DS, Murata N, Kuwabara A, Ito S et al.. (2015)
Characterization of Imidazopyridine Compounds as Negative Allosteric Modulators of Proton-Sensing GPR4 in Extracellular Acidification-Induced Responses. PLoS ONE, 10 (6): e0129334. [PMID:26070068] |
|
11. Witte ON, Kabarowski JH, Xu Y, Le LQ, Zhu K. (2005)
Retraction. Science, 307 (5707): 206. [PMID:15653487] |
|
12. Yang LV, Radu CG, Roy M, Lee S, McLaughlin J, Teitell MA, Iruela-Arispe ML, Witte ON. (2007)
Vascular abnormalities in mice deficient for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR4 that functions as a pH sensor. Mol Cell Biol, 27 (4): 1334-47. [PMID:17145776] |
|
13. Zhu K, Baudhuin LM, Hong G, Williams FS, Cristina KL, Kabarowski JH, Witte ON, Xu Y. (2001)
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine are ligands for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR4. J Biol Chem, 276 (44): 41325-35. [PMID:11535583] |