GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
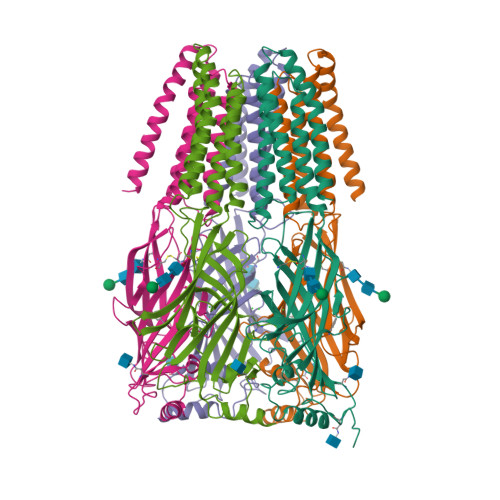
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Channel Blockers
- Allosteric Modulators
- Tissue Distribution
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 4 | 473 | 15q12 | GABRB3 | gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit beta3 | 6-7 |
| Mouse | 4 | 473 | 7 33.53 cM | Gabrb3 | GABRB3, gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit beta 3 | 2 |
| Rat | 4 | 473 | 1q22 | Gabrb3 | gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit beta 3 | 4,8 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | P28472 (Hs), P63080 (Mm), P63079 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 2.70.170.10 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1847 (Hs), CHEMBL4296058 (Mm), CHEMBL4296062 (Rn), CHEMBL4296048 (Rn), CHEMBL4296050 (Rn), CHEMBL4296051 (Rn), CHEMBL3883322 (Rn), CHEMBL4296054 (Rn), CHEMBL4296049 (Rn), CHEMBL4296053 (Rn), CHEMBL4296060 (Rn), CHEMBL4296047 (Rn), CHEMBL4296052 (Rn), CHEMBL2111374 (Rn), CHEMBL4296061 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P28472 (Hs), P28472 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000166206 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000033676 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000060599 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 2562 (Hs), 14402 (Mm), 24922 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000166206 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:2562 (Hs), mmu:14402 (Mm), rno:24922 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 137192 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA159621 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P28472 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000814 (Hs), NM_021912 (Hs), NM_008071 (Mm), NM_017065 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_068712 (Hs), NP_000805 (Hs), NP_032097 (Mm), NP_058761 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P28472 (Hs), P63080 (Mm), P63079 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | GABRB3 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| GABA |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
References
1. Buhr A, Bianchi MT, Baur R, Courtet P, Pignay V, Boulenger JP, Gallati S, Hinkle DJ, Macdonald RL, Sigel E. (2002) Functional characterization of the new human GABA(A) receptor mutation beta3(R192H). Hum Genet, 111 (2): 154-60. [PMID:12189488]
2. Ferguson C, Hardy SL, Werner DF, Hileman SM, Delorey TM, Homanics GE. (2007) New insight into the role of the beta3 subunit of the GABAA-R in development, behavior, body weight regulation, and anesthesia revealed by conditional gene knockout. BMC Neurosci, 8: 85. [PMID:17927825]
3. Kirkness EF, Fraser CM. (1993) A strong promoter element is located between alternative exons of a gene encoding the human gamma-aminobutyric acid-type A receptor beta 3 subunit (GABRB3). J Biol Chem, 268 (6): 4420-8. [PMID:8382702]
4. Lolait SJ, O'Carroll AM, Kusano K, Muller JM, Brownstein MJ, Mahan LC. (1989) Cloning and expression of a novel rat GABAA receptor. FEBS Lett, 246 (1-2): 145-8. [PMID:2540033]
5. Miller PS, Aricescu AR. (2014) Crystal structure of a human GABAA receptor. Nature, 512 (7514): 270-5. [PMID:24909990]
6. Wagstaff J, Chaillet JR, Lalande M. (1991) The GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit gene: characterization of a human cDNA from chromosome 15q11q13 and mapping to a region of conserved synteny on mouse chromosome 7. Genomics, 11 (4): 1071-8. [PMID:1664410]
7. Wagstaff J, Knoll JH, Fleming J, Kirkness EF, Martin-Gallardo A, Greenberg F, Graham JM, Menninger J, Ward D, Venter JC. (1991) Localization of the gene encoding the GABAA receptor beta 3 subunit to the Angelman/Prader-Willi region of human chromosome 15. Am J Hum Genet, 49 (2): 330-7. [PMID:1714232]
8. Ymer S, Schofield PR, Draguhn A, Werner P, Köhler M, Seeburg PH. (1989) GABAA receptor beta subunit heterogeneity: functional expression of cloned cDNAs. EMBO J, 8 (6): 1665-70. [PMID:2548852]
9. Zezula J, Slany A, Sieghart W. (1996) Interaction of allosteric ligands with GABAA receptors containing one, two, or three different subunits. Eur J Pharmacol, 301 (1-3): 207-14. [PMID:8773466]








