GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Rank order lists
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Allosteric Modulators
- Immuno Cell Type Associations
- Immuno Process Associations
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 378 | 9q22.1 | S1PR3 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 | |
| Mouse | 7 | 378 | 13 A5 | S1pr3 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 | |
| Rat | 7 | 379 | 17 p14 | S1pr3 | sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 | |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| edg3 | endothelial differentiation G protein-coupled receptor 3 |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | s1pr3_human (Hs), s1pr3_mouse (Mm) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | Q99500 (Hs), Q9Z0U9 (Mm) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL3892 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000213694 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000067586 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000014524 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 1903 (Hs), 13610 (Mm), 306792 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000213694 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:1903 (Hs), mmu:13610 (Mm), rno:306792 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 601965 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q99500 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_005226 (Hs), NM_010101 (Mm) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_005217 (Hs), NP_034231 (Mm) |
| UniProtKB | Q99500 (Hs), Q9Z0U9 (Mm) |
| Wikipedia | S1PR3 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
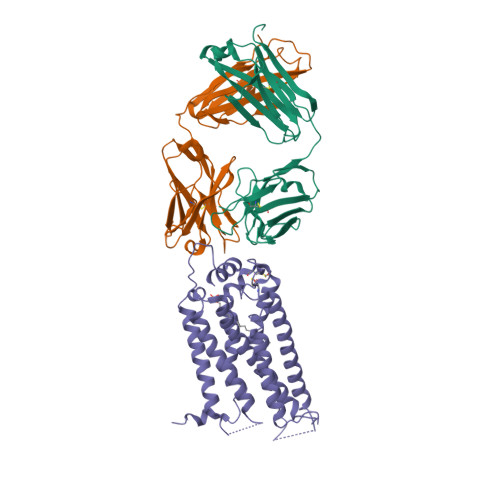
|
|
||||||||||||
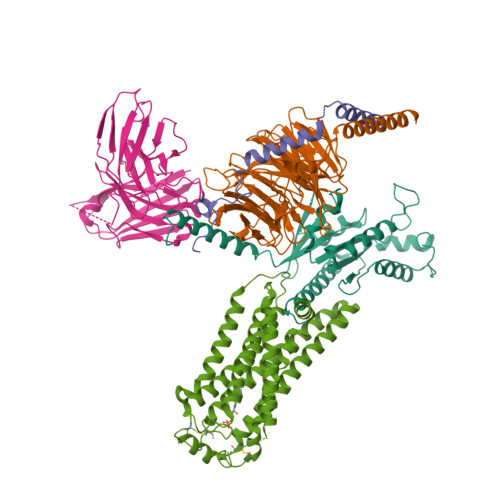
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate |
| sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| sphingosylphosphorylcholine |
| Comments: Sphingosine 1-phosphate exhibits greater potency than sphingosylphosphorylcholine |
| Potency order of endogenous ligands |
| sphingosine 1-phosphate > dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate [35] |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BML-241 (or also known as CAY10444) has been reported and widely used as S1P3 antagonist, while its potency and selectivity is equivocal [25]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric Modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cell Type Associations | ||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
| Immuno Process Associations | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
|
Gi/Go family Gq/G11 family G12/G13 family |
Adenylyl cyclase inhibition Phospholipase C stimulation |
| Comments: Activation of MAPK [36] and Akt [5-6]. | |
| References: 2,48 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| Hill et al. (2018) report on studies that show the involvement of S1PR3 in the generation of pain and itch [19]. They conclude that S1PR3 acts through TRPV1 channels (αq/PLC/PIP2 cleavage dependent) in heat nociceptors to mediate pain sensation, and through TRPA1 channels (βγ subunit dependent) in pruriceptors to mediate itch, and that identifying the role played by S1PR3 in these sensations paves the way for the development of S1PR3 modulators for managing pain and itch. |
References
1. An S, Zheng Y, Bleu T. (2000) Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell proliferation, survival, and related signaling events mediated by G protein-coupled receptors Edg3 and Edg5. J Biol Chem, 275 (1): 288-96. [PMID:10617617]
2. Ancellin N, Hla T. (1999) Differential pharmacological properties and signal transduction of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors EDG-1, EDG-3, and EDG-5. J Biol Chem, 274 (27): 18997-9002. [PMID:10383399]
3. Awojoodu AO, Ogle ME, Sefcik LS, Bowers DT, Martin K, Brayman KL, Lynch KR, Peirce-Cottler SM, Botchwey E. (2013) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 regulates recruitment of anti-inflammatory monocytes to microvessels during implant arteriogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 110 (34): 13785-90. [PMID:23918395]
4. Bajwa A, Huang L, Ye H, Dondeti K, Song S, Rosin DL, Lynch KR, Lobo PI, Li L, Okusa MD. (2012) Dendritic cell sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor-3 regulates Th1-Th2 polarity in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Immunol, 189 (5): 2584-96. [PMID:22855711]
5. Banno Y, Takuwa Y, Akao Y, Okamoto H, Osawa Y, Naganawa T, Nakashima S, Suh PG, Nozawa Y. (2001) Involvement of phospholipase D in sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt in Chinese hamster ovary cells overexpressing EDG3. J Biol Chem, 276 (38): 35622-8. [PMID:11468290]
6. Baudhuin LM, Jiang Y, Zaslavsky A, Ishii I, Chun J, Xu Y. (2004) S1P3-mediated Akt activation and cross-talk with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR). FASEB J, 18 (2): 341-3. [PMID:14657000]
7. Bolli MH, Abele S, Binkert C, Bravo R, Buchmann S, Bur D, Gatfield J, Hess P, Kohl C, Mangold C et al.. (2010) 2-imino-thiazolidin-4-one derivatives as potent, orally active S1P1 receptor agonists. J Med Chem, 53 (10): 4198-211. [PMID:20446681]
8. Brinkmann V, Davis MD, Heise CE, Albert R, Cottens S, Hof R, Bruns C, Prieschl E, Baumruker T, Hiestand P et al.. (2002) The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem, 277 (24): 21453-7. [PMID:11967257]
9. Chakrabarty S, Bui Q, Badeanlou L, Hester K, Chun J, Ruf W, Ciaraldi TP, Samad F. (2022) S1P/S1PR3 signalling axis protects against obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction. Adipocyte, 11 (1): 69-83. [PMID:35094654]
10. Cinamon G, Zachariah MA, Lam OM, Foss Jr FW, Cyster JG. (2008) Follicular shuttling of marginal zone B cells facilitates antigen transport. Nat Immunol, 9 (1): 54-62. [PMID:18037889]
11. Davis MD, Clemens JJ, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2005) Sphingosine 1-phosphate analogs as receptor antagonists. J Biol Chem, 280 (11): 9833-41. [PMID:15590668]
12. Demont EH, Bailey JM, Bit RA, Brown JA, Campbell CA, Deeks N, Dowell SJ, Eldred C, Gaskin P, Gray JR et al.. (2016) Discovery of Tetrahydropyrazolopyridine as Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 3 (S1P3)-Sparing S1P1 Agonists Active at Low Oral Doses. J Med Chem, 59 (3): 1003-20. [PMID:26751273]
13. Deng Q, Clemas JA, Chrebet G, Fischer P, Hale JJ, Li Z, Mills SG, Bergstrom J, Mandala S, Mosley R et al.. (2007) Identification of Leu276 of the S1P1 receptor and Phe263 of the S1P3 receptor in interaction with receptor specific agonists by molecular modeling, site-directed mutagenesis, and affinity studies. Mol Pharmacol, 71 (3): 724-35. [PMID:17170199]
14. Donovan EE, Pelanda R, Torres RM. (2010) S1P3 confers differential S1P-induced migration by autoreactive and non-autoreactive immature B cells and is required for normal B-cell development. Eur J Immunol, 40 (3): 688-98. [PMID:20039302]
15. Forrest M, Sun SY, Hajdu R, Bergstrom J, Card D, Doherty G, Hale J, Keohane C, Meyers C, Milligan J et al.. (2004) Immune cell regulation and cardiovascular effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists in rodents are mediated via distinct receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 309 (2): 758-68. [PMID:14747617]
16. Foss FW, Snyder AH, Davis MD, Rouse M, Okusa MD, Lynch KR, Macdonald TL. (2007) Synthesis and biological evaluation of gamma-aminophosphonates as potent, subtype-selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists and antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem, 15 (2): 663-77. [PMID:17113298]
17. Fujishiro J, Kudou S, Iwai S, Takahashi M, Hakamata Y, Kinoshita M, Iwanami S, Izawa S, Yasue T, Hashizume K et al.. (2006) Use of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor agonist, KRP-203, in combination with a subtherapeutic dose of cyclosporine A for rat renal transplantation. Transplantation, 82 (6): 804-12. [PMID:17006328]
18. Herr DR, Lee CW, Wang W, Ware A, Rivera R, Chun J. (2013) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors are essential mediators of eyelid closure during embryonic development. J Biol Chem, 288 (41): 29882-9. [PMID:24003216]
19. Hill RZ, Morita T, Brem RB, Bautista DM. (2018) S1PR3 Mediates Itch and Pain via Distinct TRP Channel-Dependent Pathways. J Neurosci, 38 (36): 7833-7843. DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1266-18.2018 [PMID:30082422]
20. Hou J, Chen Q, Wu X, Zhao D, Reuveni H, Licht T, Xu M, Hu H, Hoeft A, Ben-Sasson SA et al.. (2017) S1PR3 Signaling Drives Bacterial Killing and Is Required for Survival in Bacterial Sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 196 (12): 1559-1570. [PMID:28850247]
21. Idzko M, Panther E, Corinti S, Morelli A, Ferrari D, Herouy Y, Dichmann S, Mockenhaupt M, Gebicke-Haerter P, Di Virgilio F et al.. (2002) Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces chemotaxis of immature and modulates cytokine-release in mature human dendritic cells for emergence of Th2 immune responses. FASEB J, 16 (6): 625-7. [PMID:11919175]
22. Im DS, Clemens J, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2001) Characterization of the human and mouse sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, S1P5 (Edg-8): structure-activity relationship of sphingosine1-phosphate receptors. Biochemistry, 40 (46): 14053-60. [PMID:11705398]
23. Ishii I, Friedman B, Ye X, Kawamura S, McGiffert C, Contos JJ, Kingsbury MA, Zhang G, Brown JH, Chun J. (2001) Selective loss of sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling with no obvious phenotypic abnormality in mice lacking its G protein-coupled receptor, LP(B3)/EDG-3. J Biol Chem, 276 (36): 33697-704. [PMID:11443127]
24. Jo E, Bhhatarai B, Repetto E, Guerrero M, Riley S, Brown SJ, Kohno Y, Roberts E, Schürer SC, Rosen H. (2012) Novel selective allosteric and bitopic ligands for the S1P(3) receptor. ACS Chem Biol, 7 (12): 1975-83. [PMID:22971058]
25. Jongsma M, Hendriks-Balk MC, Michel MC, Peters SL, Alewijnse AE. (2006) BML-241 fails to display selective antagonism at the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor, S1P(3). Br J Pharmacol, 149 (3): 277-82. [PMID:16940990]
26. Kennedy PC, Zhu R, Huang T, Tomsig JL, Mathews TP, David M, Peyruchaud O, Macdonald TL, Lynch KR. (2011) Characterization of a sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor antagonist prodrug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 338 (3): 879-89. [PMID:21632869]
27. Kon J, Sato K, Watanabe T, Tomura H, Kuwabara A, Kimura T, Tamama K, Ishizuka T, Murata N, Kanda T et al.. (1999) Comparison of intrinsic activities of the putative sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor subtypes to regulate several signaling pathways in their cDNA-transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem, 274 (34): 23940-7. [PMID:10446161]
28. Kono M, Mi Y, Liu Y, Sasaki T, Allende ML, Wu YP, Yamashita T, Proia RL. (2004) The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors S1P1, S1P2, and S1P3 function coordinately during embryonic angiogenesis. J Biol Chem, 279 (28): 29367-73. [PMID:15138255]
29. Li Z, Chen W, Hale JJ, Lynch CL, Mills SG, Hajdu R, Keohane CA, Rosenbach MJ, Milligan JA, Shei GJ et al.. (2005) Discovery of potent 3,5-diphenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole sphingosine-1-phosphate-1 (S1P1) receptor agonists with exceptional selectivity against S1P2 and S1P3. J Med Chem, 48 (20): 6169-73. [PMID:16190743]
30. Maeda S, Shiimura Y, Asada H, Hirata K, Luo F, Nango E, Tanaka N, Toyomoto M, Inoue A, Aoki J et al.. (2021) Endogenous agonist-bound S1PR3 structure reveals determinants of G protein-subtype bias. Sci Adv, 7 (24). [PMID:34108205]
31. Means CK, Xiao CY, Li Z, Zhang T, Omens JH, Ishii I, Chun J, Brown JH. (2007) Sphingosine 1-phosphate S1P2 and S1P3 receptor-mediated Akt activation protects against in vivo myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 292 (6): H2944-51. [PMID:17293497]
32. Murakami A, Takasugi H, Ohnuma S, Koide Y, Sakurai A, Takeda S, Hasegawa T, Sasamori J, Konno T, Hayashi K et al.. (2010) Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) regulates vascular contraction via S1P3 receptor: investigation based on a new S1P3 receptor antagonist. Mol Pharmacol, 77 (4): 704-13. [PMID:20097776]
33. Nofer JR, van der Giet M, Tölle M, Wolinska I, von Wnuck Lipinski K, Baba HA, Tietge UJ, Gödecke A, Ishii I, Kleuser B et al.. (2004) HDL induces NO-dependent vasorelaxation via the lysophospholipid receptor S1P3. J Clin Invest, 113 (4): 569-81. [PMID:14966566]
34. Ogle ME, Olingy CE, Awojoodu AO, Das A, Ortiz RA, Cheung HY, Botchwey EA. (2017) Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor-3 Supports Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Residence Within the Bone Marrow Niche. Stem Cells, 35 (4): 1040-1052. [PMID:28026131]
35. Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Gonda K, Okazaki H, Chang K, Yatomi Y, Shigematsu H, Takuwa Y. (1998) EDG1 is a functional sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor that is linked via a Gi/o to multiple signaling pathways, including phospholipase C activation, Ca2+ mobilization, Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, and adenylate cyclase inhibition. J Biol Chem, 273 (42): 27104-10. [PMID:9765227]
36. Okamoto H, Takuwa N, Yatomi Y, Gonda K, Shigematsu H, Takuwa Y. (1999) EDG3 is a functional receptor specific for sphingosine 1-phosphate and sphingosylphosphorylcholine with signaling characteristics distinct from EDG1 and AGR16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 260 (1): 203-8. [PMID:10381367]
37. Pan S, Gray NS, Gao W, Mi Y, Fan Y, Wang X, Tuntland T, Che J, Lefebvre S, Chen Y et al.. (2013) Discovery of BAF312 (Siponimod), a Potent and Selective S1P Receptor Modulator. ACS Med Chem Lett, 4 (3): 333-7. [PMID:24900670]
38. Pan S, Mi Y, Pally C, Beerli C, Chen A, Guerini D, Hinterding K, Nuesslein-Hildesheim B, Tuntland T, Lefebvre S et al.. (2006) A monoselective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 agonist prevents allograft rejection in a stringent rat heart transplantation model. Chem Biol, 13 (11): 1227-34. [PMID:17114004]
39. Riganti L, Antonucci F, Gabrielli M, Prada I, Giussani P, Viani P, Valtorta F, Menna E, Matteoli M, Verderio C. (2016) Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P) Impacts Presynaptic Functions by Regulating Synapsin I Localization in the Presynaptic Compartment. J Neurosci, 36 (16): 4624-34. [PMID:27098703]
40. Sanna MG, Liao J, Jo E, Alfonso C, Ahn MY, Peterson MS, Webb B, Lefebvre S, Chun J, Gray N et al.. (2004) Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor subtypes S1P1 and S1P3, respectively, regulate lymphocyte recirculation and heart rate. J Biol Chem, 279 (14): 13839-48. [PMID:14732717]
41. Sanna MG, Vincent KP, Repetto E, Nguyen N, Brown SJ, Abgaryan L, Riley SW, Leaf NB, Cahalan SM, Kiosses WB et al.. (2016) Bitopic Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor 3 (S1P3) Antagonist Rescue from Complete Heart Block: Pharmacological and Genetic Evidence for Direct S1P3 Regulation of Mouse Cardiac Conduction. Mol Pharmacol, 89 (1): 176-86. [PMID:26494861]
42. Scott FL, Clemons B, Brooks J, Brahmachary E, Powell R, Dedman H, Desale HG, Timony GA, Martinborough E, Rosen H et al.. (2016) Ozanimod (RPC1063) is a potent sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1 ) and receptor-5 (S1P5 ) agonist with autoimmune disease-modifying activity. Br J Pharmacol, 173 (11): 1778-92. [PMID:26990079]
43. Tedford K, Steiner M, Koshutin S, Richter K, Tech L, Eggers Y, Jansing I, Schilling K, Hauser AE, Korthals M et al.. (2017) The opposing forces of shear flow and sphingosine-1-phosphate control marginal zone B cell shuttling. Nat Commun, 8 (1): 2261. [PMID:29273735]
44. Theilmeier G, Schmidt C, Herrmann J, Keul P, Schäfers M, Herrgott I, Mersmann J, Larmann J, Hermann S, Stypmann J et al.. (2006) High-density lipoproteins and their constituent, sphingosine-1-phosphate, directly protect the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo via the S1P3 lysophospholipid receptor. Circulation, 114 (13): 1403-9. [PMID:16982942]
45. Tian Y, Jin J, Wang X, Han W, Li G, Zhou W, Xiao Q, Qi J, Chen X, Yin D. (2013) Design, synthesis and docking-based 3D-QSAR study of novel 2-substituted 2-aminopropane-1,3-diols as potent and selective agonists of sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 (S1P1) receptor. Med Chem Comm, 4: 1267-1274. DOI: 10.1039/C3MD00079F
46. Van Brocklyn JR, Tu Z, Edsall LC, Schmidt RR, Spiegel S. (1999) Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell rounding and neurite retraction are mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor H218. J Biol Chem, 274 (8): 4626-32. [PMID:9988698]
47. Weth-Malsch D, Langeslag M, Beroukas D, Zangrandi L, Kastenberger I, Quarta S, Malsch P, Kalpachidou T, Schwarzer C, Proia RL et al.. (2016) Ablation of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Subtype 3 Impairs Hippocampal Neuron Excitability In vitro and Spatial Working Memory In vivo. Front Cell Neurosci, 10: 258. [PMID:27872583]
48. Windh RT, Lee MJ, Hla T, An S, Barr AJ, Manning DR. (1999) Differential coupling of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors Edg-1, Edg-3, and H218/Edg-5 to the G(i), G(q), and G(12) families of heterotrimeric G proteins. J Biol Chem, 274 (39): 27351-8. [PMID:10488065]
49. Xiao Q, Jin J, Wang X, Hu J, Xi M, Tian Y, Yin D. (2016) Synthesis, identification, and biological activity of metabolites of two novel selective S1P1 agonists. Bioorg Med Chem, 24 (10): 2273-9. [PMID:27068143]
50. Yamamoto R, Okada Y, Hirose J, Koshika T, Kawato Y, Maeda M, Saito R, Hattori K, Harada H, Nagasaka Y et al.. (2014) ASP4058, a novel agonist for sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors 1 and 5, ameliorates rodent experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with a favorable safety profile. PLoS ONE, 9 (10): e110819. [PMID:25347187]
51. Yang AH, Ishii I, Chun J. (2002) In vivo roles of lysophospholipid receptors revealed by gene targeting studies in mice. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1582 (1-3): 197-203. [PMID:12069829]
52. Yasuda S, Sumioka T, Iwanishi H, Okada Y, Miyajima M, Ichikawa K, Reinach PS, Saika S. (2021) Loss of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 gene function impairs injury-induced stromal angiogenesis in mouse cornea. Lab Invest, 101 (2): 245-257. [PMID:36775489]
53. Zhang G, Contos JJ, Weiner JA, Fukushima N, Chun J. (1999) Comparative analysis of three murine G-protein coupled receptors activated by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Gene, 227 (1): 89-99. [PMID:9931453]
54. Zhao C, Cheng L, Wang W, Wang H, Luo Y, Feng Y, Wang X, Fu H, Cai Y, Yang S et al.. (2022) Structural insights into sphingosine-1-phosphate recognition and ligand selectivity of S1PR3-Gi signaling complexes. Cell Res, 32 (2): 218-221. [PMID:34545189]