GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Transduction Mechanisms
- Tissue Distribution
- Expression Datasets
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| class A G protein-coupled receptor | ||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 7 | 462 | 4p16.3 | ADRA2C | adrenoceptor alpha 2C | 49 |
| Mouse | 7 | 458 | 5 18.09 cM | Adra2c | adrenergic receptor, alpha 2c | 36 |
| Rat | 7 | 458 | 14q21 | Adra2c | adrenoceptor alpha 2C | 22 |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| GPCRdb | ada2c_human (Hs), ada2c_mouse (Mm), ada2c_rat (Rn) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | P18825 (Hs), Q01337 (Mm), P22086 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1916 (Hs), CHEMBL4826 (Mm), CHEMBL314 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P18825 (Hs), P18825 (Hs), P18825 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000184160 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000045318 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000009299 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 152 (Hs), 11553 (Mm), 24175 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000184160 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:152 (Hs), mmu:11553 (Mm), rno:24175 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 104250 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P18825 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_000683 (Hs), NM_007418 (Mm), NM_138506 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_000674 (Hs), NP_031444 (Mm), NP_612515 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P18825 (Hs), Q01337 (Mm), P22086 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | ADRA2C (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
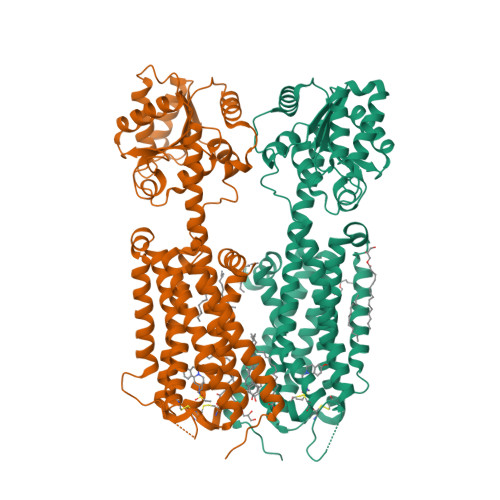
|
|
||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| (-)-adrenaline |
| (-)-noradrenaline |
| Comments: Adrenaline exhibits similar potency, affinity and efficacy to noradrenaline. |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [125I]p-iodoclonidine binds to the human α2C receptor with a pKd of 8.9 [46]. Many of the compounds listed as agonists will behave as full or partial agonists depending on the system in which they are studied and tend towards full agonism in recombinant systems with high receptor expression. Guanabenz order of affinity is α2A-AR>α2B-AR>α2C-AR [2]. There are currently no selective α2C-AR selective agonists available. Clinical uses: Clonidine is used to treat high blood pressure, guanfacine for ADHD and tizanidine to relieve muscle spasticity. Apraclonidine [40] and brimonidine are used in eye drops to relieve glaucoma. Dexmedetomidine (stereoisomer of medetomidine) and xylazine are used for their hypnotic, anxiolytic and analgesic properties as pre-operatives prior to surgery but they may also be used to control agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Xylazine has recently emerged in the North American illegal drug markets as a common admixture with synthetic opioids particularly fentanyl and is associated with a marked increase in the number of fatalities associated with drug overdose. While opioid antagonists such as naloxone can rapidly reverse the effects of fentanyl, they do not counteract the sedation, bradycardia and hypotension due to xylazine. The α2A-AR antagonist atipamezole is widely used to reverse the effects of xylazine in veterinary medicine but this role has yet to be established in the clinic. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mirtazapine is an antagonist of α2-adrenoceptors and serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. JP1302 displays some α2C-AR selectivity as does MK912 that has very high affinity for α2C-AR. Highly selective and potent α2C-AR antagonists are emerging- ORM-10921 and ORM-12741 (10-100 fold selective vs. α1A- and α1B-AR) - that cross the BBB and have potential utility for treatment of cognitive dysfunction and neuropsychiatric symptoms. Rauwolscine is a stereoisomer of yohimbine. Bromocriptine can act as a partial agonist in some α2-AR assay systems. Clinical uses: Atipamezole is an α2-AR antagonist used in veterinary medicine to reverse the effects of dexmedetomidine. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Primary Transduction Mechanisms 
|
|
| Transducer | Effector/Response |
| Gi/Go family |
Potassium channel Calcium channel Other - See Comments |
|
Comments:
ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Inhibition of voltage dependent Ca2+ channels Augmentation of inwardly rectifying K+ channels. |
|
| References: 7,35,48 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Expression Datasets  |
|
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||
|
References
1. Arponen E, Helin S, Marjamäki P, Grönroos T, Holm P, Löyttyniemi E, Någren K, Scheinin M, Haaparanta-Solin M, Sallinen J et al.. (2014) A PET Tracer for Brain α2C Adrenoceptors, (11)C-ORM-13070: Radiosynthesis and Preclinical Evaluation in Rats and Knockout Mice. J Nucl Med, 55 (7): 1171-7. [PMID:24799619]
2. Auerbach SS, DrugMatrix® and ToxFX® Coordinator National Toxicology Program. National Toxicology Program: Dept of Health and Human Services. Accessed on 02/05/2014. Modified on 02/05/2014. DrugMatrix, https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/drugmatrix/index.html
3. Barra R, Soto-Moyano R, Valladares L, Morgan C, Pérez H, Burgos H, Olivares R, Sáez-Briones P, Laurido C, Hernández A. (2012) Knockdown of α2C-adrenoceptors in the occipital cortex rescued long-term potentiation in hidden prenatally malnourished rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem, 98 (3): 228-34. [PMID:22892388]
4. Bellot M, Galandrin S, Boularan C, Matthies HJ, Despas F, Denis C, Javitch J, Mazères S, Sanni SJ, Pons V et al.. (2015) Dual agonist occupancy of AT1-R-α2C-AR heterodimers results in atypical Gs-PKA signaling. Nat Chem Biol, 11 (4): 271-9. [PMID:25706338]
5. Blaxall HS, Hass NA, Bylund DB. (1994) Expression of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor genes in rat tissues. Receptor, 4 (3): 191-9. [PMID:7812219]
6. Bylund DB, Blaxall HS, Iversen LJ, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Lomasney JW. (1992) Pharmacological characteristics of alpha 2-adrenergic receptors: comparison of pharmacologically defined subtypes with subtypes identified by molecular cloning. Mol Pharmacol, 42: 1-5. [PMID:1353247]
7. Bylund DB, Ray-Prenger C. (1989) Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: attenuation of cyclic AMP production in cell lines containing only one receptor subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 251 (2): 640-4. [PMID:2553931]
8. Chen X, Xu Y, Qu L, Wu L, Han GW, Guo Y, Wu Y, Zhou Q, Sun Q, Chu C et al.. (2019) Molecular Mechanism for Ligand Recognition and Subtype Selectivity of α2C Adrenergic Receptor. Cell Rep, 29 (10): 2936-2943.e4. [PMID:31801061]
9. Couto GK, Davel AP, Brum PC, Rossoni LV. (2014) Double disruption of α2A- and α2C-adrenoceptors induces endothelial dysfunction in mouse small arteries: role of nitric oxide synthase uncoupling. Exp Physiol, 99 (10): 1427-38. [PMID:25037566]
10. Cruz Grecco Teixeira MB, Martins GM, Miranda-Rodrigues M, De Araújo IF, Oliveira R, Brum PC, Azevedo Gouveia CH. (2016) Lack of α2C-Adrenoceptor Results in Contrasting Phenotypes of Long Bones and Vertebra and Prevents the Thyrotoxicosis-Induced Osteopenia. PLoS One, 11 (1): e0146795. [PMID:26815679]
11. Deupree JD, Hinton KA, Cerutis DR, Bylund DB. (1996) Buffers differentially alter the binding of [3H]rauwolscine and [3H]RX821002 to the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 278 (3): 1215-27. [PMID:8819505]
12. Devedjian JC, Esclapez F, Denis-Pouxviel C, Paris H. (1994) Further characterization of human alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes: [3H]RX821002 binding and definition of additional selective drugs. Eur J Pharmacol, 252 (1): 43-9. [PMID:7908642]
13. Diamanti E, Del Bello F, Carbonara G, Carrieri A, Fracchiolla G, Giannella M, Mammoli V, Piergentili A, Pohjanoksa K, Quaglia W et al.. (2012) Might the observed α(2A)-adrenoreceptor agonism or antagonism of allyphenyline analogues be ascribed to different molecular conformations?. Bioorg Med Chem, 20 (6): 2082-90. [PMID:22341244]
14. Docherty JR. (1998) Subtypes of functional alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 361 (1): 1-15. [PMID:9851536]
15. Eason MG, Liggett SB. (1993) Human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype distribution: widespread and subtype-selective expression of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2 mRNA in multiple tissues. Mol Pharmacol, 44 (1): 70-5. [PMID:7688069]
16. Eisenberg DM, Kessler RC, Van Rompay MI, Kaptchuk TJ, Wilkey SA, Appel S, Davis RB. (2001) Perceptions about complementary therapies relative to conventional therapies among adults who use both: results from a national survey. Ann Intern Med, 135 (5): 344-51. [PMID:11529698]
17. Evdokimovskii EV, Jeon R, Park S, Pimenov OY, Alekseev AE. (2021) Role of α2-Adrenoceptor Subtypes in Suppression of L-Type Ca2+ Current in Mouse Cardiac Myocytes. Int J Mol Sci, 22 (8). [PMID:33923625]
18. Fagerholm V, Rokka J, Nyman L, Sallinen J, Tiihonen J, Tupala E, Haaparanta M, Hietala J. (2008) Autoradiographic characterization of alpha(2C)-adrenoceptors in the human striatum. Synapse, 62 (7): 508-15. [PMID:18435421]
19. Fardoun MM, Issa K, Maaliki D, Nasser SA, Baydoun E, Eid AH. (2020) Estrogen increases expression of vascular alpha 2C adrenoceptor through the cAMP/Epac/JNK/AP-1 pathway and potentiates cold-induced vasoconstriction. Vascul Pharmacol, 131: 106690. [PMID:32407896]
20. Fardoun MM, Nassif J, Issa K, Baydoun E, Eid AH. (2016) Raynaud's Phenomenon: A Brief Review of the Underlying Mechanisms. Front Pharmacol, 7: 438. [PMID:27899893]
21. Fernández J, Alonso JM, Andrés JI, Cid JM, Díaz A, Iturrino L, Gil P, Megens A, Sipido VK, Trabanco AA. (2005) Discovery of new tetracyclic tetrahydrofuran derivatives as potential broad-spectrum psychotropic agents. J Med Chem, 48 (6): 1709-12. [PMID:15771415]
22. Flordellis CS, Handy DE, Bresnahan MR, Zannis VI, Gavras H. (1991) Cloning and expression of a rat brain alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 88 (3): 1019-23. [PMID:1704126]
23. Gacsályi I, Nagy K, Pallagi K, Lévay G, Hársing Jr LG, Móricz K, Kertész S, Varga P, Haller J, Gigler G et al.. (2013) Egis-11150: a candidate antipsychotic compound with procognitive efficacy in rodents. Neuropharmacology, 64: 254-63. [PMID:22824189]
24. Gavin KT, Colgan MP, Moore D, Shanik G, Docherty JR. (1997) Alpha 2C-adrenoceptors mediate contractile responses to noradrenaline in the human saphenous vein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 355 (3): 406-11. [PMID:9089673]
25. Handy DE, Flordellis CS, Bogdanova NN, Bresnahan MR, Gavras H. (1993) Diverse tissue expression of rat alpha 2-adrenergic receptor genes. Hypertension, 21 (6 Pt 1): 861-5. [PMID:7684725]
26. Hein L, Altman JD, Kobilka BK. (1999) Two functionally distinct alpha2-adrenergic receptors regulate sympathetic neurotransmission. Nature, 402 (6758): 181-4. [PMID:10647009]
27. Ishibashi T, Horisawa T, Tokuda K, Ishiyama T, Ogasa M, Tagashira R, Matsumoto K, Nishikawa H, Ueda Y, Toma S et al.. (2010) Pharmacological profile of lurasidone, a novel antipsychotic agent with potent 5-hydroxytryptamine 7 (5-HT7) and 5-HT1A receptor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 334 (1): 171-81. [PMID:20404009]
28. Jasper JR, Lesnick JD, Chang LK, Yamanishi SS, Chang TK, Hsu SA, Daunt DA, Bonhaus DW, Eglen RM. (1998) Ligand efficacy and potency at recombinant alpha2 adrenergic receptors: agonist-mediated [35S]GTPgammaS binding. Biochem Pharmacol, 55 (7): 1035-43. [PMID:9605427]
29. Kable JW, Murrin LC, Bylund DB. (2000) In vivo gene modification elucidates subtype-specific functions of alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 293 (1): 1-7. [PMID:10734146]
30. Kennis LE, Bischoff FP, Mertens CJ, Love CJ, Van den Keybus FA, Pieters S, Braeken M, Megens AA, Leysen JE. (2000) New 2-substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzofuro[3,2-c]pyridine having highly active and potent central alpha 2-antagonistic activity as potential antidepressants. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 10 (1): 71-4. [PMID:10636247]
31. Kiss L, Cselenyák A, Visegrády A. (2019) Label-free drug screening assay multiplexed with an orthogonal time-resolved fluorescence labeled assay. Anal Biochem, 566: 126-132. [PMID:30452893]
32. Kurko D, Kapui Z, Nagy J, Lendvai B, Kolok S. (2014) Analysis of functional selectivity through G protein-dependent and -independent signaling pathways at the adrenergic α(2C) receptor. Brain Res Bull, 107: 89-101. [PMID:25080296]
33. Lehto J, Hirvonen MM, Johansson J, Kemppainen J, Luoto P, Naukkarinen T, Oikonen V, Arponen E, Rouru J, Sallinen J et al.. (2015) Validation of [(11) C]ORM-13070 as a PET tracer for alpha2c -adrenoceptors in the human brain. Synapse, 69 (3): 172-81. [PMID:25530024]
34. Lehto J, Virta JR, Oikonen V, Roivainen A, Luoto P, Arponen E, Helin S, Hietamäki J, Holopainen A, Kailajärvi M et al.. (2015) Test-retest reliability of (11)C-ORM-13070 in PET imaging of α2C-adrenoceptors in vivo in the human brain. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 42 (1): 120-7. [PMID:25201008]
35. Limbird LE. (1988) Receptors linked to inhibition of adenylate cyclase: additional signaling mechanisms. FASEB J, 2 (11): 2686-95. [PMID:2840317]
36. Link R, Daunt D, Barsh G, Chruscinski A, Kobilka B. (1992) Cloning of two mouse genes encoding alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtypes and identification of a single amino acid in the mouse alpha 2-C10 homolog responsible for an interspecies variation in antagonist binding. Mol Pharmacol, 42 (1): 16-27. [PMID:1353249]
37. Link RE, Desai K, Hein L, Stevens ME, Chruscinski A, Bernstein D, Barsh GS, Kobilka BK. (1996) Cardiovascular regulation in mice lacking alpha2-adrenergic receptor subtypes b and c. Science, 273 (5276): 803-5. [PMID:8670422]
38. MacDonald E, Kobilka BK, Scheinin M. (1997) Gene targeting--homing in on alpha 2-adrenoceptor-subtype function. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 18 (6): 211-9. [PMID:9227000]
39. Millan MJ, Maiofiss L, Cussac D, Audinot V, Boutin JA, Newman-Tancredi A. (2002) Differential actions of antiparkinson agents at multiple classes of monoaminergic receptor. I. A multivariate analysis of the binding profiles of 14 drugs at 21 native and cloned human receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 303 (2): 791-804. [PMID:12388666]
40. Munk SA, Harcourt D, Ambrus G, Denys L, Gluchowski C, Burke JA, Kharlamb AB, Manlapaz CA, Padillo EU, Runde E et al.. (1996) Synthesis and evaluation of 2-[(5-methylbenz-1-ox-4-azin-6-yl)imino]imidazoline, a potent, peripherally acting alpha 2 adrenoceptor agonist. J Med Chem, 39 (18): 3533-8. [PMID:8784451]
41. Nicholas AP, Pieribone V, Hökfelt T. (1993) Distributions of mRNAs for alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol, 328 (4): 575-94. [PMID:8381444]
42. Peltonen JM, Pihlavisto M, Scheinin M. (1998) Subtype-specific stimulation of [35S]GTPgammaS binding by recombinant alpha2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 355 (2-3): 275-9. [PMID:9760042]
43. Perälä M, Hirvonen H, Kalimo H, Ala-Uotila S, Regan JW, Akerman KE, Scheinin M. (1992) Differential expression of two alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype mRNAs in human tissues. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 16 (1-2): 57-63. [PMID:1334200]
44. Philippens IH, Joosen MJ, Ahnaou A, Andres I, Drinkenburg WP. (2014) Anti-Parkinson effects of a selective alpha2C-adrenoceptor antagonist in the MPTP marmoset model. Behav Brain Res, 269: 81-6. [PMID:24769173]
45. Pihlavisto M, Sjöholm B, Scheinin M, Wurster S. (1998) Modulation of agonist binding to recombinant human alpha2-adrenoceptors by sodium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1448 (1): 135-46. [PMID:9824686]
46. Piletz JE, Zhu H, Chikkala DN. (1996) Comparison of ligand binding affinities at human I1-imidazoline binding sites and the high affinity state of alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 279 (2): 694-702. [PMID:8930173]
47. Proudman RGW, Akinaga J, Baker JG. (2022) The affinity and selectivity of α-adrenoceptor antagonists, antidepressants and antipsychotics for the human α2A, α2B, and α2C-adrenoceptors and comparison with human α1 and β-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 10 (2): e00936. [PMID:35224877]
48. Proudman RGW, Akinaga J, Baker JG. (2022) The signaling and selectivity of α-adrenoceptor agonists for the human α2A, α2B and α2C-adrenoceptors and comparison with human α1 and β-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 10 (5): e01003. [PMID:36101495]
49. Regan JW, Kobilka TS, Yang-Feng TL, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Kobilka BK. (1988) Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 85 (17): 6301-5. [PMID:2842764]
50. Rivero G, Martín-Guerrero I, de Prado E, Gabilondo AM, Callado LF, García-Sevilla JA, García-Orad Á, Meana JJ. (2016) Alpha2C-adrenoceptor Del322-325 polymorphism and risk of psychiatric disorders: significant association with opiate abuse and dependence. World J Biol Psychiatry, 17 (4): 308-15. [PMID:27007576]
51. Romana-Souza B, Nascimento AP, Brum PC, Monte-Alto-Costa A. (2014) Deletion of the α2A/α2C-adrenoceptors accelerates cutaneous wound healing in mice. Int J Exp Pathol, 95 (5): 330-41. [PMID:25186490]
52. Sallinen J, Holappa J, Koivisto A, Kuokkanen K, Chapman H, Lehtimäki J, Piepponen P, Mijatovic J, Tanila H, Virtanen R et al.. (2013) Pharmacological characterisation of a structurally novel α2C-adrenoceptor antagonist ORM-10921 and its effects in neuropsychiatric models. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, 113 (4): 239-49. [PMID:23718812]
53. Sallinen J, Höglund I, Engström M, Lehtimäki J, Virtanen R, Sirviö J, Wurster S, Savola JM, Haapalinna A. (2007) Pharmacological characterization and CNS effects of a novel highly selective alpha2C-adrenoceptor antagonist JP-1302. Br J Pharmacol, 150 (4): 391-402. [PMID:17220913]
54. Savolainen K, Ihalainen J, Hämäläinen E, Tanila H, Forsberg MM. (2021) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive impairments in repeated touchscreen visual reversal learning tests in rats. Behav Brain Res, 404: 113057. [PMID:33316322]
55. Scheinin M, Lomasney JW, Hayden-Hixson DM, Schambra UB, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Fremeau Jr RT. (1994) Distribution of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype gene expression in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 21 (1-2): 133-49. [PMID:8164514]
56. Shahid M, Rinne JO, Scheinin M, Virta J, Marjamäki P, Solin O, Arponen E, Sallinen J, Kuokkanen K, Rouru J. (2020) Application of the PET ligand [11C]ORM-13070 to examine receptor occupancy by the α2C-adrenoceptor antagonist ORM-12741: translational validation of target engagement in rat and human brain. EJNMMI Res, 10 (1): 152. [PMID:33296042]
57. Shimokawa T, Tsutsui H, Miura T, Takama M, Hayashi K, Nishinaka T, Terada T, Yoneda K, Yamagata M, Yukimura T. (2019) Post-treatment with JP-1302 protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in rats. J Pharmacol Sci, 139 (3): 137-142. [PMID:30665845]
58. Thapa D, Valente JS, Barrett B, Smith MJ, Argunhan F, Lee SY, Nikitochkina S, Kodji X, Brain SD. (2021) Dysfunctional TRPM8 signalling in the vascular response to environmental cold in ageing. Elife, 10. [PMID:34726597]
59. Tsutsui H, Shimokawa T, Miura T, Takama M, Nishinaka T, Terada T, Yamagata M, Yukimura T. (2018) Inhibition of α2C-adrenoceptors ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Eur J Pharmacol, 838: 113-119. [PMID:30201375]
60. Uhlén S, Schiöth HB, Jahnsen JA. (2016) A new, simple and robust radioligand binding method used to determine kinetic off-rate constants for unlabeled ligands. Application at α2A- and α2C-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol, 788: 113-121. [PMID:27318322]
61. Uhlén S, Porter AC, Neubig RR. (1994) The novel alpha-2 adrenergic radioligand [3H]-MK912 is alpha-2C selective among human alpha-2A, alpha-2B and alpha-2C adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 271 (3): 1558-65. [PMID:7996470]
62. Uys MM, Shahid M, Harvey BH. (2017) Therapeutic Potential of Selectively Targeting the α2C-Adrenoceptor in Cognition, Depression, and Schizophrenia-New Developments and Future Perspective. Front Psychiatry, 8: 144. [PMID:28855875]
63. Uys MM, Shahid M, Sallinen J, Harvey BH. (2017) The α2C-adrenoceptor antagonist, ORM-10921, exerts antidepressant-like effects in the Flinders Sensitive Line rat. Behav Pharmacol, 28 (1): 9-18. [PMID:27749317]














