GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
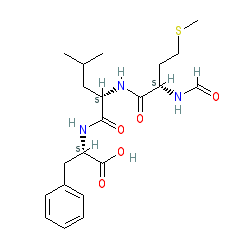
Abbreviated name: fMLP
Synonyms: fMetLeuPhe | fMLF | formyl-Met-Leu-Phe
Compound class:
Peptide
Comment: From the bacterium E.coli
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Buyse M, Charrier L, Sitaraman S, Gewirtz A, Merlin D. (2003)
Interferon-gamma increases hPepT1-mediated uptake of di-tripeptides including the bacterial tripeptide fMLP in polarized intestinal epithelia. Am J Pathol, 163 (5): 1969-77. [PMID:14578196] |
|
2. Charrier L, Driss A, Yan Y, Nduati V, Klapproth JM, Sitaraman SV, Merlin D. (2006)
hPepT1 mediates bacterial tripeptide fMLP uptake in human monocytes. Lab Invest, 86 (5): 490-503. [PMID:16568107] |
|
3. Clish CB, O'Brien JA, Gronert K, Stahl GL, Petasis NA, Serhan CN. (1999)
Local and systemic delivery of a stable aspirin-triggered lipoxin prevents neutrophil recruitment in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96 (14): 8247-52. [PMID:10393980] |
|
4. Fiore S, Maddox JF, Perez HD, Serhan CN. (1994)
Identification of a human cDNA encoding a functional high affinity lipoxin A4 receptor. J Exp Med, 180 (1): 253-60. [PMID:8006586] |
|
5. Fiore S, Serhan CN. (1995)
Lipoxin A4 receptor activation is distinct from that of the formyl peptide receptor in myeloid cells: inhibition of CD11/18 expression by lipoxin A4-lipoxin A4 receptor interaction. Biochemistry, 34 (51): 16678-86. [PMID:8527441] |
|
6. Freer RJ, Day AR, Radding JA, Schiffmann E, Aswanikumar S, Showell HJ, Becker EL. (1980)
Further studies on the structural requirements for synthetic peptide chemoattractants. Biochemistry, 19 (11): 2404-10. [PMID:7387981] |
|
7. Gronert K, Martinsson-Niskanen T, Ravasi S, Chiang N, Serhan CN. (2001)
Selectivity of recombinant human leukotriene D(4), leukotriene B(4), and lipoxin A(4) receptors with aspirin-triggered 15-epi-LXA(4) and regulation of vascular and inflammatory responses. Am J Pathol, 158 (1): 3-9. [PMID:11141472] |
|
8. Hartt JK, Barish G, Murphy PM, Gao JL. (1999)
N-formylpeptides induce two distinct concentration optima for mouse neutrophil chemotaxis by differential interaction with two N-formylpeptide receptor (FPR) subtypes. Molecular characterization of FPR2, a second mouse neutrophil FPR. J Exp Med, 190 (5): 741-7. [PMID:10477558] |
|
9. Le Y, Murphy PM, Wang JM. (2002)
Formyl-peptide receptors revisited. Trends Immunol, 23 (11): 541-8. [PMID:12401407] |
|
10. Merlin D, Si-Tahar M, Sitaraman SV, Eastburn K, Williams I, Liu X, Hediger MA, Madara JL. (2001)
Colonic epithelial hPepT1 expression occurs in inflammatory bowel disease: transport of bacterial peptides influences expression of MHC class 1 molecules. Gastroenterology, 120 (7): 1666-79. [PMID:11375948] |
|
11. Merlin D, Steel A, Gewirtz AT, Si-Tahar M, Hediger MA, Madara JL. (1998)
hPepT1-mediated epithelial transport of bacteria-derived chemotactic peptides enhances neutrophil-epithelial interactions. J Clin Invest, 102 (11): 2011-8. [PMID:9835627] |
|
12. Quehenberger O, Prossnitz ER, Cavanagh SL, Cochrane CG, Ye RD. (1993)
Multiple domains of the N-formyl peptide receptor are required for high-affinity ligand binding. Construction and analysis of chimeric N-formyl peptide receptors. J Biol Chem, 268 (24): 18167-75. [PMID:8349692] |
|
13. Showell HJ, Freer RJ, Zigmond SH, Schiffmann E, Aswanikumar S, Corcoran B, Becker EL. (1976)
The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med, 143 (5): 1154-69. [PMID:1262785] |
|
14. Southgate EL, He RL, Gao JL, Murphy PM, Nanamori M, Ye RD. (2008)
Identification of formyl peptides from Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus as potent chemoattractants for mouse neutrophils. J Immunol, 181 (2): 1429-37. [PMID:18606697] |
|
15. Sun R, Iribarren P, Zhang N, Zhou Y, Gong W, Cho EH, Lockett S, Chertov O, Bednar F, Rogers TJ, Oppenheim JJ, Wang JM. (2004)
Identification of neutrophil granule protein cathepsin G as a novel chemotactic agonist for the G protein-coupled formyl peptide receptor. J Immunology, 173: 428-436. [PMID:15210802] |
|
16. Takano T, Fiore S, Maddox JF, Brady HR, Petasis NA, Serhan CN. (1997)
Aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and LXA4 stable analogues are potent inhibitors of acute inflammation: evidence for anti-inflammatory receptors. J Exp Med, 185 (9): 1693-704. [PMID:9151906] |
|
17. Wu SP, Smith DE. (2013)
Impact of intestinal PepT1 on the kinetics and dynamics of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine, a bacterially-produced chemotactic peptide. Mol Pharm, 10 (2): 677-84. [PMID:23259992] |