GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
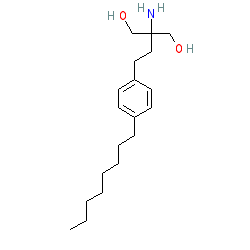
Synonyms: FTY-720 | FTY720 | Gilenya®
fingolimod is an approved drug (FDA (2010), EMA (2011))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Fingolimod was the first approved oral therapy for multiple sclerosis.
Fingolimod FTY720) is the prodrug of a S1P receptor agonist [4]. When fingolimod binds to S1P1R the complex is internalised and then degraded, so the drug acts as an indirect functional antagonist by preventing intracellular signalling. It acts as a lymphocyte migration inhibitor, promoting lymphocyte retention in lymphoid tissues, whilst preserving lymphocyte function [7]. Clinical efficacy results from modulation of S1P1 receptors. Adverse effects are thought to be caused by fingolimod's off-target effects on other S1P receptor subtypes. Selective S1P1R agonists are being developed and investigated for immunomodulatory/immunosuppresant potential. COVID-19: Fingolimod has been evaluated in a small study of patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 (n=19), with mixed results [10]. Three days of treatment (in addition to standard interventions) did not reduce intubation or mortality rates, compared to placebo controls (n= 21), but it did signficantly reduce the re-admission rate. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: fingolimod |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Used in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS) [5]. In May 2018, the FDA approved the use of fingolimod as a treatment for relapsing MS in pediatric patients. This is the first drug to be approved for treating MS in this patient group. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Fingolimod is metabolised to the active metabolite fingolimod phosphate by the enzyme sphingosine kinase. Fingolimod phosphate is a modulator of sphingosine receptors (S1P receptors), and its mechanism of action in the treatment of multiple sclerosis is derived from preventing the migration of lymphocytes into the central nervous system where they are implicated in autoimmune-driven demyelination associated with the disease. Clinical side effects (bradycardia, AV block, macular edema) are mostly (but not entirely) linked to S1P3R agonism [1,3,9]. Hence the development of S1P3R-sparing agonists such as compound 43 [PMID: 26751273] [2]. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT04280588 | Fingolimod in COVID-19 | Phase 2 Interventional | First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University | Fingolimod is being evaluated as a therapy for patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, as a method to prevent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) respiratory failure. | |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com European Medicines Agency (EMA) |