GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
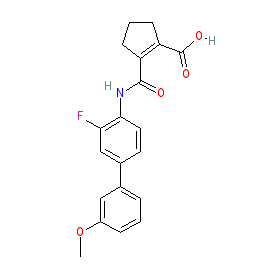
Synonyms: 4SC-101 | IMU-838 (vidofludimus calcium) | SC12267
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Vidofludimus (4SC-101) is a small molecule dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHOD) inhibitor that was developed for immunosuppressive potential [3]. It has an improved toxicity profile in comparison to the clinically used disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) leflunomide.
Since its initial development, vidofludimus has been superceded by IMU-838 which is an orally active polymorph of vidofludimus calcium (PubChem CID: 56944639) [5]. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Fitzpatrick LR, Deml L, Hofmann C, Small JS, Groeppel M, Hamm S, Lemstra S, Leban J, Ammendola A. (2010)
4SC-101, a novel immunosuppressive drug, inhibits IL-17 and attenuates colitis in two murine models of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 16 (10): 1763-77. [PMID:20310011] |
|
2. Herrlinger KR, Diculescu M, Fellermann K, Hartmann H, Howaldt S, Nikolov R, Petrov A, Reindl W, Otte JM, Stoynov S et al.. (2013)
Efficacy, safety and tolerability of vidofludimus in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the ENTRANCE study. J Crohns Colitis, 7 (8): 636-43. [PMID:23078909] |
|
3. Kulkarni OP, Sayyed SG, Kantner C, Ryu M, Schnurr M, Sárdy M, Leban J, Jankowsky R, Ammendola A, Doblhofer R et al.. (2010)
4SC-101, a novel small molecule dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitor, suppresses systemic lupus erythematosus in MRL-(Fas)lpr mice. Am J Pathol, 176 (6): 2840-7. [PMID:20413687] |
|
4. Leban J, Vitt D. (2011)
Human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors, a novel approach for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Arzneimittelforschung, 61 (1): 66-72. [PMID:21355448] |
|
5. Muehler A, Kohlhof H, Groeppel M, Vitt D. (2020)
Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Vidofludimus calcium (IMU-838) After Single and Multiple Ascending Oral Doses in Healthy Male Subjects. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 45 (5): 557-573. [PMID:32361977] |
|
6. Muehler A, Peelen E, Kohlhof H, Gröppel M, Vitt D. (2020)
Vidofludimus calcium, a next generation DHODH inhibitor for the Treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord, 43: 102129. [PMID:32428844] |
|
7. Vietor J, Gege C, Stiller T, Busch R, Schallmayer E, Kohlhof H, Höfner G, Pabel J, Marschner JA, Merk D. (2023)
Development of a Potent Nurr1 Agonist Tool for In Vivo Applications. J Med Chem,. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00415 |