GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: compound 47 [PMID: 27433829] | EGF-816 | EGF816
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: EGF816 is an irreversible and selective inhibitor of EGFRs harbouring gatekeeper T790M, and sensitising L858R mutations, whilst sparing the wild-type receptor (such compounds are termed third generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors) [3]. It has been developed to overcome acquired resistance to, and side-effect liabilities of first and second generation EGFR inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Small-molecule EGFR T790M inhibitors and the development of novel compounds in the discovery pipeline are reviewed by Song et al. (2016) [5].
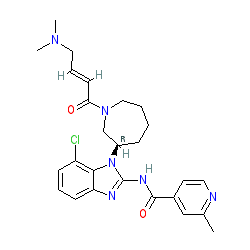
EGF816 is claimed in Novartis' patent WO2015085482 [4], where it is named (R,E)-N-(7-chloro-l-(l-(4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enoyl)azepan-3-yl)-lH-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-2-methylisonicotinamide, which resolves to the IUPAC name presented here. Preclinical characterisation is reported in [1]. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| EGF816 is being evaluated in Phase 1/2 clinical trial NCT02108964 in patients with advanced EGFR mutant NSCLC. Mutations included in the study are EGFR activating mutations (i.e. L858R and/or ex19del) and acquired or de novo gatekeeper mutation T790M. EGF816 is also in clinical trail in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors: anti-PD-1 nivolumab (NCT02323126, Phase 2, previously treated NSCLC), and anti-PD-1 spartalizumab (PDR001; NCT02900664, Phase 1, advanced/metastatic cancers). |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| EGF816 selectively and irreversibly inhibits de novo and acquired EGFR-activating mutations, to achieve its in vivo anticancer effects [1]. Kobayashi and Mitsudomi (2016) comment on the prospects for individualised NSCLC treatment based not only on the most common cancer-associated EGFR mutations, but also rare mutations which have shown sensitivity to specific inhibitors [2]. These authors suggest that EGF816 is a promising therapy for the majority of NSCLC EGFR mutations detected so far. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT02108964 | A Phase I/II, Multicenter, Open-label Study of EGFRmut-TKI EGF816, Administered Orally in Adult Patients With EGFRmut Solid Malignancies | Phase 1/Phase 2 Interventional | Novartis | ||
| NCT02323126 | Study of Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab in Combination With EGF816 and of Nivolumab in Combination With INC280 in Patients With Previously Treated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer | Phase 2 Interventional | Novartis | ||
| NCT02900664 | A Study of PDR001 in Combination With CJM112, EGF816, Ilaris® (Canakinumab) or Mekinist® (Trametinib) | Phase 1 Interventional | Novartis | ||