GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
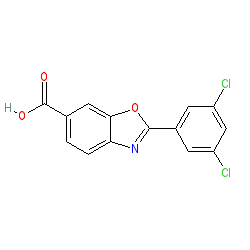
Synonyms: FX-1006 | Vyndamax® | Vyndaqel®
tafamidis is an approved drug (EMA and UK (2011), FDA (2019))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Tafamidis binds potently and selectively to transthyretin (TTR), stabilising protein tetramers, thereby inhibiting the formation of amyloid fibrils [2]. The trade name for this drug is Vyndaqel which contains tafamidis meglumine (PubChem CID 24970412). The Vyndamax brand contains tafamidis parent molecule.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Tafamidis is approved to treat transthyretin (TTR)-mediated amyloidosis (aka familial amyloid polyneuropathy or FAP), a rare hereditary disease caused by amyloid build up in tissues around the body including around the nerves. Its use can reduce cardiovascular mortality and cardiovascular-related hospitalisations in patients with cardiomyopathy resulting from TTR-mediated amyloidosis [4,6]. The drug was granted orphan designation in the EU (2012) for the treatment of senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA), another TTR amyloid disease [7]. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Tafamidis stabilises TTR tetramer formation, preventing the dissociation which underlies the mis-folding and aggregation of TTR into amyloid fibrils. The deposition of these fibrils eventually causes degradation of the autonomic nervous system [1]. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) European Medicines Agency (EMA) |