GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
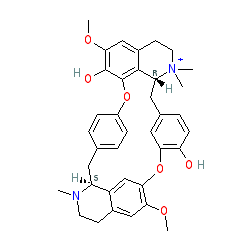
Synonyms: (+)-tubocurarine | d-tubocurarine
tubocurarine is an approved drug (FDA (1945))
Compound class:
Natural product
Comment: Tubocurarine is a skeletal muscle relaxant. The structure as specified by the FDA and the INN document shows the compound in complex with chloride (see PubChem CID 9917490). As our data specifies the parent compound, it is this structure we have chosen to display here, and which the majority of entries linked to from the table above display.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bioactivity Comments |
| Due to the complex and varied nature of the precise subunit composition of nACh channels, and a paucity of affinity data with definitive molecular details, we have not tagged a primary target for this drug. |
| Transporters Moving this Compound Across a Lipid Membrane | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| Selectivity at ion channels | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional information and targets (data relate to human unless otherwise stated) | ||
| Description | Data | Reference |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α2 subunit | α2β2: DHβE (KB = 0.9 μM), tubocurarine (KB = 1.4 μM); α2β4: DHβE (KB = 3.6 μM), tubocurarine (KB = 4.2 μM) | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α3 subunit | α3β2: DHβE (KB = 1.6 μM, IC50 = 2.0 μM), tubocurarine (KB = 2.4 μM); α3β4: DHβE (KB = 19 μM, IC50 = 26 μM), tubocurarine (KB = 2.2 μM) | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α8 subunit (avian) | (α8)5: α-bungarotoxin > atropine ≥ tubocurarine ≥ strychnine | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α4 subunit | α4β2: DHβE (KB = 0.1 μM; IC50 = 0.08 - 0.9 μM), tubocurarine (KB = 3.2 μM, IC50 = 34 μM); α4β4: DHβE (KB = 0.01 μM, IC50 = 0.19 – 1.2 μM), tubocurarine (KB = 0.2 μM, IC50 = 50 μM) | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α9 subunit | (α9)5: α-bungarotoxin > methyllycaconitine > strychnine ~ tropisetron > tubocurarine; α9α10: α-bungarotoxin > tropisetron = strychnine > tubocurarine | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α10 subunit | α9α10: α-bungarotoxin > tropisetron = strychnine > tubocurarine | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit | (α7)5: DHβE (IC50 = 8 - 20 μM); (α7)5: tubocurarine (IC50 = 3.1 μM) | |
| Commonly used antagonists at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α1 subunit | (α1)2β1γδ and (α1)2β1δε: α-bungarotoxin > pancuronium > vecuronium > rocuronium > tubocurarine (IC50 = 43 - 82 nM) | |
| Ligand mentioned in the following text fields |
| ZAC overview |
| ZAC comments |