GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
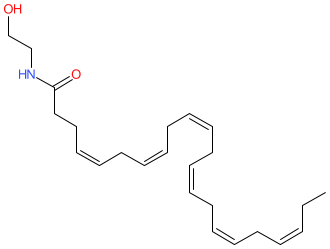
Synonyms: N-docosahexaenoylethanolamine
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Synaptamide is an endocannabinoid-like derivative of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) that is biosynthesised in the brain. It has cannabinoid-independent activities.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selectivity at GPCRs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Targets where the ligand is described in the comment field | |
| Target | Comment |
| ADGRF1 | Coupling with all major G protein families is reported [4], including Gs and Gq [3,12], and Gαs and Gαq/11 [15]. N-Docosahexaenoylethanolamine (synaptamide) is an agonist at ADGRF1 supporting neurogenesis [6]. The cryo-EM structure of the 7-helix transmembrane domain with its intramolecular agonist has been determined [10,15]. Furthermore, the domain structure of the N terminus (SEA, HormR, GAIN) has been solved by X-ray crystallography [13]. The structural basis for G protein-coupling has also been reported [4]. Expressed in kidney and prostate [8,11], spleen, liver, and adrenal gland [9]. ADGRF1 may be a prognositic marker for uterine corpus endometrial cancer [7]. Tumour-promoting function in HER2-positive breast cancer has been reported [1-2], as has a role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression [14]. |