GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: achromycin
Compound class:
Natural product
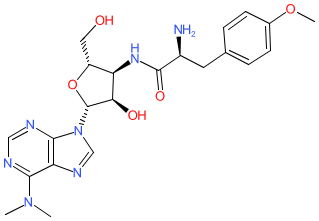
Comment: Puromycin is an aminoacyl nucleoside antimicrobial compound, originally isolated from Streptomyces alboniger [4]. It is a potent inhibitor of protein translation in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms [5] and has not been of clinical utility due to its non-selective systemic toxicity. Instead it is used extensively in the laboratory to study mechanisms of protein synthesis and also as a selective agent in mammalian cell culture systems (reviewed in [2]).
Please note that puromycin was formerly known as achromycin, which was also a trade name used for tetracycline. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bioactivity Comments |
| Puromycin is effective against Gram-positive bacteria but has limited activity against Gram-negative pathogens due to its low permeability. Resistance to puromycin is conferred by the puromycin N-acetyltranferase (pac) gene, that was isolated from S. alboniger, and is used as a selection marker for the isolation of stably transfected mammalian cells lines [3]. |
| Selectivity at enzymes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||