GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Compound class:
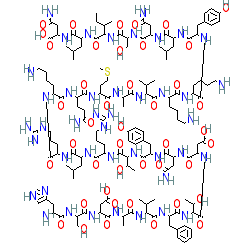
Endogenous peptide in human, mouse or rat
Comment: Sequences of human, mouse and rat VIP are identical
VIP was first isolated and sequenced from pig small intestine [12,15]. As with many peptide molecules, there is ambiguity surrounding representations of the exact stereochemistry of VIP. The structure shown here does not specify stereochemistry.
Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: vasoactive intestinal peptide |
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| In addition to its vascular and cardioprotective functions, VIP also regulates immune function and inflammatory responses. In a mouse model of autoimmune myocarditis, admninistration of VIP reduced signs of heart damage and reduced myocardial inflammatory infiltration and levels of myocardial autoantibodies [1]. In an atherosclerosis model, the anti-inflammatory effects of VIP included a reduction in Th1-driven inflammatory responses and an elevation in regulatory T cell numbers in atherosclerotic arteries and their draining lymph nodes. Together these findings suggest that VIP may be a valid therapeutic option for the treatment of heart inflammation and atherosclerosis. |