GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
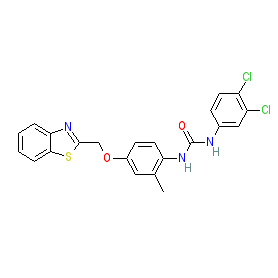
Comment: Diflapolin is reported as the first dual inhibitor of 5-LOX activating protein and soluble epoxide hydrolase [1]. Whilst 5-LOX activating protein facilitates 5-LOX-mediated conversion of arachidonic acid to pro-inflammatory leukotrienes, soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) degrades anti-inflammatory epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Dual inhibition might therefore offer increased efficacy as an anti-inflammatory intervention compared to single target agents.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bioactivity Comments |
| Diflapolin does not inhibit isolated 5-LOX or other enzymes related to arachidonic acid metabolism (including COX1/2, 12/15-LOX, LTA4H, LTC4S, mPGES1, and cPLA2) [1]. |
| Selectivity at enzymes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selectivity at ligand targets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||