GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Voltage Dependence
- Activators
- Inhibitors
- Gating Inhibitors
- Channel Blockers
- Tissue Distribution
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- General Comments
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 24 | 1 | 1988 | 2q24.3 | SCN9A | sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 9 | 54 |
| Mouse | 24 | 1 | 1984 | 2 39.13 cM | Scn9a | sodium channel, voltage-gated, type IX, alpha | 4,55 |
| Rat | 24 | 1 | 1984 | 3q21 | Scn9a | sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 9 | 69,78 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q15858 (Hs), Q62205 (Mm), O08562 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL4296 (Hs), CHEMBL3414411 (Mm), CHEMBL3312 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | Q15858 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000169432 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000075316 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000006639 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 6335 (Hs), 20274 (Mm), 78956 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000169432 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:6335 (Hs), mmu:20274 (Mm), rno:78956 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 603415 (Hs) |
| Orphanet | ORPHA118525 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q15858 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_002977 (Hs), NM_001290674 (Mm), NM_133289 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_002968 (Hs), NP_001277603 (Mm), NP_579823 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q15858 (Hs), Q62205 (Mm), O08562 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | SCN9A (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
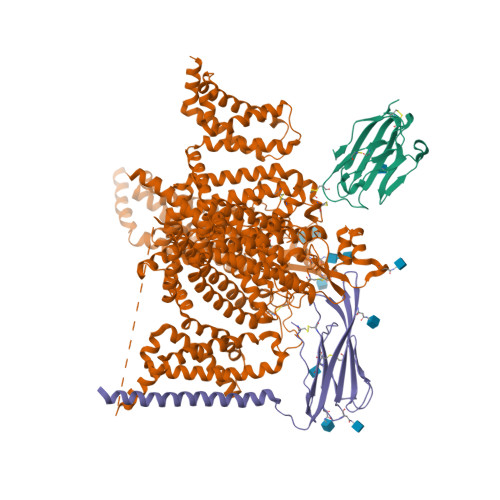
|
|
||||||||||
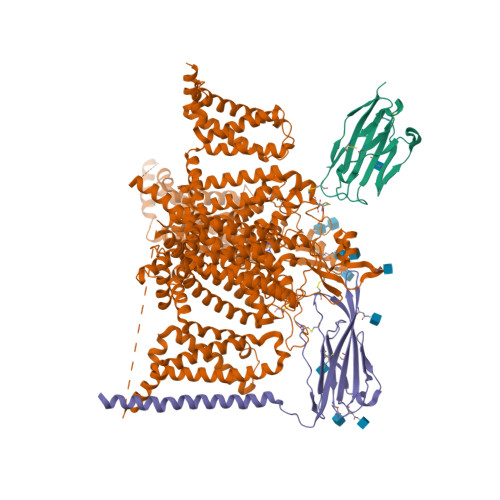
|
|
||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Functional Characteristics  |
|
| Activation V0.5 = -27 mV. Fast inactivation (0.5 ms) | |
Ion Selectivity and Conductance  |
||||||
|
||||||
|
Voltage Dependence  |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific inhibitor tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gating inhibitors 
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scorpion toxins are known inhibitors of Nav1.7 for example the α-scorpion toxins (Odonthobuthus doriae) [58] and other scopion toxins (Lqh-2 and Lqh-3) [7]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Channel Blockers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific channel blocker tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| Strong genetic evidence (either gain-of-function or loss-of-function) supports the crucial role of NaV1.7 (SCN9A) in pain sensation [18,39,84]. As a result, there is pharmaceutical industry interest in developing small molecule NaV1.7 inhibitors as analgesics [3,76]. |
References
1. Ahn HS, Dib-Hajj SD, Cox JJ, Tyrrell L, Elmslie FV, Clarke AA, Drenth JP, Woods CG, Waxman SG. (2010) A new Nav1.7 sodium channel mutation I234T in a child with severe pain. Eur J Pain, 14 (9): 944-50. [PMID:20385509]
2. Alexandrou AJ, Brown AR, Chapman ML, Estacion M, Turner J, Mis MA, Wilbrey A, Payne EC, Gutteridge A, Cox PJ et al.. (2016) Subtype-Selective Small Molecule Inhibitors Reveal a Fundamental Role for Nav1.7 in Nociceptor Electrogenesis, Axonal Conduction and Presynaptic Release. PLoS One, 11 (4): e0152405. [PMID:27050761]
3. Bagal SK, Chapman ML, Marron BE, Prime R, Storer RI, Swain NA. (2014) Recent progress in sodium channel modulators for pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 24 (16): 3690-9. [PMID:25060923]
4. Beckers MC, Ernst E, Belcher S, Howe J, Levenson R, Gros P. (1996) A new sodium channel alpha-subunit gene (Scn9a) from Schwann cells maps to the Scn1a, Scn2a, Scn3a cluster of mouse chromosome 2. Genomics, 36 (1): 202-5. [PMID:8812438]
5. Catterall WA, Yu FH. (2006) Painful channels. Neuron, 52 (5): 743-4. [PMID:17145494]
6. Chakka N, Bregman H, Du B, Nguyen HN, Buchanan JL, Feric E, Ligutti J, Liu D, McDermott JS, Zou A et al.. (2012) Discovery and hit-to-lead optimization of pyrrolopyrimidines as potent, state-dependent Na(v)1.7 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22 (5): 2052-62. [PMID:22318156]
7. Chen H, Lu S, Leipold E, Gordon D, Hansel A, Heinemann SH. (2002) Differential sensitivity of sodium channels from the central and peripheral nervous system to the scorpion toxins Lqh-2 and Lqh-3. Eur J Neurosci, 16 (4): 767-70. [PMID:12270053]
8. Cheng X, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Te Morsche RH, Drenth JP, Waxman SG. (2011) Deletion mutation of sodium channel Na(V)1.7 in inherited erythromelalgia: enhanced slow inactivation modulates dorsal root ganglion neuron hyperexcitability. Brain, 134 (Pt 7): 1972-86. [PMID:21705421]
9. Cheng X, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Waxman SG. (2008) Mutation I136V alters electrophysiological properties of the Na(v)1.7 channel in a family with onset of erythromelalgia in the second decade. Mol Pain, 4: 1. [PMID:18171466]
10. Cheng X, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Wright DA, Fischer TZ, Waxman SG. (2010) Mutations at opposite ends of the DIII/S4-S5 linker of sodium channel Na V 1.7 produce distinct pain disorders. Mol Pain, 6: 24. [PMID:20429905]
11. Chevrier P, Vijayaragavan K, Chahine M. (2004) Differential modulation of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 peripheral nerve sodium channels by the local anesthetic lidocaine. Br J Pharmacol, 142 (3): 576-84. [PMID:15148257]
12. Choi JS, Boralevi F, Brissaud O, Sánchez-Martín J, Te Morsche RH, Dib-Hajj SD, Drenth JP, Waxman SG. (2011) Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder: a molecular lesion of peripheral neurons. Nat Rev Neurol, 7 (1): 51-5. [PMID:21079636]
13. Choi JS, Cheng X, Foster E, Leffler A, Tyrrell L, Te Morsche RH, Eastman EM, Jansen HJ, Huehne K, Nau C et al.. (2010) Alternative splicing may contribute to time-dependent manifestation of inherited erythromelalgia. Brain, 133 (Pt 6): 1823-35. [PMID:20478850]
14. Choi JS, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2006) Inherited erythermalgia: limb pain from an S4 charge-neutral Na channelopathy. Neurology, 67 (9): 1563-7. [PMID:16988069]
15. Choi JS, Zhang L, Dib-Hajj SD, Han C, Tyrrell L, Lin Z, Wang X, Yang Y, Waxman SG. (2009) Mexiletine-responsive erythromelalgia due to a new Na(v)1.7 mutation showing use-dependent current fall-off. Exp Neurol, 216 (2): 383-9. [PMID:19162012]
16. Chowdhury S, Chafeev M, Liu S, Sun J, Raina V, Chui R, Young W, Kwan R, Fu J, Cadieux JA. (2011) Discovery of XEN907, a spirooxindole blocker of NaV1.7 for the treatment of pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 21 (12): 3676-81. [PMID:21570288]
17. Coulter DA, Rafiq A, Shumate M, Gong QZ, DeLorenzo RJ, Lyeth BG. (1996) Brain injury-induced enhanced limbic epileptogenesis: anatomical and physiological parallels to an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res, 26 (1): 81-91. [PMID:8985690]
18. Cox JJ, Reimann F, Nicholas AK, Thornton G, Roberts E, Springell K, Karbani G, Jafri H, Mannan J, Raashid Y et al.. (2006) An SCN9A channelopathy causes congenital inability to experience pain. Nature, 444 (7121): 894-8. [PMID:17167479]
19. Cummins TR, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2004) Electrophysiological properties of mutant Nav1.7 sodium channels in a painful inherited neuropathy. J Neurosci, 24 (38): 8232-6. [PMID:15385606]
20. Dib-Hajj SD, Cummins TR, Black JA, Waxman SG. (2010) Sodium channels in normal and pathological pain. Annu Rev Neurosci, 33: 325-47. [PMID:20367448]
21. Dib-Hajj SD, Estacion M, Jarecki BW, Tyrrell L, Fischer TZ, Lawden M, Cummins TR, Waxman SG. (2008) Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder M1627K mutation in human Nav1.7 renders DRG neurons hyperexcitable. Mol Pain, 4: 37. [PMID:18803825]
22. Dib-Hajj SD, Rush AM, Cummins TR, Hisama FM, Novella S, Tyrrell L, Marshall L, Waxman SG. (2005) Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons. Brain, 128 (Pt 8): 1847-54. [PMID:15958509]
23. Drenth JP, te Morsche RH, Guillet G, Taieb A, Kirby RL, Jansen JB. (2005) SCN9A mutations define primary erythermalgia as a neuropathic disorder of voltage gated sodium channels. J Invest Dermatol, 124 (6): 1333-8. [PMID:15955112]
24. Estacion M, Choi JS, Eastman EM, Lin Z, Li Y, Tyrrell L, Yang Y, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2010) Can robots patch-clamp as well as humans? Characterization of a novel sodium channel mutation. J Physiol (Lond.), 588 (Pt 11): 1915-27. [PMID:20123784]
25. Estacion M, Dib-Hajj SD, Benke PJ, Te Morsche RH, Eastman EM, Macala LJ, Drenth JP, Waxman SG. (2008) NaV1.7 gain-of-function mutations as a continuum: A1632E displays physiological changes associated with erythromelalgia and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations and produces symptoms of both disorders. J Neurosci, 28 (43): 11079-88. [PMID:18945915]
26. Estacion M, Han C, Choi JS, Hoeijmakers JG, Lauria G, Drenth JP, Gerrits MM, Dib-Hajj SD, Faber CG, Merkies IS et al.. (2011) Intra- and interfamily phenotypic diversity in pain syndromes associated with a gain-of-function variant of NaV1.7. Mol Pain, 7: 92. [PMID:22136189]
27. Estacion M, Harty TP, Choi JS, Tyrrell L, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2009) A sodium channel gene SCN9A polymorphism that increases nociceptor excitability. Ann Neurol, 66 (6): 862-6. [PMID:20033988]
28. Eubanks J, Srinivasan J, Dinulos MB, Disteche CM, Catterall WA. (1997) Structure and chromosomal localization of the beta2 subunit of the human brain sodium channel. Neuroreport, 8 (12): 2775-9. [PMID:9295116]
29. Faber CG, Hoeijmakers JG, Ahn HS, Cheng X, Han C, Choi JS, Estacion M, Lauria G, Vanhoutte EK, Gerrits MM et al.. (2012) Gain of function Naν1.7 mutations in idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. Ann Neurol, 71 (1): 26-39. [PMID:21698661]
30. Farmer C, Cox JJ, Fletcher EV, Woods CG, Wood JN, Schorge S. (2012) Splice variants of Na(V)1.7 sodium channels have distinct β subunit-dependent biophysical properties. PLoS ONE, 7 (7): e41750. [PMID:22911851]
31. Felts PA, Yokoyama S, Dib-Hajj S, Black JA, Waxman SG. (1997) Sodium channel alpha-subunit mRNAs I, II, III, NaG, Na6 and hNE (PN1): different expression patterns in developing rat nervous system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 45 (1): 71-82. [PMID:9105672]
32. Fertleman CR, Baker MD, Parker KA, Moffatt S, Elmslie FV, Abrahamsen B, Ostman J, Klugbauer N, Wood JN, Gardiner RM, Rees M. (2006) SCN9A mutations in paroxysmal extreme pain disorder: allelic variants underlie distinct channel defects and phenotypes. Neuron, 52 (5): 767-74. [PMID:17145499]
33. Fischer TZ, Gilmore ES, Estacion M, Eastman E, Taylor S, Melanson M, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2009) A novel Nav1.7 mutation producing carbamazepine-responsive erythromelalgia. Ann Neurol, 65 (6): 733-41. [PMID:19557861]
34. Focken T, Chowdhury S, Zenova A, Grimwood ME, Chabot C, Sheng T, Hemeon I, Decker SM, Wilson M, Bichler P et al.. (2018) Design of Conformationally Constrained Acyl Sulfonamide Isosteres: Identification of N-([1,2,4]Triazolo[4,3- a]pyridin-3-yl)methane-sulfonamides as Potent and Selective hNaV1.7 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Pain. J Med Chem, 61 (11): 4810-4831. [PMID:29737846]
35. Ghovanloo MR, Effraim PR, Tyagi S, Zhao P, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2024) Functionally-selective inhibition of threshold sodium currents and excitability in dorsal root ganglion neurons by cannabinol. Commun Biol, 7 (1): 120. [PMID:38263462]
36. Ghovanloo MR, Estacion M, Higerd-Rusli GP, Zhao P, Dib-Hajj S, Waxman SG. (2022) Inhibition of sodium conductance by cannabigerol contributes to a reduction of dorsal root ganglion neuron excitability. Br J Pharmacol, 179 (15): 4010-4030. [PMID:35297036]
37. Ghovanloo MR, Shuart NG, Mezeyova J, Dean RA, Ruben PC, Goodchild SJ. (2018) Inhibitory effects of cannabidiol on voltage-dependent sodium currents. J Biol Chem, 293 (43): 16546-16558. [PMID:30219789]
38. Ghovanloo MR, Tyagi S, Effraim PR, Waxman SG. (2025) In vitro inhibition of voltage-dependent sodium currents by the antifungal drug amorolfine. J Biol Chem, 301 (4): 108407. [PMID:40090585]
39. Goldberg YP, MacFarlane J, MacDonald ML, Thompson J, Dube MP, Mattice M, Fraser R, Young C, Hossain S, Pape T, Payne B, Radomski C, Donaldson G, Ives E, Cox J, Younghusband HB, Green R, Duff A, Boltshauser E, Grinspan GA, Dimon JH, Sibley BG, Andria G, Toscano E, Kerdraon J, Bowsher D, Pimstone SN, Samuels ME, Sherrington R, Hayden MR. (2007) Loss-of-function mutations in the Nav1.7 gene underlie congenital indifference to pain in multiple human populations. Clin Genet, 71 (4): 311-9. [PMID:17470132]
40. Han C, Dib-Hajj SD, Lin Z, Li Y, Eastman EM, Tyrrell L, Cao X, Yang Y, Waxman SG. (2009) Early- and late-onset inherited erythromelalgia: genotype-phenotype correlation. Brain, 132 (Pt 7): 1711-22. [PMID:19369487]
41. Han C, Hoeijmakers JG, Ahn HS, Zhao P, Shah P, Lauria G, Gerrits MM, te Morsche RH, Dib-Hajj SD, Drenth JP et al.. (2012) Nav1.7-related small fiber neuropathy: impaired slow-inactivation and DRG neuron hyperexcitability. Neurology, 78 (21): 1635-43. [PMID:22539570]
42. Han C, Hoeijmakers JG, Liu S, Gerrits MM, te Morsche RH, Lauria G, Dib-Hajj SD, Drenth JP, Faber CG, Merkies IS et al.. (2012) Functional profiles of SCN9A variants in dorsal root ganglion neurons and superior cervical ganglion neurons correlate with autonomic symptoms in small fibre neuropathy. Brain, 135 (Pt 9): 2613-28. [PMID:22826602]
43. Han C, Rush AM, Dib-Hajj SD, Li S, Xu Z, Wang Y, Tyrrell L, Wang X, Yang Y, Waxman SG. (2006) Sporadic onset of erythermalgia: a gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7. Ann Neurol, 59 (3): 553-8. [PMID:16392115]
44. Harty TP, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Blackman R, Hisama FM, Rose JB, Waxman SG. (2006) Na(V)1.7 mutant A863P in erythromelalgia: effects of altered activation and steady-state inactivation on excitability of nociceptive dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci, 26 (48): 12566-75. [PMID:17135418]
45. Hinckley CA, Kuryshev Y, Sers A, Barre A, Buisson B, Naik H, Hajos M. (2021) Characterization of Vixotrigine, a Broad-Spectrum Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Blocker. Mol Pharmacol, 99 (1): 49-59. [PMID:33298520]
46. Hoeijmakers JG, Han C, Merkies IS, Macala LJ, Lauria G, Gerrits MM, Dib-Hajj SD, Faber CG, Waxman SG. (2012) Small nerve fibres, small hands and small feet: a new syndrome of pain, dysautonomia and acromesomelia in a kindred with a novel NaV1.7 mutation. Brain, 135 (Pt 2): 345-58. [PMID:22286749]
47. Huang J, Fan X, Jin X, Jo S, Zhang HB, Fujita A, Bean BP, Yan N. (2023) Cannabidiol inhibits Nav channels through two distinct binding sites. Nat Commun, 14 (1): 3613. [PMID:37330538]
48. Isom LL, De Jongh KS, Patton DE, Reber BF, Offord J, Charbonneau H, Walsh K, Goldin AL, Catterall WA. (1992) Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science, 256 (5058): 839-42. [PMID:1375395]
49. Isom LL, Ragsdale DS, De Jongh KS, Westenbroek RE, Reber BF, Scheuer T, Catterall WA. (1995) Structure and function of the beta 2 subunit of brain sodium channels, a transmembrane glycoprotein with a CAM motif. Cell, 83 (3): 433-42. [PMID:8521473]
50. Jarecki BW, Sheets PL, Jackson JO, Cummins TR. (2008) Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder mutations within the D3/S4-S5 linker of Nav1.7 cause moderate destabilization of fast inactivation. J Physiol (Lond.), 586 (Pt 17): 4137-53. [PMID:18599537]
51. Jarecki BW, Sheets PL, Xiao Y, Jackson JO, Cummins TR. (2009) Alternative splicing of Na(V)1.7 exon 5 increases the impact of the painful PEPD mutant channel I1461T. Channels (Austin), 3 (4): 259-67. [PMID:19633428]
52. Jo S, Bean BP. (2020) Lidocaine Binding Enhances Inhibition of Nav1.7 Channels by the Sulfonamide PF-05089771. Mol Pharmacol, 97 (6): 377-383. [PMID:32193331]
53. Kamei T, Kudo T, Yamane H, Ishibashi F, Takada Y, Honda S, Maezawa Y, Ikeda K, Oyamada Y. (2024) Unique electrophysiological property of a novel Nav1.7, Nav1.8, and Nav1.9 sodium channel blocker, ANP-230. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 721: 150126. [PMID:38776832]
54. Klugbauer N, Lacinova L, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F. (1995) Structure and functional expression of a new member of the tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-activated sodium channel family from human neuroendocrine cells. EMBO J, 14 (6): 1084-90. [PMID:7720699]
55. Kozak CA, Sangameswaran L. (1996) Genetic mapping of the peripheral sodium channel genes, Scn9a and Scn10a, in the mouse. Mamm Genome, 7 (10): 787-8. [PMID:8854872]
56. Lampert A, Dib-Hajj SD, Eastman EM, Tyrrell L, Lin Z, Yang Y, Waxman SG. (2009) Erythromelalgia mutation L823R shifts activation and inactivation of threshold sodium channel Nav1.7 to hyperpolarized potentials. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 390 (2): 319-24. [PMID:19800314]
57. Lampert A, Dib-Hajj SD, Tyrrell L, Waxman SG. (2006) Size matters: Erythromelalgia mutation S241T in Nav1.7 alters channel gating. J Biol Chem, 281 (47): 36029-35. [PMID:17008310]
58. Maertens C, Cuypers E, Amininasab M, Jalali A, Vatanpour H, Tytgat J. (2006) Potent modulation of the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 by OD1, a toxin from the scorpion Odonthobuthus doriae. Mol Pharmacol, 70 (1): 405-14. [PMID:16641312]
59. McClatchey AI, Cannon SC, Slaugenhaupt SA, Gusella JF. (1993) The cloning and expression of a sodium channel beta 1-subunit cDNA from human brain. Hum Mol Genet, 2 (6): 745-9. [PMID:8394762]
60. McCormack K, Santos S, Chapman ML, Krafte DS, Marron BE, West CW, Krambis MJ, Antonio BM, Zellmer SG, Printzenhoff D et al.. (2013) Voltage sensor interaction site for selective small molecule inhibitors of voltage-gated sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 110 (29): E2724-32. [PMID:23818614]
61. McKerrall SJ, Nguyen T, Lai KW, Bergeron P, Deng L, DiPasquale A, Chang JH, Chen J, Chernov-Rogan T, Hackos DH et al.. (2019) Structure- and Ligand-Based Discovery of Chromane Arylsulfonamide Nav1.7 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. J Med Chem, 62 (8): 4091-4109. [PMID:30943032]
62. Michiels JJ, te Morsche RH, Jansen JB, Drenth JP. (2005) Autosomal dominant erythermalgia associated with a novel mutation in the voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit Nav1.7. Arch Neurol, 62 (10): 1587-90. [PMID:16216943]
63. Minett MS, Nassar MA, Clark AK, Passmore G, Dickenson AH, Wang F, Malcangio M, Wood JN. (2012) Distinct Nav1.7-dependent pain sensations require different sets of sensory and sympathetic neurons. Nat Commun, 3: 791. [PMID:22531176]
64. Mulcahy JV, Pajouhesh H, Beckley JT, Delwig A, Du Bois J, Hunter JC. (2019) Challenges and Opportunities for Therapeutics Targeting the Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Isoform NaV1.7. J Med Chem, 62 (19): 8695-8710. [PMID:31012583]
65. Nguyen HN, Bregman H, Buchanan JL, Du B, Feric E, Huang L, Li X, Ligutti J, Liu D, Malmberg AB et al.. (2012) Discovery and optimization of aminopyrimidinones as potent and state-dependent Nav1.7 antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 22 (2): 1055-60. [PMID:22209205]
66. Patel MV, Peltier HM, Matulenko MA, Koenig JR, C Scanio MJ, Gum RJ, El-Kouhen OF, Fricano MM, Lundgaard GL, Neelands T et al.. (2022) Discovery of (R)-(3-fluoropyrrolidin-1-yl)(6-((5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl)oxy)quinolin-2-yl)methanone (ABBV-318) and analogs as small molecule Nav1.7/ Nav1.8 blockers for the treatment of pain. Bioorg Med Chem, 63: 116743. [PMID:35436748]
67. Reimann F, Cox JJ, Belfer I, Diatchenko L, Zaykin DV, McHale DP, Drenth JP, Dai F, Wheeler J, Sanders F et al.. (2010) Pain perception is altered by a nucleotide polymorphism in SCN9A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107 (11): 5148-53. [PMID:20212137]
68. Rush AM, Bräu ME, Elliott AA, Elliott JR. (1998) Electrophysiological properties of sodium current subtypes in small cells from adult rat dorsal root ganglia. J Physiol (Lond.), 511 ( Pt 3): 771-89. [PMID:9714859]
69. Sangameswaran L, Fish LM, Koch BD, Rabert DK, Delgado SG, Ilnicka M, Jakeman LB, Novakovic S, Wong K, Sze P et al.. (1997) A novel tetrodotoxin-sensitive, voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in rat and human dorsal root ganglia. J Biol Chem, 272 (23): 14805-9. [PMID:9169448]
70. Sheets PL, Heers C, Stoehr T, Cummins TR. (2008) Differential block of sensory neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels by lacosamide [(2R)-2-(acetylamino)-N-benzyl-3-methoxypropanamide], lidocaine, and carbamazepine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 326 (1): 89-99. [PMID:18378801]
71. Shen H, Liu D, Wu K, Lei J, Yan N. (2019) Structures of human Nav1.7 channel in complex with auxiliary subunits and animal toxins. Science, 363 (6433): 1303-1308. [PMID:30765606]
72. Shields SD, Cheng X, Uçeyler N, Sommer C, Dib-Hajj SD, Waxman SG. (2012) Sodium channel Na(v)1.7 is essential for lowering heat pain threshold after burn injury. J Neurosci, 32 (32): 10819-32. [PMID:22875917]
73. Shinozuka T, Kobayashi H, Suzuki S, Tanaka K, Karanjule N, Hayashi N, Tsuda T, Tokumaru E, Inoue M, Ueda K et al.. (2020) Discovery of DS-1971a, a Potent, Selective NaV1.7 Inhibitor. J Med Chem, 63 (18): 10204-10220. [PMID:32392056]
74. Singh NA, Pappas C, Dahle EJ, Claes LR, Pruess TH, De Jonghe P, Thompson J, Dixon M, Gurnett C, Peiffer A et al.. (2009) A role of SCN9A in human epilepsies, as a cause of febrile seizures and as a potential modifier of Dravet syndrome. PLoS Genet, 5 (9): e1000649. [PMID:19763161]
75. Staud R, Price DD, Janicke D, Andrade E, Hadjipanayis AG, Eaton WT, Kaplan L, Wallace MR. (2011) Two novel mutations of SCN9A (Nav1.7) are associated with partial congenital insensitivity to pain. Eur J Pain, 15 (3): 223-30. [PMID:20692858]
76. Sun S, Cohen CJ, Dehnhardt CM. (2014) Inhibitors of voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7: patent applications since 2010. Pharm Pat Anal, 3 (5): 509-21. [PMID:25374320]
77. Theile JW, Jarecki BW, Piekarz AD, Cummins TR. (2011) Nav1.7 mutations associated with paroxysmal extreme pain disorder, but not erythromelalgia, enhance Navbeta4 peptide-mediated resurgent sodium currents. J Physiol (Lond.), 589 (Pt 3): 597-608. [PMID:21115638]
78. Toledo-Aral JJ, Moss BL, He ZJ, Koszowski AG, Whisenand T, Levinson SR, Wolf JJ, Silos-Santiago I, Halegoua S, Mandel G. (1997) Identification of PN1, a predominant voltage-dependent sodium channel expressed principally in peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 94 (4): 1527-32. [PMID:9037087]
79. Vijayaragavan K, Boutjdir M, Chahine M. (2004) Modulation of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 peripheral nerve sodium channels by protein kinase A and protein kinase C. J Neurophysiol, 91 (4): 1556-69. [PMID:14657190]
80. Walker JR, Novick PA, Parsons WH, McGregor M, Zablocki J, Pande VS, Du Bois J. (2012) Marked difference in saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin affinity for the human nociceptive voltage-gated sodium channel (Nav1.7) [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109 (44): 18102-7. [PMID:23077250]
81. Wang L, Zellmer SG, Printzenhoff DM, Castle NA. (2018) PF-06526290 can both enhance and inhibit conduction through voltage-gated sodium channels. Br J Pharmacol, 175 (14): 2926-2939. [PMID:29791744]
82. Waxman SG, Dib-Hajj S. (2005) Erythermalgia: molecular basis for an inherited pain syndrome. Trends Mol Med, 11 (12): 555-62. [PMID:16278094]
83. Wu B, Murray JK, Andrews KL, Sham K, Long J, Aral J, Ligutti J, Amagasu S, Liu D, Zou A et al.. (2018) Discovery of Tarantula Venom-Derived NaV1.7-Inhibitory JzTx-V Peptide 5-Br-Trp24 Analogue AM-6120 with Systemic Block of Histamine-Induced Pruritis. J Med Chem, 61 (21): 9500-9512. [PMID:30346167]
84. Yang Y, Wang Y, Li S, Xu Z, Li H, Ma L, Fan J, Bu D, Liu B, Fan Z et al.. (2004) Mutations in SCN9A, encoding a sodium channel alpha subunit, in patients with primary erythermalgia. J Med Genet, 41 (3): 171-4. [PMID:14985375]
85. Yuan J, Matsuura E, Higuchi Y, Hashiguchi A, Nakamura T, Nozuma S, Sakiyama Y, Yoshimura A, Izumo S, Takashima H. (2013) Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type IID caused by an SCN9A mutation. Neurology, 80 (18): 1641-9. [PMID:23596073]












