GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Associated Proteins
- Functional Characteristics
- Ion Selectivity and Conductance
- Voltage Dependence
- Activators
- Inhibitors
- Gating Inhibitors
- Channel Blockers
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Functions
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- Gene Expression and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||||
| Species | TM | P Loops | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 6 | 1 | 553 | 1p22.3 | MCOLN3 | mucolipin TRP cation channel 3 | 5 |
| Mouse | 6 | 1 | 553 | 3 71.03 cM | Mcoln3 | mucolipin 3 | 5 |
| Rat | 6 | 1 | 553 | 2q44 | Mcoln3 | mucolipin TRP cation channel 3 | |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| Mucolipin3 | mucolipin 3 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q8TDD5 (Hs), Q8R4F0 (Mm) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL1293243 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000055732 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000036853 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000015024 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 55283 (Hs), 171166 (Mm), 308022 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000055732 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:55283 (Hs), mmu:171166 (Mm), rno:308022 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 607400 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q8TDD5 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_018298 (Hs), NM_134160 (Mm), NM_001012059 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_060768 (Hs), NP_598921 (Mm), NP_001012059 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q8TDD5 (Hs), Q8R4F0 (Mm) |
| Wikipedia | MCOLN3 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
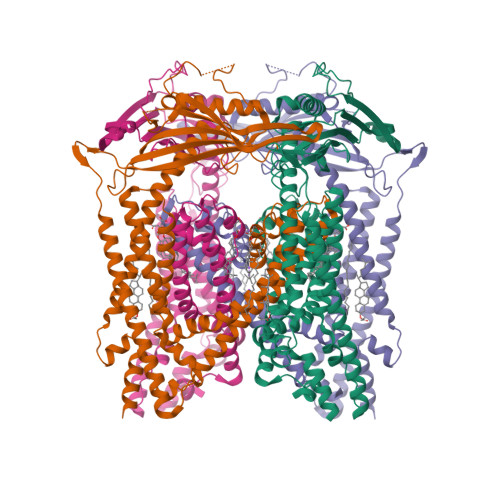
|
|
||||||||||
Associated Proteins  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ion Selectivity and Conductance Comments |
| The varitint-waddler mutation of mouse TRPML3 (A419P or Va mutation) is a non-selective inwardly rectifying ion channel permeant to Na+, K+, Cs+, Mg2+ and Ca2+, but does not conduct protons [8,23]. Ion selectivity rank order: Na+~ K+> Cs+ (pS=50 at negative voltages, [16,23] measured using the activation mutation A419P; Ca2+> Na+>K+>>Cs+>Sr2+ or Ba2+ or Mg2+ [13]. Wild type TRPML3 appears to primarily span intracellular membranes of lysosomes and endosomes. The current attributed to this channel in [16] may result from other plasma membrane TRP channels. |
| Voltage Dependence Comments |
| Strong inwardly rectifying, activation only at negative voltages: instantaneous but not time-dependent [23]. |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific activator tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Activator Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phosphatidyl (3,5) inositol bisphosphate [13] and ML SA1 [19] are both activators of TRPML3. Other synthetic activators of TRPML3 are SF-22, SF-23, SF-24, SF-31, SF-32, SF-33, SF-41, SF-51, SF-61, SF-71 and SF-81 [9]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gating Inhibitor Comments | ||
| High Na+ concentration (140mM, [9,12-13]), H+ (pH 6.42, extracellular or luminal side, [13]) and high concentrations of verapamil (1mM, [23]) all block TRPML3 activation. |
| Channel Blockers | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene Expression and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||
|
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||
|
References
1. Castiglioni AJ, Remis NN, Flores EN, García-Añoveros J. (2011) Expression and vesicular localization of mouse Trpml3 in stria vascularis, hair cells, and vomeronasal and olfactory receptor neurons. J Comp Neurol, 519 (6): 1095-114. [PMID:21344404]
2. Cuajungco MP, Samie MA. (2008) The varitint-waddler mouse phenotypes and the TRPML3 ion channel mutation: cause and consequence. Pflugers Arch, 457 (2): 463-73. [PMID:18504603]
3. Curcio-Morelli C, Zhang P, Venugopal B, Charles FA, Browning MF, Cantiello HF, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2010) Functional multimerization of mucolipin channel proteins. J Cell Physiol, 222 (2): 328-35. [PMID:19885840]
4. Deol MS. (1954) The anomalies of the labyrinth of the mutants varitint-waddler, shaker-2 and jerker in the mouse. Journal of Genetics, 52: 558.
5. Di Palma F, Belyantseva IA, Kim HJ, Vogt TF, Kachar B, Noben-Trauth K. (2002) Mutations in Mcoln3 associated with deafness and pigmentation defects in varitint-waddler (Va) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99 (23): 14994-9. [PMID:12403827]
6. Dong XP, Shen D, Wang X, Dawson T, Li X, Zhang Q, Cheng X, Zhang Y, Weisman LS, Delling M et al.. (2010) PI(3,5)P(2) controls membrane trafficking by direct activation of mucolipin Ca(2+) release channels in the endolysosome. Nat Commun, 1: 38. [PMID:20802798]
7. Grimm C. (2016) Endolysosomal Cation Channels as Therapeutic Targets—Pharmacology of TRPML Channels. Messenger, 5 (1/2): 30-36.
8. Grimm C, Cuajungco MP, van Aken AF, Schnee M, Jörs S, Kros CJ, Ricci AJ, Heller S. (2007) A helix-breaking mutation in TRPML3 leads to constitutive activity underlying deafness in the varitint-waddler mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (49): 19583-8. [PMID:18048323]
9. Grimm C, Jörs S, Guo Z, Obukhov AG, Heller S. (2012) Constitutive activity of TRPML2 and TRPML3 channels versus activation by low extracellular sodium and small molecules. J Biol Chem, 287 (27): 22701-8. [PMID:22753890]
10. Grimm C, Jörs S, Saldanha SA, Obukhov AG, Pan B, Oshima K, Cuajungco MP, Chase P, Hodder P, Heller S. (2010) Small molecule activators of TRPML3. Chem Biol, 17 (2): 135-48. [PMID:20189104]
11. Hirschi M, Herzik Jr MA, Wie J, Suo Y, Borschel WF, Ren D, Lander GC, Lee SY. (2017) Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the lysosomal calcium-permeable channel TRPML3. Nature, 550 (7676): 411-414. [PMID:29019979]
12. Kim HJ, Li Q, Tjon-Kon-Sang S, So I, Kiselyov K, Muallem S. (2007) Gain-of-function mutation in TRPML3 causes the mouse Varitint-Waddler phenotype. J Biol Chem, 282 (50): 36138-42. [PMID:17962195]
13. Kim HJ, Li Q, Tjon-Kon-Sang S, So I, Kiselyov K, Soyombo AA, Muallem S. (2008) A novel mode of TRPML3 regulation by extracytosolic pH absent in the varitint-waddler phenotype. EMBO J, 27 (8): 1197-205. [PMID:18369318]
14. Kim HJ, Soyombo AA, Tjon-Kon-Sang S, So I, Muallem S. (2009) The Ca(2+) channel TRPML3 regulates membrane trafficking and autophagy. Traffic, 10 (8): 1157-67. [PMID:19522758]
15. Martina JA, Lelouvier B, Puertollano R. (2009) The calcium channel mucolipin-3 is a novel regulator of trafficking along the endosomal pathway. Traffic, 10 (8): 1143-56. [PMID:19497048]
16. Nagata K, Zheng L, Madathany T, Castiglioni AJ, Bartles JR, García-Añoveros J. (2008) The varitint-waddler (Va) deafness mutation in TRPML3 generates constitutive, inward rectifying currents and causes cell degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 105 (1): 353-8. [PMID:18162548]
17. Rautenberg S, Keller M, Leser C, Chen CC, Bracher F, Grimm C. (2023) Expanding the Toolbox: Novel Modulators of Endolysosomal Cation Channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol, 278: 249-276. [PMID:35902436]
18. Rühl P, Rosato AS, Urban N, Gerndt S, Tang R, Abrahamian C, Leser C, Sheng J, Jha A, Vollmer G et al.. (2021) Estradiol analogs attenuate autophagy, cell migration and invasion by direct and selective inhibition of TRPML1, independent of estrogen receptors. Sci Rep, 11 (1): 8313. [PMID:33859333]
19. Shen D, Wang X, Li X, Zhang X, Yao Z, Dibble S, Dong XP, Yu T, Lieberman AP, Showalter HD et al.. (2012) Lipid storage disorders block lysosomal trafficking by inhibiting a TRP channel and lysosomal calcium release. Nat Commun, 3: 731. [PMID:22415822]
20. Spix B, Butz ES, Chen CC, Rosato AS, Tang R, Jeridi A, Kudrina V, Plesch E, Wartenberg P, Arlt E et al.. (2022) Lung emphysema and impaired macrophage elastase clearance in mucolipin 3 deficient mice. Nat Commun, 13 (1): 318. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-27860-x [PMID:35031603]
21. Venkatachalam K, Hofmann T, Montell C. (2006) Lysosomal localization of TRPML3 depends on TRPML2 and the mucolipidosis-associated protein TRPML1. J Biol Chem, 281 (25): 17517-27. [PMID:16606612]
22. Venugopal B, Mesires NT, Kennedy JC, Curcio-Morelli C, Laplante JM, Dice JF, Slaugenhaupt SA. (2009) Chaperone-mediated autophagy is defective in mucolipidosis type IV. J Cell Physiol, 219 (2): 344-53. [PMID:19117012]
23. Xu H, Delling M, Li L, Dong X, Clapham DE. (2007) Activating mutation in a mucolipin transient receptor potential channel leads to melanocyte loss in varitint-waddler mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 104 (46): 18321-6. [PMID:17989217]
24. Yamaguchi S, Jha A, Li Q, Soyombo AA, Dickinson GD, Churamani D, Brailoiu E, Patel S, Muallem S. (2011) Transient receptor potential mucolipin 1 (TRPML1) and two-pore channels are functionally independent organellar ion channels. J Biol Chem, 286 (26): 22934-42. [PMID:21540176]
25. Zeevi DA, Lev S, Frumkin A, Minke B, Bach G. (2010) Heteromultimeric TRPML channel assemblies play a crucial role in the regulation of cell viability models and starvation-induced autophagy. J Cell Sci, 123 (Pt 18): 3112-24. [PMID:20736310]








