Contents:
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | - | 848 | 7p21.1 | AHR | aryl hydrocarbon receptor | |
| Mouse | - | 848 | 12 15.78 cM | Ahr | aryl-hydrocarbon receptor | |
| Rat | - | 853 | 6q16 | Ahr | aryl hydrocarbon receptor | |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | P35869 (Hs), P30561 (Mm), P41738 (Rn) |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL3201 (Hs), CHEMBL6099 (Mm), CHEMBL5400 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000106546 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000019256 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000004342 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 196 (Hs), 11622 (Mm), 25690 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000106546 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:196 (Hs), mmu:11622 (Mm), rno:25690 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 600253 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P35869 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001621 (Hs), NM_001314027 (Mm), NM_001308254 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_001612 (Hs), NP_001300956 (Mm), NP_001295183 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | P35869 (Hs), P30561 (Mm), P41738 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | AHR (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||
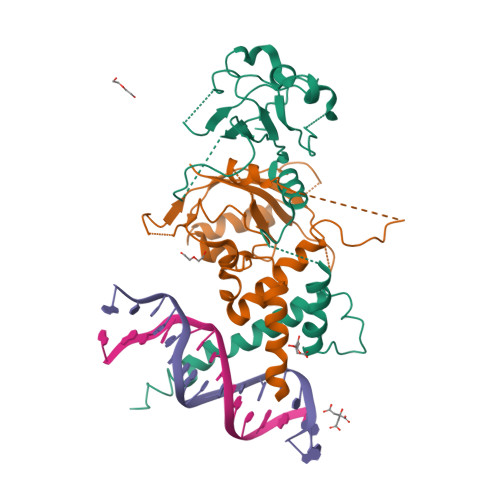
|
|
||||||||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Agonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonists | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immunopharmacology Comments |
| The AhR is activated by small signalling molecules derived from the diet, microorganisms and environmental agents, and when expressed by immune cells, it integrates the effects of the environment and metabolism on the immune response [9]. The AhR is a critical regulator of innate and adaptive immune responses that influences the balance of Th17 and Treg cells [2,7]. A role in environmentally-induced fibrosis is reported [11]. AhR is widely expressed in the skin where it is important for the development and maintenance of the skin barrier [12], and is also implicated in lung epithelial barrier immune surveillance [6,14]. AhR agonists are now being exploited for immunomodulatory potential, particulary for anti-inflammatory activity [3] in skin diseases like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis (see tapinarof for example [13]) [4,8,16]. The role of the AhR in modulating the immune response in health and disease is reviewed by Gutiérrez-Vázquez and Quintana (2018) [5]. |
| Immuno Process Associations | ||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
| General Comments |
| The AhR is a cytosolic ligand-activated transcription factor. It senses a wide range of endogenous and exogenous molecules, recruiting downstream pathways that impact on a variety of biological processes. |
References
1. Bjeldanes LF, Kim JY, Grose KR, Bartholomew JC, Bradfield CA. (1991) Aromatic hydrocarbon responsiveness-receptor agonists generated from indole-3-carbinol in vitro and in vivo: comparisons with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 88 (21): 9543-7. [PMID:1658785]
2. Bock KW. (2020) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) functions: Balancing opposing processes including inflammatory reactions. Biochem Pharmacol, 178: 114093. [PMID:32535108]
3. Di Meglio P, Duarte JH, Ahlfors H, Owens ND, Li Y, Villanova F, Tosi I, Hirota K, Nestle FO, Mrowietz U et al.. (2014) Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor dampens the severity of inflammatory skin conditions. Immunity, 40 (6): 989-1001. [PMID:24909886]
4. Gargaro M, Pirro M, Romani R, Zelante T, Fallarino F. (2016) Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Dependent Pathways in Immune Regulation. Am J Transplant, 16 (8): 2270-6. [PMID:26751261]
5. Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Quintana FJ. (2018) Regulation of the Immune Response by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor. Immunity, 48 (1): 19-33. [PMID:29343438]
6. Lee SM, Park HY, Suh YS, Yoon EH, Kim J, Jang WH, Lee WS, Park SG, Choi IW, Choi I et al.. (2017) Inhibition of acute lethal pulmonary inflammation by the IDO-AhR pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114 (29): E5881-E5890. [PMID:28673995]
7. Mascanfroni ID, Takenaka MC, Yeste A, Patel B, Wu Y, Kenison JE, Siddiqui S, Basso AS, Otterbein LE, Pardoll DM et al.. (2015) Metabolic control of type 1 regulatory T cell differentiation by AHR and HIF1-α. Nat Med, 21 (6): 638-46. [PMID:26005855]
8. Mulero-Navarro S, Fernandez-Salguero PM. (2016) New Trends in Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Biology. Front Cell Dev Biol, 4: 45. [PMID:27243009]
9. Rothhammer V, Quintana FJ. (2019) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: an environmental sensor integrating immune responses in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol, 19 (3): 184-197. [PMID:30718831]
10. Seok SH, Lee W, Jiang L, Molugu K, Zheng A, Li Y, Park S, Bradfield CA, Xing Y. (2017) Structural hierarchy controlling dimerization and target DNA recognition in the AHR transcriptional complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114 (21): 5431-5436. [PMID:28396409]
11. Shi Y, Zeng Z, Yu J, Tang B, Tang R, Xiao R. (2020) The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: An environmental effector in the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Pharmacol Res, 160: 105180. [PMID:32877693]
12. Smith KJ, Boyer JA, Muku GE, Murray IA, Gowda K, Desai D, Amin SG, Glick AB, Perdew GH. (2017) Editor's Highlight: Ah Receptor Activation Potentiates Neutrophil Chemoattractant (C-X-C Motif) Ligand 5 Expression in Keratinocytes and Skin. Toxicol Sci, 160 (1): 83-94. [PMID:28973351]
13. Smith SH, Jayawickreme C, Rickard DJ, Nicodeme E, Bui T, Simmons C, Coquery CM, Neil J, Pryor WM, Mayhew D et al.. (2017) Tapinarof Is a Natural AhR Agonist that Resolves Skin Inflammation in Mice and Humans. J Invest Dermatol, 137 (10): 2110-2119. [PMID:28595996]
14. Thatcher TH, Williams MA, Pollock SJ, McCarthy CE, Lacy SH, Phipps RP, Sime PJ. (2016) Endogenous ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulate lung dendritic cell function. Immunology, 147 (1): 41-54. [PMID:26555456]
15. Wilkinson IVL, Perkins KJ, Dugdale H, Moir L, Vuorinen A, Chatzopoulou M, Squire SE, Monecke S, Lomow A, Geese M et al.. (2020) Chemical Proteomics and Phenotypic Profiling Identifies the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor as a Molecular Target of the Utrophin Modulator Ezutromid. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 59 (6): 2420-2428. [PMID:31755636]
16. Zhou L. (2016) AHR Function in Lymphocytes: Emerging Concepts. Trends Immunol, 37 (1): 17-31. [PMID:26700314]
How to cite this page
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Last modified on 23/02/2021. Accessed on 26/04/2024. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY, https://www.guidetomalariapharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=2951.