GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: qinghaosu
Compound class:
Natural product
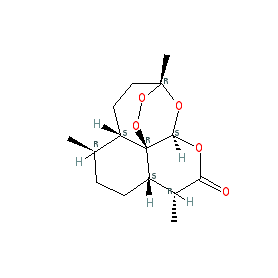
Comment: Artemisinin is a sesquiterpene lactone with an unusual endoperoxide bridge, believed to be responsible for the antimalarial activity of the compound. It is a natural product, isolated from the qinghao or sweet wormwood plant (Artemisia annua) and used in Chinese traditional medicine to treat fever.
Artemisinin is a prodrug that is converted to the active metabolite artenimol (dihydroartemisinin). We show one representation of artemisinin here. As with other natural products, there are alternative chemical structures due to the complex stereochemistry. The Malaria tab on this ligand page provides additional curator comments of relevance to the Guide to MALARIA PHARMACOLOGY. |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Delves M, Plouffe D, Scheurer C, Meister S, Wittlin S, Winzeler EA, Sinden RE, Leroy D. (2012)
The activities of current antimalarial drugs on the life cycle stages of Plasmodium: a comparative study with human and rodent parasites. PLoS Med, 9 (2): e1001169. [PMID:22363211] |
|
2. Duc DD, de Vries PJ, Nguyen XK, Le Nguyen B, Kager PA, van Boxtel CJ. (1994)
The pharmacokinetics of a single dose of artemisinin in healthy Vietnamese subjects. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 51 (6): 785-90. [PMID:7810812] |
|
3. Geng Y, Li W, Wong NK, Xue F, Li Q, Zhang Y, Xu J, Deng Z, Zhou Y. (2024)
Discovery of Artemisinins as Microsomal Prostaglandins Synthase-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer via Chemoproteomics. J Med Chem, 67 (3): 2083-2094. [PMID:38287228] |
|
4. Li W, Zhou Y, Tang G, Xiao Y. (2016)
Characterization of the Artemisinin Binding Site for Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) by Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry. Bioconjug Chem, 27 (12): 2828-2833. [PMID:27998071] |
|
5. Lynes EM, Bui M, Yap MC, Benson MD, Schneider B, Ellgaard L, Berthiaume LG, Simmen T. (2012)
Palmitoylated TMX and calnexin target to the mitochondria-associated membrane. EMBO J, 31 (2): 457-70. [PMID:22045338] |
|
6. Qiu N, Abegg D, Guidi M, Gilmore K, Seeberger PH, Adibekian A. (2022)
Artemisinin inhibits NRas palmitoylation by targeting the protein acyltransferase ZDHHC6. Cell Chem Biol, 29 (3): 530-537.e7. [PMID:34358442] |
|
7. Takusagawa F. (2013)
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase type 2 (mPGES2) is a glutathione-dependent heme protein, and dithiothreitol dissociates the bound heme to produce active prostaglandin E2 synthase in vitro. J Biol Chem, 288 (14): 10166-10175. [PMID:23426368] |
|
8. Tu Y. (2016)
Artemisinin-A Gift from Traditional Chinese Medicine to the World (Nobel Lecture). Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 55 (35): 10210-26. [PMID:27488942] |
|
9. Yamada T, Komoto J, Watanabe K, Ohmiya Y, Takusagawa F. (2005)
Crystal structure and possible catalytic mechanism of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase type 2 (mPGES-2). J Mol Biol, 348 (5): 1163-76. [PMID:15854652] |
|
10. Yamada T, Takusagawa F. (2007)
PGH2 degradation pathway catalyzed by GSH-heme complex bound microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase type 2: the first example of a dual-function enzyme. Biochemistry, 46 (28): 8414-24. [PMID:17585783] |
|
11. (2015)
Treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. In Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria. Third edition. (World Health Organization) . [PMID:26020088] [ISBN:9789241549127] |