GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
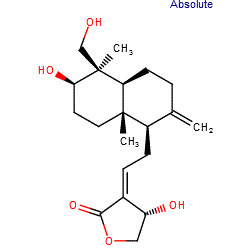
Comment: Andrographolide is a major component of the leaves of the traditionally used medicinal plant Andrographis paniculata (Acanthaceae) [6]. Andrographolide and analogues are being investigated for their potential anti-inflammatory activities [4], but andrographolide has also shown anti-viral, anti-thrombotic, hepatoprotective and anti-cancer properties [6]. Accumulated evidence indicates that the principal mechanism undelying andrographolide's anti-inflammatory action is inhibition of NF-κB. Additional studies show that Nrf2 activation by andrographolide likely enhances endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms. Direct covalent interaction with Cys62, and non-covalent binding are both required for andrographolide-induced inhibition of NF-κB p50 [3].
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Behrens M, Brockhoff A, Batram C, Kuhn C, Appendino G, Meyerhof W. (2009)
The human bitter taste receptor hTAS2R50 is activated by the two natural bitter terpenoids andrographolide and amarogentin. J Agric Food Chem, 57 (21): 9860-6. [PMID:19817411] |
|
2. Fotsing JR, Darmohusodo V, Patron AP, Ching BW, Brady T, Arellano M, Chen Q, Davis TJ, Liu H, Servant G et al.. (2020)
Discovery and Development of S6821 and S7958 as Potent TAS2R8 Antagonists. J Med Chem, 63 (9): 4957-4977. [PMID:32330040] |
|
3. Nguyen VS, Loh XY, Wijaya H, Wang J, Lin Q, Lam Y, Wong WS, Mok YK. (2015)
Specificity and inhibitory mechanism of andrographolide and its analogues as antiasthma agents on NF-κB p50. J Nat Prod, 78 (2): 208-17. [PMID:25615020] |
|
4. Peng S, Gao J, Liu W, Jiang C, Yang X, Sun Y, Guo W, Xu Q. (2016)
Andrographolide ameliorates OVA-induced lung injury in mice by suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Oncotarget, 7 (49): 80262-80274. [PMID:27793052] |
|
5. Roudnitzky N, Behrens M, Engel A, Kohl S, Thalmann S, Hübner S, Lossow K, Wooding SP, Meyerhof W. (2015)
Receptor Polymorphism and Genomic Structure Interact to Shape Bitter Taste Perception. PLoS Genet, 11 (9): e1005530. [PMID:26406243] |
|
6. Tan WSD, Liao W, Zhou S, Wong WSF. (2017)
Is there a future for andrographolide to be an anti-inflammatory drug? Deciphering its major mechanisms of action. Biochem Pharmacol, 139: 71-81. [PMID:28377280] |