GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
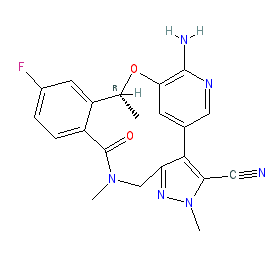
Synonyms: (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-4,8-methenopyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile | Lorbrena® | Lorviqua® | PF-06463922 | PF06463922
lorlatinib is an approved drug (FDA (2018), EMA (2019))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Lorlatinib (PF-06463922) is a kinase inhibitor with action on ALK and ROS1 proto-oncogenes [3,7]. It is a reversible, ATP-competitive small molecule inhibitor. Lorlatinib is a third generation ALK inhibitor designed to have improved blood-brain barrier penetrance compared to older second generation ALK inhibitors such as the approved drugs ceritinib, alectinib, and brigatinib, with the aim of better targeting metastatic NSCLC lesions in the brain. Advanced generation ALK inhibitors are those which target acquired ALK mutations resistant to the original first generation inhibitor crizotinib, which occur in virtually all AKL-rearranged NSCLC tumours within a year of starting crizotinib therapy. In fact, the cyano group of lortatinib is highly selective for the ALK mutation L1196M [4]. Facchinetti et al. (2016) [1] review the progress in ALK inhibitor development and discuss the importance of targeting therapies based on individual patient tumour profiles. Shaw et al.(2016) [5] publish a case report of a patient with metastatic ALK-rearranged NSCLC whose tumours acquired sequential resistance to crizotinib, ceritinib and finally lorlatinib. However, the patient subsequently showed a resensitization to crizotinib. This patient was identified in a substudy of Phase 1/2 clinical trial NCT01970865, which is designed to compare lorlatinib against crizotinib in advanced NSCLC harbouring specific molecular alterations, such as the lorlatinib resistance-conferring mutation L1198F. The molecular biology behind this pheomenon is outlined in the Nature Reviews Cancer Research Highlight commentary by Shipman (2016) [6].
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Facchinetti F, Tiseo M, Di Maio M, Graziano P, Bria E, Rossi G, Novello S. (2016)
Tackling ALK in non-small cell lung cancer: the role of novel inhibitors. Transl Lung Cancer Res, 5 (3): 301-21. [PMID:27413712] |
|
2. Helen Y. Zou HY, Engstrom LR, Li Q, Lu MW, Tang RW, Wang H, Tsaparikos K, Timofeevski S, Lam J, Yamazaki J et al.. (2013)
Abstract A277: PF-06463922, a novel ROS1/ALK inhibitor, demonstrates sub-nanomolar potency against oncogenic ROS1 fusions and capable of blocking the resistant ROS1G2032R mutant in preclinical tumor models. Mol Cancer Ther, (12): A277 Meeting abstract. |
|
3. Johnson TW, Richardson PF, Bailey S, Brooun A, Burke BJ, Collins MR, Cui JJ, Deal JG, Deng YL, Dinh D et al.. (2014)
Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J Med Chem, 57 (11): 4720-44. [PMID:24819116] |
|
4. Saha D, Kharbanda A, Yan W, Lakkaniga NR, Frett B, Li HY. (2020)
The Exploration of Chirality for Improved Druggability within the Human Kinome. J Med Chem, 63 (2): 441-469. [PMID:31550151] |
|
5. Shaw AT, Friboulet L, Leshchiner I, Gainor JF, Bergqvist S, Brooun A, Burke BJ, Deng YL, Liu W, Dardaei L et al.. (2016)
Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F. N Engl J Med, 374 (1): 54-61. [PMID:26698910] |
|
6. Shipman L. (2016)
Resistance: Crizotinib makes a comeback. Nat Rev Cancer, 16 (2): 69. [PMID:26797648] |
|
7. Zou HY, Li Q, Engstrom LD, West M, Appleman V, Wong KA, McTigue M, Deng YL, Liu W, Brooun A et al.. (2015)
PF-06463922 is a potent and selective next-generation ROS1/ALK inhibitor capable of blocking crizotinib-resistant ROS1 mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 112 (11): 3493-8. [PMID:25733882] |