GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
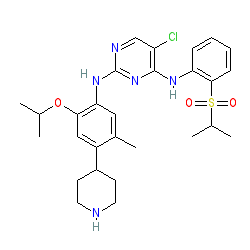
Synonyms: compound 15b [PMID 23742252] | LDK378 | NVP-LDK378-NX | Zykadia®
ceritinib is an approved drug (FDA (2014), EMA (2015))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Ceritinib is a novel, highly selective, second generation ALK inhibitor [2].
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: ceritinib |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Oroginally approved for the treatment of patients with non-small cell lung cancer with activating rearrangements in their ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) gene (aka ALK +ve NSCLC), who have previously been treated with crizotinib and in whom drug resistance has developed [3]. In May 2017, approval was expanded to cover all patients with ALK+ve NSCLC, including previously untreated patients. A list of clinical trials involving this drug, under its research code LDK378, is available at ClinicalTrials.gov. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a receptor tyrosine kinase of the insulin receptor superfamily. Ceritinib inhibits the activity of ALK in cancers driven by activating ALK gene rearrangements [2-3]. The drug discovery article by Marsilje et al (2014) reviews the types of activating ALK mutations so far identified in different neoplasms. Ceritinib (compound 15b in the article) has been designed to posess superior ALK selectivity and appears to be able to overcome the problem of crizotinib resistance, which may be caused by aquired mutation in the gatekeeper residue protecting the kinase ATP binding pocket (explanation of possible mechanisms in [4] and [1]). ALK selectivity is apparent across a large panel of tested kinases, with ceritinib having an IC50 of 0.2nM for ALK [2]. |
Pharmacokinetics  |
| Absorption/Distribution |
| Cmax is achieved approximately 6 hours after dosing, with steady-state drug level achieved by approximately day 15 [3]. |
| Biotransformation/Metabolism |
| Terminal half-life of ceritinib is approximately 40 hours [3]. |
| Population pharmacokinetics |
| Not yet dertermined. |
| Organ function impairment |
| Not yet dertermined. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Drugs.com European Medicines Agency (EMA) |