GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
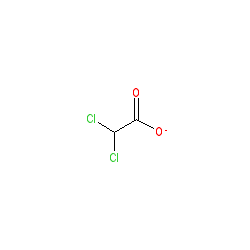
Abbreviated name: DCA
Synonyms: dichloroacetic acid
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Dichloroacetate (DCA) is an orally available small molecule pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor [4]. It acts as a metabolic regulator and has anti-cancer potential by promoting glucose oxidation over glycolysis, glycolysis being the metabolic pathway (Warburg effect) utilised by most cancer cells to resist apoptosis and gain proliferative advantage [1-3].
ChEMBL represents this compound without the charge (see link above). |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Evidence in the literature indicates that dichloroacetate was used to treat inherited mitochondrial disorders that result in lactic acidosis, pulmonary hypertension and several types of solid tumours. However, we can find no proof of marketing authorisations from the FDA, EMA or UK agencies. EMA orphan drug designation for the treatment of systemic monochloroacetate poisoning was withdrawn in 2008 at the request of the sponsor. There is one ongoing Phase 3 clinical trial in patients with pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency (NCT02616484) registered on ClinicalTrials.gov. An older Phase 2 study for metastatic breast cancer and lung cancer (NCT01029925) was terminated due to higher than expected risk/safety concerns. |
| Clinical Trials | |||||
| Clinical Trial ID | Title | Type | Source | Comment | References |
| NCT01029925 | Dichloroacetate (DCA) in Patients With Previously Treated Metastatic Breast or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCL) | Phase 2 Interventional | Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center | ||
| NCT02616484 | Trial of Dichloroacetate in Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Deficiency: | Phase 3 Interventional | University of Florida | ||