GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
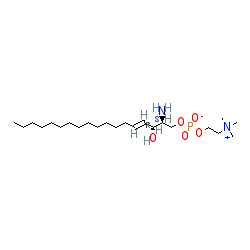
Abbreviated name: SPC
Synonyms: sphingosyl phosphorylcholine
Compound class:
Metabolite
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Davenport AP, Alexander SP, Sharman JL, Pawson AJ, Benson HE, Monaghan AE, Liew WC, Mpamhanga CP, Bonner TI, Neubig RR et al.. (2013)
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXXVIII. G protein-coupled receptor list: recommendations for new pairings with cognate ligands. Pharmacol Rev, 65 (3): 967-86. [PMID:23686350] |
|
2. Ignatov A, Lintzel J, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Kreienkamp HJ, Joost P, Thomsen S, Methner A, Schaller HC. (2003)
Role of the G-protein-coupled receptor GPR12 as high-affinity receptor for sphingosylphosphorylcholine and its expression and function in brain development. J Neurosci, 23 (3): 907-14. [PMID:12574419] |
|
3. No authors listed. (2005)
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine are ligands for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR4. (Retraction). J Biol Chem, 280 (52): 43280. [PMID:16498716] |
|
4. Russell JL, Goetsch SC, Aguilar HR, Coe H, Luo X, Liu N, van Rooij E, Frantz DE, Schneider JW. (2012)
Regulated expression of pH sensing G Protein-coupled receptor-68 identified through chemical biology defines a new drug target for ischemic heart disease. ACS Chem Biol, 7 (6): 1077-83. [PMID:22462679] |
|
5. Seuwen K, Ludwig MG, Wolf RM. (2006)
Receptors for protons or lipid messengers or both?. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 26 (5-6): 599-610. [PMID:17118800] |
|
6. Tobo A, Tobo M, Nakakura T, Ebara M, Tomura H, Mogi C, Im DS, Murata N, Kuwabara A, Ito S et al.. (2015)
Characterization of Imidazopyridine Compounds as Negative Allosteric Modulators of Proton-Sensing GPR4 in Extracellular Acidification-Induced Responses. PLoS ONE, 10 (6): e0129334. [PMID:26070068] |
|
7. Xu Y, Zhu K, Hong G, Wu W, Baudhuin LM, Xiao Y, Damron DS. (2000)
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine is a ligand for ovarian cancer G-protein-coupled receptor 1. Nat Cell Biol, 2 (5): 261-7 RETRACTED. [PMID:10806476] |
|
8. Xu Y, Zhu K, Hong G, Wu W, Baudhuin LM, Xiao Y, Damron DS. (2006)
Retraction. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine is a ligand for ovarian cancer G-protein-coupled receptor 1. Nat Cell Biol, 8 (3): 299. [PMID:16508674] |
|
9. Yang LV, Radu CG, Roy M, Lee S, McLaughlin J, Teitell MA, Iruela-Arispe ML, Witte ON. (2007)
Vascular abnormalities in mice deficient for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR4 that functions as a pH sensor. Mol Cell Biol, 27 (4): 1334-47. [PMID:17145776] |
|
10. Zhu K, Baudhuin LM, Hong G, Williams FS, Cristina KL, Kabarowski JH, Witte ON, Xu Y. (2001)
Sphingosylphosphorylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine are ligands for the G protein-coupled receptor GPR4. J Biol Chem, 276 (44): 41325-35 RETRACTED. [PMID:11535583] |