GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: Draxxin® (veterinary) | tulathromycin A
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
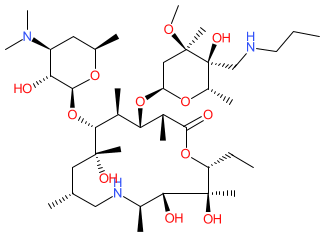
Comment: Tulathromycin is a macrolide (triamilide subclass) antibacterial that was developed for use in veterinary medicine [3]. It consists of an equilibrated mixture of a 15-membered and a 13-membered ring component in a 9:1 ratio [2]. We show the structure for tulathromycin A, the 15-membered isomer.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| The macrolide class of antibacterials inhibit protein synthesis by blocking function of the bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit. Tulathromycin binds to the same site on the ribosome as erythromycin and is not active against erythromycin-resistant ribosomes [4]. |