GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
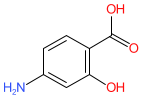
Synonyms: 4-aminosalicylic acid | Granupas® | p-aminosalicylic acid | Paser® | Rezipas®
para-aminosalicylic acid is an approved drug (FDA, EMA (2014))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Para-aminosalicylic acid is a structural analogue of 4-aminobenzoic acid (pABA) with activity against mycobacteria. It was one of the first drugs to be introduced as a treatment for tuberculosis (TB) [2-3].
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| In Mycobacterium tuberculosis, studies indicate that para-aminosalicylic acid acts as a prodrug that is bioactivated within the folate pathway, leading to disruption of folate synthesis by inhibition of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) [1,4]. |
External links  |
|
For extended ADME data see the following: Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) Drugs.com European Medicines Agency (EMA) |