GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Compound class:
Natural product
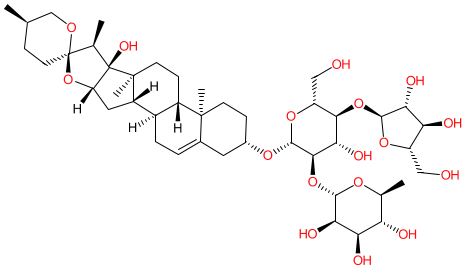
Comment: Polyphyllin H is a plant-derived saponin. Its chemical structure is taken from [2]. Polyphyllin H is reported as a bioactive component of the traditional Chinese herbal medicine Rhizoma Paridis (ChongLou in the Chinese Pharmacopeia) that is used to treat treat inflammation, infection, and bleeding. Studies have demonstrated a variety of Polyphyllin H-mediated pharmacological activities [1,3,5]. Most recently (2024), polyphyllin H was reported as an inhibitor of select Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) [4], behaving as a competitive inhibitor of CYPs 1A2 and 2D6 and a non-competitive inhibitor of CYP3A4. It is suggested that this mechanism may contribute to the hepatic toxicity of R. paridis extracts.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Li J, Jia J, Zhu W, Chen J, Zheng Q, Li D. (2023)
Therapeutic effects on cancer of the active ingredients in rhizoma paridis. Front Pharmacol, 14: 1095786. [PMID:36895945] |
|
2. Lu W, Pan M, Zhang P, Zheng T, Huang L, Ye F, Lei P. (2020)
The Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distributions of Nine Steroidal Saponins from Paris polyphylla in Rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 45 (5): 665-673. [PMID:32661907] |
|
3. Quan Q, Weng D, Li X, An Q, Yang Y, Yu B, Ma Y, Wang J. (2022)
Analysis of drug efficacy for inflammatory skin on an organ-chip system. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 10: 939629. [PMID:36118585] |
|
4. Wang E, Wang M, Gao M. (2024)
Probe substrates assay estimates the effect of polyphyllin H on the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes in human liver microsomes. Pharmacol Res Perspect, 12 (5): e70002. [PMID:39210686] |
|
5. Yang Y, Wang C, Wang J, Yang L, Lv Z, An Q, Wang Y, Shao X, Wang F, Huo T et al.. (2024)
Rhizoma Paridis saponins attenuate Gram-negative bacteria-induced inflammatory acne by binding to KEAP1 and modulating Nrf2 and MAPK pathways. J Cell Mol Med, 28 (6): e18146. [PMID:38426932] |