GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
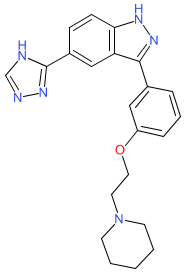
Synonyms: CC401
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: CC-401 was originally identified as a c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor. It was developed by Celgene who advanced it into clinical trial for anti-leukemia potential [3], but this programme was abandoned. CC-401 was subsequently found to inhibit DYRK1A and DYRK1B [1]. It promotes replication of pancreatic β-cells in vitro (rat and human) and in vivo (rat) via DYRK1A/B-dependent mechanisms.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Abdolazimi Y, Zhao Z, Lee S, Xu H, Allegretti P, Horton TM, Yeh B, Moeller HP, Nichols RJ, McCutcheon D et al.. (2018)
CC-401 Promotes β-Cell Replication via Pleiotropic Consequences of DYRK1A/B Inhibition. Endocrinology, 159 (9): 3143-3157. [PMID:29514186] |
|
2. Edupuganti R, Taliaferro JM, Wang Q, Xie X, Cho EJ, Vidhu F, Ren P, Anslyn EV, Bartholomeusz C, Dalby KN. (2017)
Discovery of a potent inhibitor of MELK that inhibits expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1 and TNBC cell growth. Bioorg Med Chem, 25 (9): 2609-2616. [PMID:28351607] |
|
3. Han SY. (2008)
c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Signaling Inhibitors Under Development. Toxicol Res, 24 (2): 93-100. [PMID:32038782] |