GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Constitutive androstane receptor
Target id: 607
Nomenclature: Constitutive androstane receptor
Systematic Nomenclature: NR1I3
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Activators
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- DNA Binding
- Main Co-regulators
- Main Target Genes
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- References
- Contributors
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||
| Species | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 352 | 1q23.3 | NR1I3 | nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 3 | 1 |
| Mouse | 358 | 1 79.21 cM | Nr1i3 | nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 3 | 2 |
| Rat | 358 | 13q24 | Nr1i3 | nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 3 | 22 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| CAR | Constitutive activator of retinoid response | orphan nuclear receptor MB67 | Care2 | CAR1 | MB67 | nuclear receptor subfamily 1 |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | Q14994 (Hs), Q3V008 (Mm), Q9QUS1 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 3.30.50.10 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL5503 (Hs), CHEMBL3509594 (Rn) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000143257 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000005677 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000003260 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 9970 (Hs), 12355 (Mm), 65035 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000143257 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:9970 (Hs), mmu:12355 (Mm), rno:65035 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 603881 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q14994 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_001077481 (Hs), NM_001243062 (Mm), NM_009803 (Mm), NM_001243063 (Mm), NM_022941 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_005113 (Hs), NP_033933 (Mm), NP_001229991 (Mm), NP_001229992 (Mm), NP_075230 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
6443 (in complex with androstenol) 6440 (in complex with CITCO) |
| UniProtKB | Q14994 (Hs), Q3V008 (Mm), Q9QUS1 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | NR1I3 (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
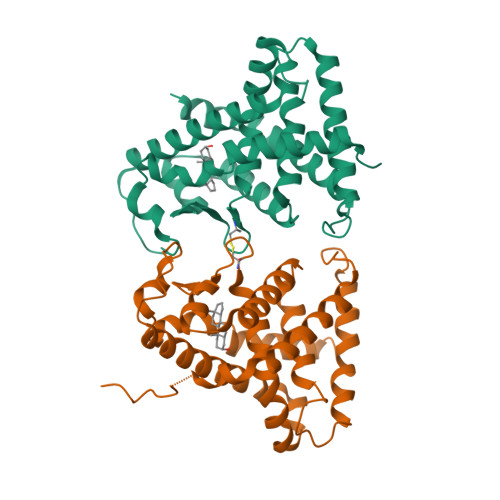
|
|
||||||||||||
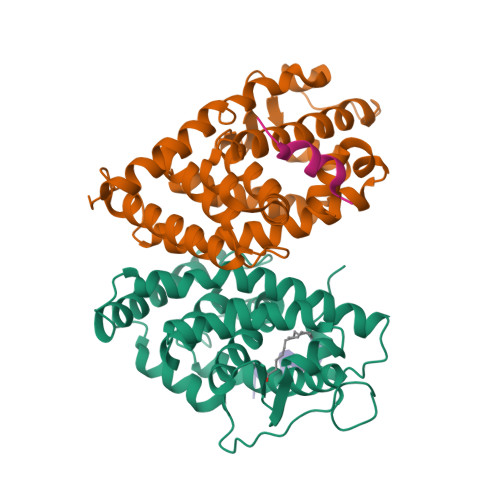
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| Comments: Xenobiotics and androstanes have been proposed as the natural ligands |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Activators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Agonists  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenobarbital, chlorpromazine [16] and acetoaminophen [23] can activate CAR, but they do not bind directly to CAR. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Antagonists  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clotrimazole has also been reported to have a pIC50 of 7.24 [11]. Meclizine and clotrimazole suppress hCAR transcriptional activity by about 50%, but androstanol and androstenol suppress mCAR activity almost completely at about 10μM. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DNA Binding  |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| DNA Binding Comments | |||||||
| It has been reported that CAR may bind DNA as monomers [4]. In addition to DR4, CAR may also bind to DR3/5 or ER6/8 [1,9,18]. | |||||||
Main Co-regulators  |
||||||
| Name | Activity | Specific | Ligand dependent | AF-2 dependent | Comments | References |
| NCOA1 | Co-activator | No | No | No | 3 | |
| MED1 | Co-activator | No | No | No | 8 | |
| PPARGC1A | Co-activator | No | No | No | 15 | |
Main Target Genes  |
|||||
| Name | Species | Effect | Technique | Comments | References |
| UGT1A1 | Human | Activated | Transient transfection, EMSA | 17 | |
| Mdm2 | Mouse | Activated | Transient transfection, EMSA, Other | 6 | |
| Abcc2 | Mouse | Activated | Transient transfection, EMSA | Human MRP2 is also a target gene | 9 |
| cytochrome P450 | None | Activated | Transient transfection, EMSA, Other | mCYP2B10, hCYP2B6, rCYP2B1, mCYP3A11, hCYP3A4, hCYP2C9 | 5 |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
| Tissue Distribution Comments | ||||||||
| Similar patterns are observed in mice. | ||||||||
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
1. Baes M, Gulick T, Choi HS, Martinoli MG, Simha D, Moore DD. (1994) A new orphan member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that interacts with a subset of retinoic acid response elements. Mol Cell Biol, 14 (3): 1544-52. [PMID:8114692]
2. Choi HS, Chung M, Tzameli I, Simha D, Lee YK, Seol W, Moore DD. (1997) Differential transactivation by two isoforms of the orphan nuclear hormone receptor CAR. J Biol Chem, 272 (38): 23565-71. [PMID:9295294]
3. Forman BM, Tzameli I, Choi HS, Chen J, Simha D, Seol W, Evans RM, Moore DD. (1998) Androstane metabolites bind to and deactivate the nuclear receptor CAR-beta. Nature, 395 (6702): 612-5. [PMID:9783588]
4. Frank C, Gonzalez MM, Oinonen C, Dunlop TW, Carlberg C. (2003) Characterization of DNA complexes formed by the nuclear receptor constitutive androstane receptor. J Biol Chem, 278 (44): 43299-310. [PMID:12896978]
5. Honkakoski P, Sueyoshi T, Negishi M. (2003) Drug-activated nuclear receptors CAR and PXR. Ann Med, 35 (3): 172-82. [PMID:12822739]
6. Huang W, Zhang J, Washington M, Liu J, Parant JM, Lozano G, Moore DD. (2005) Xenobiotic stress induces hepatomegaly and liver tumors via the nuclear receptor constitutive androstane receptor. Mol Endocrinol, 19 (6): 1646-53. [PMID:15831521]
7. Huang W, Zhang J, Wei P, Schrader WT, Moore DD. (2004) Meclizine is an agonist ligand for mouse constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) and an inverse agonist for human CAR. Mol Endocrinol, 18 (10): 2402-8. [PMID:15272053]
8. Jia Y, Guo GL, Surapureddi S, Sarkar J, Qi C, Guo D, Xia J, Kashireddi P, Yu S, Cho YW, Rao MS, Kemper B, Ge K, Gonzalez FJ, Reddy JK. (2005) Transcription coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-binding protein/mediator 1 deficiency abrogates acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102 (35): 12531-6. [PMID:16109766]
9. Kast HR, Goodwin B, Tarr PT, Jones SA, Anisfeld AM, Stoltz CM, Tontonoz P, Kliewer S, Willson TM, Edwards PA. (2002) Regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (ABCC2) by the nuclear receptors pregnane X receptor, farnesoid X-activated receptor, and constitutive androstane receptor. J Biol Chem, 277 (4): 2908-15. [PMID:11706036]
10. Liang D, Li L, Ai Y, Li Z, Hedrich WD, Sakamuru S, Lynch C, Yu W, Watts-Ouattara I, Heyward S et al.. (2025) Potent and Selective Human Constitutive Androstane Receptor Activator DL5055 Facilitates Cyclophosphamide-Based Chemotherapies. J Med Chem, 68 (7): 7044-7061. [PMID:40145447]
11. Maglich JM, Parks DJ, Moore LB, Collins JL, Goodwin B, Billin AN, Stoltz CA, Kliewer SA, Lambert MH, Willson TM, Moore JT. (2003) Identification of a novel human constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) agonist and its use in the identification of CAR target genes. J Biol Chem, 278 (19): 17277-83. [PMID:12611900]
12. Moore LB, Parks DJ, Jones SA, Bledsoe RK, Consler TG, Stimmel JB, Goodwin B, Liddle C, Blanchard SG, Willson TM, Collins JL, Kliewer SA. (2000) Orphan nuclear receptors constitutive androstane receptor and pregnane X receptor share xenobiotic and steroid ligands. J Biol Chem, 275 (20): 15122-7. [PMID:10748001]
13. Nishimura M, Naito S, Yokoi T. (2004) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human nuclear receptor subfamilies. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet, 19 (2): 135-49. [PMID:15499180]
14. Shan L, Vincent J, Brunzelle JS, Dussault I, Lin M, Ianculescu I, Sherman MA, Forman BM, Fernandez EJ. (2004) Structure of the murine constitutive androstane receptor complexed to androstenol: a molecular basis for inverse agonism. Mol Cell, 16 (6): 907-17. [PMID:15610734]
15. Shiraki T, Sakai N, Kanaya E, Jingami H. (2003) Activation of orphan nuclear constitutive androstane receptor requires subnuclear targeting by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha. A possible link between xenobiotic response and nutritional state. J Biol Chem, 278 (13): 11344-50. [PMID:12551939]
16. Sueyoshi T, Kawamoto T, Zelko I, Honkakoski P, Negishi M. (1999) The repressed nuclear receptor CAR responds to phenobarbital in activating the human CYP2B6 gene. J Biol Chem, 274 (10): 6043-6. [PMID:10037683]
17. Sugatani J, Kojima H, Ueda A, Kakizaki S, Yoshinari K, Gong QH, Owens IS, Negishi M, Sueyoshi T. (2001) The phenobarbital response enhancer module in the human bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1A1 gene and regulation by the nuclear receptor CAR. Hepatology, 33 (5): 1232-8. [PMID:11343253]
18. Tzameli I, Pissios P, Schuetz EG, Moore DD. (2000) The xenobiotic compound 1,4-bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene is an agonist ligand for the nuclear receptor CAR. Mol Cell Biol, 20 (9): 2951-8. [PMID:10757780]
19. Wei P, Zhang J, Dowhan DH, Han Y, Moore DD. (2002) Specific and overlapping functions of the nuclear hormone receptors CAR and PXR in xenobiotic response. Pharmacogenomics J, 2 (2): 117-26. [PMID:12049174]
20. Wei P, Zhang J, Egan-Hafley M, Liang S, Moore DD. (2000) The nuclear receptor CAR mediates specific xenobiotic induction of drug metabolism. Nature, 407 (6806): 920-3. [PMID:11057673]
21. Xu SZ, Zeng F, Boulay G, Grimm C, Harteneck C, Beech DJ. (2005) Block of TRPC5 channels by 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate: a differential, extracellular and voltage-dependent effect. Br J Pharmacol, 145 (4): 405-14. [PMID:15806115]
22. Yoshinari K, Sueyoshi T, Moore R, Negishi M. (2001) Nuclear receptor CAR as a regulatory factor for the sexually dimorphic induction of CYB2B1 gene by phenobarbital in rat livers. Mol Pharmacol, 59 (2): 278-84. [PMID:11160864]
23. Zhang J, Huang W, Chua SS, Wei P, Moore DD. (2002) Modulation of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by the xenobiotic receptor CAR. Science, 298 (5592): 422-4. [PMID:12376703]