1. Adamusiak AM, Stasikowska-Kanicka O, Lewandowska-Polak A, Danilewicz M, Wagrowska-Danilewicz M, Jankowski A, Kowalski ML, Pawliczak R. (2012) Expression of arachidonate metabolism enzymes and receptors in nasal polyps of aspirin-hypersensitive asthmatics.
Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 157 (4): 354-62.
[PMID:22123288]
2. Barajas-Espinosa A, Ni NC, Yan D, Zarini S, Murphy RC, Funk CD. (2012) The cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor mediates retinal edema and pathological neovascularization in a murine model of oxygen-induced retinopathy.
FASEB J, 26 (3): 1100-9.
[PMID:22131271]
3. Barajas-Espinosa A, Ochoa-Cortes F, Moos MP, Ramirez FD, Vanner SJ, Funk CD. (2011) Characterization of the cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor in novel expression sites of the gastrointestinal tract.
Am J Pathol, 178 (6): 2682-9.
[PMID:21641390]
4. Barrett NA, Fernandez JM, Maekawa A, Xing W, Li L, Parsons MW, Austen KF, Kanaoka Y. (2012) Cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor on dendritic cells negatively regulates ligand-dependent allergic pulmonary inflammation.
J Immunol, 189 (9): 4556-65.
[PMID:23002438]
5. Beller TC, Maekawa A, Friend DS, Austen KF, Kanaoka Y. (2004) Targeted gene disruption reveals the role of the cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor in increased vascular permeability and in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice.
J Biol Chem, 279 (44): 46129-34.
[PMID:15328359]
6. Capra V, Carnini C, Accomazzo MR, Di Gennaro A, Fiumicelli M, Borroni E, Brivio I, Buccellati C, Mangano P, Carnevali S et al.. (2015) Autocrine activity of cysteinyl leukotrienes in human vascular endothelial cells: Signaling through the CysLT₂ receptor.
Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat, 120: 115-25.
[PMID:25839425]
7. Capra V, Nicosia S, Ragnini D, Mezzetti M, Keppler D, Rovati GE. (1998) Identification and characterization of two cysteinyl-leukotriene high affinity binding sites with receptor characteristics in human lung parenchyma.
Mol Pharmacol, 53 (4): 750-8.
[PMID:9547367]
8. Carnini C, Accomazzo MR, Borroni E, Vitellaro-Zuccarello L, Durand T, Folco G, Rovati GE, Capra V, Sala A. (2011) Synthesis of cysteinyl leukotrienes in human endothelial cells: subcellular localization and autocrine signaling through the CysLT2 receptor.
FASEB J, 25 (10): 3519-28.
[PMID:21753081]
9. Ceraudo E, Horioka M, Mattheisen JM, Hitchman TD, Moore AR, Kazmi MA, Chi P, Chen Y, Sakmar TP, Huber T. (2021) Direct evidence that the GPCR CysLTR2 mutant causative of uveal melanoma is constitutively active with highly biased signaling.
J Biol Chem, 296: 100163.
[PMID:33288675]
10. Corrigan C, Mallett K, Ying S, Roberts D, Parikh A, Scadding G, Lee T. (2005) Expression of the cysteinyl leukotriene receptors cysLT(1) and cysLT(2) in aspirin-sensitive and aspirin-tolerant chronic rhinosinusitis.
J Allergy Clin Immunol, 115 (2): 316-22.
[PMID:15696087]
11. Dannull J, Schneider T, Lee WT, de Rosa N, Tyler DS, Pruitt SK. (2012) Leukotriene C4 induces migration of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells without loss of immunostimulatory function.
Blood, 119 (13): 3113-22.
[PMID:22323449]
12. Dartt DA, Hodges RR, Li D, Shatos MA, Lashkari K, Serhan CN. (2011) Conjunctival goblet cell secretion stimulated by leukotrienes is reduced by resolvins D1 and E1 to promote resolution of inflammation.
J Immunol, 186 (7): 4455-66.
[PMID:21357260]
13. Datta YH, Romano M, Jacobson BC, Golan DE, Serhan CN, Ewenstein BM. (1995) Peptido-leukotrienes are potent agonists of von Willebrand factor secretion and P-selectin surface expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Circulation, 92 (11): 3304-11.
[PMID:7586318]
14. Figueroa DJ, Borish L, Baramki D, Philip G, Austin CP, Evans JF. (2003) Expression of cysteinyl leukotriene synthetic and signalling proteins in inflammatory cells in active seasonal allergic rhinitis.
Clin Exp Allergy, 33 (10): 1380-8.
[PMID:14519144]
15. Fukai H, Ogasawara Y, Migita O, Koga M, Ichikawa K, Shibasaki M, Arinami T, Noguchi E. (2004) Association between a polymorphism in cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 on chromosome 13q14 and atopic asthma.
Pharmacogenetics, 14 (10): 683-90.
[PMID:15454733]
16. Gauvreau GM, Plitt JR, Baatjes A, MacGlashan DW. (2005) Expression of functional cysteinyl leukotriene receptors by human basophils.
J Allergy Clin Immunol, 116 (1): 80-7.
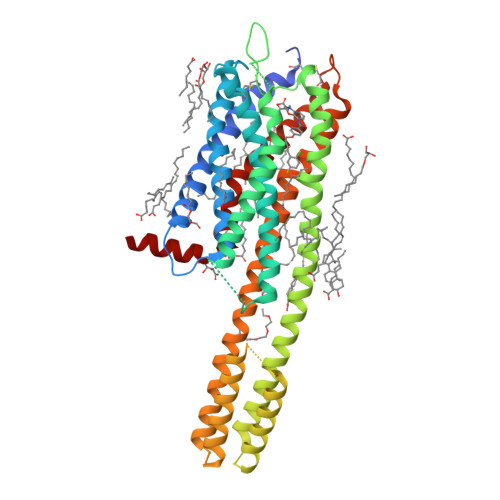
[PMID:15990778]
17. Gusach A, Luginina A, Marin E, Brouillette RL, Besserer-Offroy É, Longpré JM, Ishchenko A, Popov P, Patel N, Fujimoto T et al.. (2019) Structural basis of ligand selectivity and disease mutations in cysteinyl leukotriene receptors.
Nat Commun, 10 (1): 5573.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13348-2
[PMID:31811124]
18. Hasegawa S, Ichiyama T, Hashimoto K, Suzuki Y, Hirano R, Fukano R, Furukawa S. (2010) Functional expression of cysteinyl leukotriene receptors on human platelets.
Platelets, 21 (4): 253-9.
[PMID:20433311]
19. Heise CE, O'Dowd BF, Figueroa DJ, Sawyer N, Nguyen T, Im DS, Stocco R, Bellefeuille JN, Abramovitz M, Cheng R et al.. (2000) Characterization of the human cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor.
J Biol Chem, 275 (39): 30531-6.
[PMID:10851239]
20. Hu H, Chen G, Zhang JM, Zhang WP, Zhang L, Ge QF, Yao HT, Ding W, Chen Z, Wei EQ. (2005) Distribution of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 in human traumatic brain injury and brain tumors.
Acta Pharmacol Sin, 26 (6): 685-90.
[PMID:15916734]
21. Huang XJ, Zhang WP, Li CT, Shi WZ, Fang SH, Lu YB, Chen Z, Wei EQ. (2008) Activation of CysLT receptors induces astrocyte proliferation and death after oxygen-glucose deprivation.
Glia, 56 (1): 27-37.
[PMID:17910051]
22. Hui Y, Cheng Y, Smalera I, Jian W, Goldhahn L, Fitzgerald GA, Funk CD. (2004) Directed vascular expression of human cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor modulates endothelial permeability and systemic blood pressure.
Circulation, 110 (21): 3360-6.
[PMID:15545522]
23. Hui Y, Yang G, Galczenski H, Figueroa DJ, Austin CP, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Funk CD. (2001) The murine cysteinyl leukotriene 2 (CysLT2) receptor. cDNA and genomic cloning, alternative splicing, and in vitro characterization.
J Biol Chem, 276 (50): 47489-95.
[PMID:11591709]
24. Jiang W, Hall SR, Moos MP, Cao RY, Ishii S, Ogunyankin KO, Melo LG, Funk CD. (2008) Endothelial cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor expression mediates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Am J Pathol, 172 (3): 592-602.
[PMID:18276782]
25. Kamohara M, Takasaki J, Matsumoto M, Matsumoto Si, Saito T, Soga T, Matsushime H, Furuichi K. (2001) Functional characterization of cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT(2) receptor on human coronary artery smooth muscle cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 287 (5): 1088-92.
[PMID:11587533]
26. Klotsman M, York TP, Pillai SG, Vargas-Irwin C, Sharma SS, van den Oord EJ, Anderson WH. (2007) Pharmacogenetics of the 5-lipoxygenase biosynthetic pathway and variable clinical response to montelukast.
Pharmacogenet Genomics, 17 (3): 189-96.
[PMID:17460547]
27. Labat C, Ortiz JL, Norel X, Gorenne I, Verley J, Abram TS, Cuthbert NJ, Tudhope SR, Norman P, Gardiner P et al.. (1992) A second cysteinyl leukotriene receptor in human lung.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 263 (2): 800-5.
[PMID:1331415]
28. Lötzer K, Spanbroek R, Hildner M, Urbach A, Heller R, Bretschneider E, Galczenski H, Evans JF, Habenicht AJ. (2003) Differential leukotriene receptor expression and calcium responses in endothelial cells and macrophages indicate 5-lipoxygenase-dependent circuits of inflammation and atherogenesis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 23 (8): e32-6.
[PMID:12816882]
29. Magnusson C, Ehrnström R, Olsen J, Sjölander A. (2007) An increased expression of cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor in colorectal adenocarcinomas correlates with high differentiation.
Cancer Res, 67 (19): 9190-8.
[PMID:17909024]
30. Magnusson C, Mezhybovska M, Lörinc E, Fernebro E, Nilbert M, Sjölander A. (2010) Low expression of CysLT1R and high expression of CysLT2R mediate good prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Eur J Cancer, 46 (4): 826-35.
[PMID:20064706]
31. McIntyre TM, Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM. (1986) Leukotrienes C4 and D4 stimulate human endothelial cells to synthesize platelet-activating factor and bind neutrophils.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 83 (7): 2204-8.
[PMID:3457383]
32. Mechiche H, Candenas L, Pinto FM, Nazeyrollas P, Clément C, Devillier P. (2004) Characterization of cysteinyl leukotriene receptors on human saphenous veins: antagonist activity of montelukast and its metabolites.
J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 43 (1): 113-20.
[PMID:14668576]
33. Mellor EA, Frank N, Soler D, Hodge MR, Lora JM, Austen KF, Boyce JA. (2003) Expression of the type 2 receptor for cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLT2R) by human mast cells: Functional distinction from CysLT1R.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 100 (20): 11589-93.
[PMID:13679572]
34. Mita H, Hasegawa M, Saito H, Akiyama K. (2001) Levels of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor mRNA in human peripheral leucocytes: significantly higher expression of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 mRNA in eosinophils.
Clin Exp Allergy, 31 (11): 1714-23.
[PMID:11696047]
35. Ni NC, Yan D, Ballantyne LL, Barajas-Espinosa A, St Amand T, Pratt DA, Funk CD. (2011) A selective cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 antagonist blocks myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and vascular permeability in mice.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 339 (3): 768-78.
[PMID:21903747]
36. Nothacker HP, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Reinscheid RK, Lin SH, Civelli O. (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of a second human cysteinyl leukotriene receptor: discovery of a subtype selective agonist.
Mol Pharmacol, 58 (6): 1601-8.
[PMID:11093801]
37. Ogasawara H, Ishii S, Yokomizo T, Kakinuma T, Komine M, Tamaki K, Shimizu T, Izumi T. (2002) Characterization of mouse cysteinyl leukotriene receptors mCysLT1 and mCysLT2: differential pharmacological properties and tissue distribution.
J Biol Chem, 277 (21): 18763-8.
[PMID:11854273]
38. Ortiz JL, Gorenne I, Cortijo J, Seller A, Labat C, Sarria B, Abram TS, Gardiner PJ, Morcillo E, Brink C. (1995) Leukotriene receptors on human pulmonary vascular endothelium.
Br J Pharmacol, 115 (8): 1382-6.
[PMID:8564195]
39. Oyoshi MK, He R, Kanaoka Y, ElKhal A, Kawamoto S, Lewis CN, Austen KF, Geha RS. (2012) Eosinophil-derived leukotriene C4 signals via type 2 cysteinyl leukotriene receptor to promote skin fibrosis in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 109 (13): 4992-7.
[PMID:22416124]
40. Park JS, Chang HS, Park CS, Lee JH, Lee YM, Choi JH, Park HS, Kim LH, Park BL, Choi YH et al.. (2005) Association analysis of cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 2 (CYSLTR2) polymorphisms with aspirin intolerance in asthmatics.
Pharmacogenet Genomics, 15 (7): 483-92.
[PMID:15970796]
41. Pedersen KE, Bochner BS, Undem BJ. (1997) Cysteinyl leukotrienes induce P-selectin expression in human endothelial cells via a non-CysLT1 receptor-mediated mechanism.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 281 (2): 655-62.
[PMID:9152370]
42. Pillai SG, Cousens DJ, Barnes AA, Buckley PT, Chiano MN, Hosking LK, Cameron LA, Fling ME, Foley JJ, Green A et al.. (2004) A coding polymorphism in the CYSLT2 receptor with reduced affinity to LTD4 is associated with asthma.
Pharmacogenetics, 14 (9): 627-33.
[PMID:15475736]
43. Qi LL, Fang SH, Shi WZ, Huang XQ, Zhang XY, Lu YB, Zhang WP, Wei EQ. (2011) CysLT2 receptor-mediated AQP4 up-regulation is involved in ischemic-like injury through activation of ERK and p38 MAPK in rat astrocytes.
Life Sci, 88 (1-2): 50-6.
[PMID:21055410]
44. Rovati GE, Giovanazzi S, Mezzetti M, Nicosia S. (1992) Heterogeneity of binding sites for ICI 198,615 in human lung parenchyma.
Biochem Pharmacol, 44 (7): 1411-5.
[PMID:1329767]
45. Sheng WW, Li CT, Zhang WP, Yuan YM, Hu H, Fang SH, Zhang L, Wei EQ. (2006) Distinct roles of CysLT1 and CysLT2 receptors in oxygen glucose deprivation-induced PC12 cell death.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 346 (1): 19-25.
[PMID:16756959]
46. Shin JA, Chang HS, Park SM, Jang AS, Park SW, Park JS, Uh ST, Il Lim G, Rhim T, Kim MK et al.. (2009) Genetic effect of CysLTR2 polymorphisms on its mRNA synthesis and stabilization.
BMC Med Genet, 10: 106.
[PMID:19840403]
47. Shirasaki H, Kanaizumi E, Seki N, Fujita M, Kikuchi M, Himi T. (2013) Localization and up-regulation of cysteinyl leukotriene-2 receptor in human allergic nasal mucosa.
Allergol Int, 62 (2): 223-8.
[PMID:23524649]
48. Sjöström M, Johansson AS, Schröder O, Qiu H, Palmblad J, Haeggström JZ. (2003) Dominant expression of the CysLT2 receptor accounts for calcium signaling by cysteinyl leukotrienes in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 23 (8): e37-41.
[PMID:12816881]
49. Takasaki J, Kamohara M, Matsumoto M, Saito T, Sugimoto T, Ohishi T, Ishii H, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Kawai Y et al.. (2000) The molecular characterization and tissue distribution of the human cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT(2) receptor.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 274 (2): 316-22.
[PMID:10913337]
50. Thompson C, Cloutier A, Bossé Y, Poisson C, Larivée P, McDonald PP, Stankova J, Rola-Pleszczynski M. (2008) Signaling by the cysteinyl-leukotriene receptor 2. Involvement in chemokine gene transcription.
J Biol Chem, 283 (4): 1974-84.
[PMID:18048362]
51. Thompson MD, Storm van's Gravesande K, Galczenski H, Burnham WM, Siminovitch KA, Zamel N, Slutsky A, Drazen JM, George SR, Evans JF et al.. (2003) A cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor variant is associated with atopy in the population of Tristan da Cunha.
Pharmacogenetics, 13 (10): 641-9.
[PMID:14515063]
52. Tudhope SR, Cuthbert NJ, Abram TS, Jennings MA, Maxey RJ, Thompson AM, Norman P, Gardiner PJ. (1994) BAYu9773, a novel antagonist of cysteinyl-leukotrienes with activity against two receptor subtypes.
Eur J Pharmacol, 264: 317-323.
[PMID:7698171]
53. Uzonyi B, Lötzer K, Jahn S, Kramer C, Hildner M, Bretschneider E, Radke D, Beer M, Vollandt R, Evans JF et al.. (2006) Cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor and protease-activated receptor 1 activate strongly correlated early genes in human endothelial cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 103 (16): 6326-31.
[PMID:16606835]
54. Wang ML, Huang XJ, Fang SH, Yuan YM, Zhang WP, Lu YB, Ding Q, Wei EQ. (2006) Leukotriene D4 induces brain edema and enhances CysLT2 receptor-mediated aquaporin 4 expression.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 350 (2): 399-404.
[PMID:17010308]
55. Wunder F, Tinel H, Kast R, Geerts A, Becker EM, Kolkhof P, Hütter J, Ergüden J, Härter M. (2010) Pharmacological characterization of the first potent and selective antagonist at the cysteinyl leukotriene 2 (CysLT(2)) receptor.
Br J Pharmacol, 160 (2): 399-409.
[PMID:20423349]
56. Yan D, Stocco R, Sawyer N, Nesheim ME, Abramovitz M, Funk CD. (2011) Differential signaling of cysteinyl leukotrienes and a novel cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 (CysLT₂) agonist, N-methyl-leukotriene C₄, in calcium reporter and β arrestin assays.
Mol Pharmacol, 79 (2): 270-8.
[PMID:21078884]