GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Enzyme Reaction
- Inhibitors
- Antibodies
- Other Binding Ligands
- Immuno Process Associations
- Physiological Functions
- Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology
- Biologically Significant Variants
- General Comments
- References
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
||||||
| Species | TM | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | - | 692 | 1p32.3 | PCSK9 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 | |
| Mouse | - | 694 | 4 C7 | Pcsk9 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 | |
| Rat | - | 691 | 5q34 | Pcsk9 | proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 | |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| FH3 | Narc1 | neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 | proprotein convertase 9 | proprotein convertase PC9 |
Database Links  |
|
| Specialist databases | |
| MEROPS | S08.039 (Hs) |
| Other databases | |
| Alphafold | Q8NBP7 (Hs), Q80W65 (Mm), P59996 (Rn) |
| BRENDA | 3.4.21.- |
| CATH/Gene3D | 3.30.70.80, 3.40.50.200 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL2929 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000169174 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000044254 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000006280 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 255738 (Hs), 100102 (Mm), 298296 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000169174 (Hs) |
| KEGG Enzyme | 3.4.21.- |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:255738 (Hs), mmu:100102 (Mm), rno:298296 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 607786 (Hs) |
| Pharos | Q8NBP7 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_174936 (Hs), NM_153565 (Mm), NM_199253 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_777596 (Hs), NP_705793 (Mm), NP_954862 (Rn) |
| UniProtKB | Q8NBP7 (Hs), Q80W65 (Mm), P59996 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | PCSK9 (Hs) |
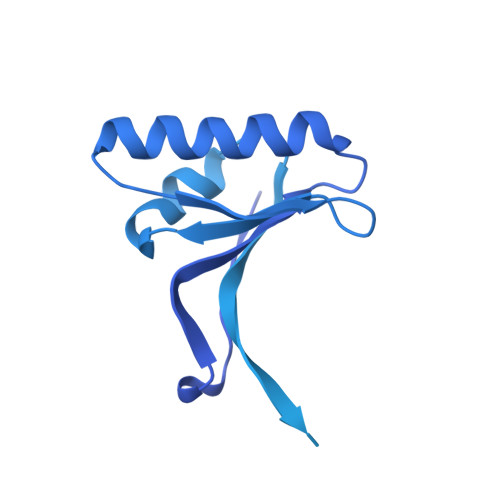
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Enzyme Reaction  |
||||
|
||||
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
| Inhibitors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antibodies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Binding Ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | Click column headers to sort | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immuno Process Associations | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Physiological Functions 
|
||||||||
|
Clinically-Relevant Mutations and Pathophysiology 
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biologically Significant Variants 
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Biologically Significant Variant Comments | ||||||||||||||||
| Healthy individuals carrying the PCSK9 R46L variant exhibit lower plasma concentrations of PCSK9 [6]. |
| General Comments |
| Mature PCSK9 protein is secreted from hepatocytes. The enzyme acts to reduce the levels of LDL receptors by binding to local LDL receptor-cholesterol complexes, inducing their endocytic internalisation and degradation [5,10,14-16,22]. This function of PCSK9 helps to modulate LDL metabolism. Inhibition of PCSK9 results in increased numbers of LDL receptors on hepatocyte membranes [11] which promotes LDL clearance. PCSK9 is being actively pursued as a mechanistic target for the development of novel agents to treat hypercholesterolemia, especially for patients who do not respond to or don't tolerate statin treatment. The focus to date has been on the development of anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies, and two such therapeutics have already reached the clinic, namely evolocumab and alirocumab [12]. Development of alternatives to the antibody-based PCSK9-inhibition strategy are the focus of multiple research projects [17]. In late 2020, the EMA approved Novartis' inclisiran (Leqvio®; ALN-60212) which is a first-in-class siRNA-based drug that reduces expression of PCSK9 and thereby lowers low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Leqvio® is indicated as a long-acting (administered twice yearly) treatment for hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia. FDA approval of Leqvio® followed in December 2021. MK-0616 is a small molecule PCSK9-targeting drug that has demonstrated therapeutic efficacy in humans [4]. |
References
1. Abdel-Meguid SS, Elshourbagy NA, Meyers HV, Mousa SA. (2017) Anti-proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (anti-pcsk9) compounds and methods of using the same in the treatment and/or prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Patent number: WO2017222953A1. Assignee: Shifa Biomedical Corporation. Priority date: 21/06/2016. Publication date: 28/12/2017.
2. Abifadel M, Elbitar S, El Khoury P, Ghaleb Y, Chémaly M, Moussalli ML, Rabès JP, Varret M, Boileau C. (2014) Living the PCSK9 Adventure: from the Identification of a New Gene in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Towards a Potential New Class of Anticholesterol Drugs. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 16 (9): 439. [PMID:25052769]
3. Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabès JP, Allard D, Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich D et al.. (2003) Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat Genet, 34 (2): 154-6. [PMID:12730697]
4. Ballantyne CM, Banka P, Mendez G, Garcia R, Rosenstock J, Rodgers A, Mendizabal G, Mitchel Y, Catapano AL. (2023) Phase 2b Randomized Trial of the Oral PCSK9 Inhibitor MK-0616. J Am Coll Cardiol, 81 (16): 1553-1564. [PMID:36889610]
5. DeVay RM, Shelton DL, Liang H. (2013) Characterization of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) trafficking reveals a novel lysosomal targeting mechanism via amyloid precursor-like protein 2 (APLP2). J Biol Chem, 288 (15): 10805-18. [PMID:23430252]
6. Humphries SE, Neely RD, Whittall RA, Troutt JS, Konrad RJ, Scartezini M, Li KW, Cooper JA, Acharya J, Neil A. (2009) Healthy individuals carrying the PCSK9 p.R46L variant and familial hypercholesterolemia patients carrying PCSK9 p.D374Y exhibit lower plasma concentrations of PCSK9. Clin Chem, 55 (12): 2153-61. [PMID:19797716]
7. Jackson SM, Shan B, Shen W, King CT. Antigen binding proteins to proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9). Patent number: US8030457. Assignee: Amgen, Inc.. Priority date: 23/08/2007. Publication date: 04/10/2011.
8. Johns DG, Campeau LC, Banka P, Bautmans A, Bueters T, Bianchi E, Branca D, Bulger PG, Crevecoeur I, Ding FX et al.. (2023) Orally Bioavailable Macrocyclic Peptide That Inhibits Binding of PCSK9 to the Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor. Circulation, 148 (2): 144-158. [PMID:37125593]
9. Liang H et al. Isolated antibody which specifically binds to PCSK9. Patent number: US8080243. Assignee: Rinat Neuroscience Corp., Pfizer Inc.. Priority date: 12/09/2008. Publication date: 20/12/2011.
10. Mbikay M, Mayne J, Chrétien M. (2013) Proprotein convertases subtilisin/kexin type 9, an enzyme turned escort protein: hepatic and extra hepatic functions. J Diabetes, 5 (4): 391-405. [PMID:23714205]
11. McNutt MC, Kwon HJ, Chen C, Chen JR, Horton JD, Lagace TA. (2009) Antagonism of secreted PCSK9 increases low density lipoprotein receptor expression in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem, 284 (16): 10561-70. [PMID:19224862]
12. Navarese EP, Kolodziejczak M, Schulze V, Gurbel PA, Tantry U, Lin Y, Brockmeyer M, Kandzari DE, Kubica JM, D'Agostino Sr RB et al.. (2015) Effects of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Antibodies in Adults With Hypercholesterolemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med, 163 (1): 40-51. [PMID:25915661]
13. Petrilli WL, Adam GC, Erdmann RS, Abeywickrema P, Agnani V, Ai X, Baysarowich J, Byrne N, Caldwell JP, Chang W et al.. (2020) From Screening to Targeted Degradation: Strategies for the Discovery and Optimization of Small Molecule Ligands for PCSK9. Cell Chem Biol, 27 (1): 32-40.e3. [PMID:31653597]
14. Qian YW, Schmidt RJ, Zhang Y, Chu S, Lin A, Wang H, Wang X, Beyer TP, Bensch WR, Li W et al.. (2007) Secreted PCSK9 downregulates low density lipoprotein receptor through receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Lipid Res, 48 (7): 1488-98. [PMID:17449864]
15. Seidah NG, Abifadel M, Prost S, Boileau C, Prat A. (2017) The Proprotein Convertases in Hypercholesterolemia and Cardiovascular Diseases: Emphasis on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9. Pharmacol Rev, 69 (1): 33-52. [PMID:27920219]
16. Seidah NG, Awan Z, Chrétien M, Mbikay M. (2014) PCSK9: a key modulator of cardiovascular health. Circ Res, 114 (6): 1022-36. [PMID:24625727]
17. Seidah NG, Prat A, Pirillo A, Catapano AL, Norata GD. (2019) Novel strategies to target proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9: beyond monoclonal antibodies. Cardiovasc Res, 115 (3): 510-518. [PMID:30629143]
18. Serrano-Wu MH, Chambers M, Goldsmith E, Tierney J, Jandu K, Clark D, Hinchcliffe P. (2022) PCSK9 inhibitors and methods of use thereof. Patent number: US11248001B2. Assignee: AstraZeneca AB. Priority date: 16/01/2020. Publication date: 15/02/2022.
19. Sleeman MW, Martin JH, Huang TT, MacDonald D. (2011) High affinity human antibodies to PCSK9. Patent number: US8062640. Assignee: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Priority date: 15/12/2008. Publication date: 22/11/2011.
20. Tang ZH, Peng J, Ren Z, Yang J, Li TT, Li TH, Wang Z, Wei DH, Liu LS, Zheng XL et al.. (2017) New role of PCSK9 in atherosclerotic inflammation promotion involving the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Atherosclerosis, 262: 113-122. [PMID:28535426]
21. Tsun A, Krauland E, Belk JP, Maio X, Zhang M, Boland N, Liu X, Yo D. (2022) Anti-PCSK9 antibody and use thereof. Patent number: US11485795B2. Assignee: Innovent Biologics Suzhou Co Ltd. Priority date: 03/04/2023. Publication date: 22/12/2017.
22. Wang Y, Huang Y, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC. (2012) Molecular characterization of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9-mediated degradation of the LDLR. J Lipid Res, 53 (9): 1932-43. [PMID:22764087]
How to cite this page
S8: Subtilisin: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9. Last modified on 10/06/2025. Accessed on 14/07/2025. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY, https://www.guidetomalariapharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=2388.