GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: ASO-10-27 | BIIB-058 | BIIB058 | Ionis-SMNrx | ISIS 396443 | ISIS SMNRx | ISIS-SMNRx | ISIS396443 | Spinraza®
nusinersen is an approved drug (FDA (2016), EMA (2017))
Compound class:
Nucleic acid
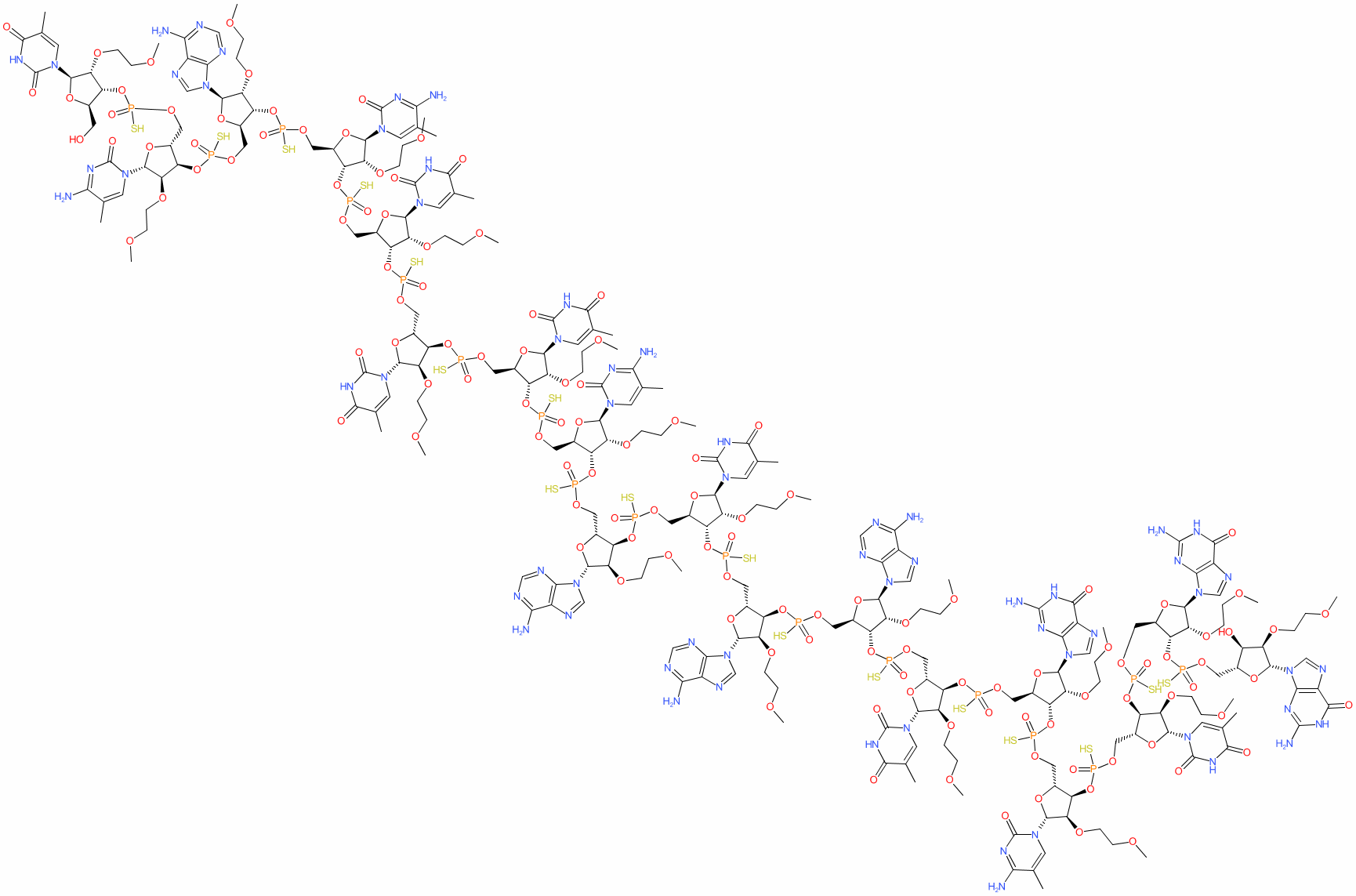
Comment: Nusinersen (ISIS 396443) is an antisense oligo(ribo)nucleotide (ASO) which induces survival motor neuron (SMN) protein expression from SMN2 genes with the exon 7-skipping mutation [7].
Nusinersen was initially available for use as a designated orphan drug (by the US FDA and EMA), and was the first drug to be fully approved for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The sequence contains 2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl) (2'-MOE)-oligoribonucleotides to reduce nuclease degradation and enhance binding affinity towards the complementary RNA. The full sequence is [2'-O-(2-methoxyethyl)](3'-5')(P-thio)(mU-mC-A-mC-mU-mU-mU-mC-A-mU-A-A-mU-G-mC-mU-G-G) as detailed in the INN record for the agent. The sequence for nusinersen is claimed in patent WO2010148249A1 as SEQ ID NO: 1 [1]. |
|
|||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Bennett CF, Hung G, Rigo F, Krainer AR, Hua Y, Passini MA, Shihabuddin L, Cheng SH, Klinger KW. (2010)
Compositions and methods for modulation of smn2 splicing in a subject. Patent number: WO2010148249A1. Assignee: Isis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Genzyme Corporation, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Priority date: 17/06/2009. Publication date: 23/12/2010. |
|
2. Chiriboga CA, Swoboda KJ, Darras BT, Iannaccone ST, Montes J, De Vivo DC, Norris DA, Bennett CF, Bishop KM. (2016)
Results from a phase 1 study of nusinersen (ISIS-SMN(Rx)) in children with spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology, 86 (10): 890-7. [PMID:26865511] |
|
3. Finkel RS, Chiriboga CA, Vajsar J, Day JW, Montes J, De Vivo DC, Yamashita M, Rigo F, Hung G, Schneider E et al.. (2017)
Treatment of infantile-onset spinal muscular atrophy with nusinersen: a phase 2, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet, 388 (10063): 3017-3026. [PMID:27939059] |
|
4. Finkel RS, Mercuri E, Darras BT, Connolly AM, Kuntz NL, Kirschner J, Chiriboga CA, Saito K, Servais L, Tizzano E et al.. (2017)
Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N Engl J Med, 377 (18): 1723-1732. [PMID:29091570] |
|
5. Mercuri E, Darras BT, Chiriboga CA, Day JW, Campbell C, Connolly AM, Iannaccone ST, Kirschner J, Kuntz NL, Saito K et al.. (2018)
Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Later-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N Engl J Med, 378 (7): 625-635. [PMID:29443664] |
|
6. Passini MA, Bu J, Richards AM, Kinnecom C, Sardi SP, Stanek LM, Hua Y, Rigo F, Matson J, Hung G et al.. (2011)
Antisense oligonucleotides delivered to the mouse CNS ameliorate symptoms of severe spinal muscular atrophy. Sci Transl Med, 3 (72): 72ra18. [PMID:21368223] |
|
7. Rigo F, Chun SJ, Norris DA, Hung G, Lee S, Matson J, Fey RA, Gaus H, Hua Y, Grundy JS et al.. (2014)
Pharmacology of a central nervous system delivered 2'-O-methoxyethyl-modified survival of motor neuron splicing oligonucleotide in mice and nonhuman primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 350 (1): 46-55. [PMID:24784568] |
|
8. Rigo F, Hua Y, Chun SJ, Prakash TP, Krainer AR, Bennett CF. (2012)
Synthetic oligonucleotides recruit ILF2/3 to RNA transcripts to modulate splicing. Nat Chem Biol, 8 (6): 555-61. [PMID:22504300] |