GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: BIM-22493 | Imcivree® | IRC-022493 | RM-493
setmelanotide is an approved drug (FDA (2020), EMA (2021))
Compound class:
Peptide
Comment: Setmelanotide is an agonist of melanocortin receptors, with approximately 20-fold selectivity for the melanocortin 4 receptor subtype [5]. Chemically it is an eight-amino-acid cyclic peptide, that is able to cross the blood-brain barrier when administered peripherally. Setmelanotide offers anti-obesity potential.
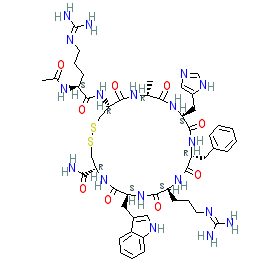
The INN record documents the sequence as N2-acetyl-L-arginyl-L-cysteinyl-D-alanyl-L-histidyl-D-phenylalanyl-L-arginyl-L-tryptophyl-L-cysteinamide, cyclic (2-8)-disulfide. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Phase 1 results from NCT01867437 indicated that short-term administration of setmelanotide (RM-493) increased resting energy expenditure and shifted substrate oxidation to fat [1]. A Phase 2 trial in an extremely restircted patient population with the ultra-rare disease, proopiomelanocortin deficiency (NCT02507492), reported a reduction in hyperphagia and substantial and sustained weight loss [6]. Phase 2 and 3 trials in patients with other genetic forms of obesity (e.g. leptin receptor deficiency, Prader-Willi syndrome, Bardet Biedl syndrome and Alström syndrome) are ongoing as of Jan 2019. Click here to link to ClinicalTrials.gov's full list of setmelanotide trials. Setmelanotide has not yet been found to cause hypertension, a common adverse effect reported with other melanocortin agonist drugs. One side-effect of setmelanotide treatment is darkening of the skin and hair, likely as a result of off-target activation of melanocortin receptors (MC1R) in peripheral melanoctyes. The FDA approved setmelanotide in 2020 to control pro-opiomelanocortin deficiency-associated hyperphagia and thereby treat the obesity that occurs in this rare, genetic, early-onset condition. In the EU, setmelanotide has been granted orphan designation for several rare genetic conditions, including pro-opiomelanocortin deficiency, Prader-Willi syndrome, Bardet Biedl syndrome, Alström syndrome and leptin receptor deficiency. In all of these conditions setmelanotide is proposed to restore appetite control and so reduce food intake and weight gain. EMA approval followed in July 2021. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) has a central role in the brain's regulation of appetite and energy control. That mutations in the gene encoding melanocortin receptor agonists, or the MC4R gene have been reported to cause obesity [4], confirms MC4R activation as a pharmacological intervention with potential benefit in obesity treatment [3]. Although not a deficiency of MC4R, proopiomelanocortin deficiency patients lack the hormones derived from proopiomelanocortin (adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and the melanocyte-stimulating hormones). So, in these patients setmelanotide is being used as hormone replacement therapy, to reinstate MC4R activity in the brain and regain control of appetite and energy expenditure. |