GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: staphylomycin S | virgimycin
Compound class:
Natural product
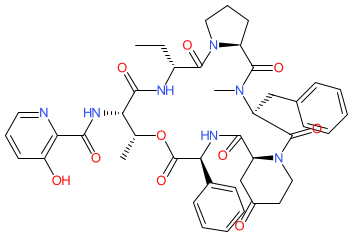
Comment: Virginiamycin S1 is a streptogramin antibacterial produced by a Streptomyces sp. related to S. virginiae [5]. It is isolated as part of a virginiamycin complex containing M components (M1 and M2) and S components (S1-S4)(reviewed in [1]). Virginiamycin S1 and pristinamycin IIA (virginiamycin M1) are the major components of virginiamycin [2], an antibacterial used in veterinary medicine and also in animal husbandry as a growth promoter.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Both components of virginiamycin bind to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, acting synergistically to inhibit protein synthesis [3]. |