GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Compound class:
Natural product
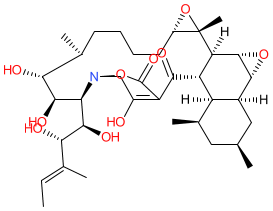
Comment: Alchivemycin A is a polycyclic polyketide that was isolated from a plant-associated actinomycete Streptomyces species [2]. Spectroscopic analysis and X-ray crystallography were used to define its structure and absolute stereo configuration. We drew the structure as depicted in [2], and the resulting SMILES mapped to the PubChem CID listed below. Alchivemycin A has antimicrobial and anticancer properties in vitro [2-5]. A complex total synthesis that integrated traditional chemical methods and biocatalysis using enzymes engineered from the source bacterium, has been reported [1].
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References |
|
1. Dong H, Guo N, Hu D, Hong B, Liao D, Zhu HJ, Yan ZY, Ge HM, Lei X. (2024)
Chemoenzymatic total synthesis of alchivemycin A. Nat Synth,. DOI: 10.1038/s44160-024-00577-7 |
|
2. Igarashi Y, Kim Y, In Y, Ishida T, Kan Y, Fujita T, Iwashita T, Tabata H, Onaka H, Furumai T. (2010)
Alchivemycin A, a bioactive polycyclic polyketide with an unprecedented skeleton from Streptomyces sp. Org Lett, 12 (15): 3402-5. [PMID:20670006] |
|
3. Kim Y, In Y, Ishida T, Onaka H, Igarashi Y. (2013)
Biosynthetic origin of alchivemycin A, a new polyketide from Streptomyces and absolute configuration of alchivemycin B. Org Lett, 15 (14): 3514-7. [PMID:23819828] |
|
4. Onaka H, Mori Y, Igarashi Y, Furumai T. (2011)
Mycolic acid-containing bacteria induce natural-product biosynthesis in Streptomyces species. Appl Environ Microbiol, 77 (2): 400-6. [PMID:21097597] |
|
5. Zhu HJ, Zhang B, Wei W, Liu SH, Xiang L, Zhu J, Jiao RH, Igarashi Y, Bashiri G, Liang Y et al.. (2022)
AvmM catalyses macrocyclization through dehydration/Michael-type addition in alchivemycin A biosynthesis. Nat Commun, 13 (1): 4499. [PMID:35922406] |