Retinoid X receptor-α
Target id: 610
Nomenclature: Retinoid X receptor-α
Systematic Nomenclature: NR2B1
Family: 2B. Retinoid X receptors
Contents:
- Gene and Protein Information
- Previous and Unofficial Names
- Database Links
- Selected 3D Structures
- Natural/Endogenous Ligands
- Agonists
- Antagonists
- Immuno Process Associations
- DNA Binding
- Co-binding Partners
- Main Co-regulators
- Tissue Distribution
- Functional Assays
- Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression
- Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models
- General Comments
- References
- How to cite this page
Gene and Protein Information  |
|||||
| Species | AA | Chromosomal Location | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Reference |
| Human | 462 | 9q34.2 | RXRA | retinoid X receptor alpha | 2,32,48 |
| Mouse | 467 | 2 19.38 cM | Rxra | retinoid X receptor alpha | 31,43-44,47 |
| Rat | 467 | 3p12 | Rxra | retinoid X receptor alpha | 25 |
Previous and Unofficial Names  |
| RXRα | nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group B member 1 | retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha | retinoid X receptor, alpha |
Database Links  |
|
| Alphafold | P19793 (Hs), P28700 (Mm), Q05343 (Rn) |
| CATH/Gene3D | 3.30.50.10 |
| ChEMBL Target | CHEMBL2061 (Hs), CHEMBL3084 (Mm), CHEMBL4431 (Rn) |
| DrugBank Target | P19793 (Hs) |
| Ensembl Gene | ENSG00000186350 (Hs), ENSMUSG00000015846 (Mm), ENSRNOG00000009446 (Rn) |
| Entrez Gene | 6256 (Hs), 20181 (Mm), 25271 (Rn) |
| Human Protein Atlas | ENSG00000186350 (Hs) |
| KEGG Gene | hsa:6256 (Hs), mmu:20181 (Mm), rno:25271 (Rn) |
| OMIM | 180245 (Hs) |
| Pharos | P19793 (Hs) |
| RefSeq Nucleotide | NM_002957 (Hs), NM_011305 (Mm), NM_012805 (Rn) |
| RefSeq Protein | NP_002948 (Hs), NP_035435 (Mm), NP_036937 (Rn) |
| SynPHARM |
6485 (in complex with alitretinoin) 6486 (in complex with bexarotene) |
| UniProtKB | P19793 (Hs), P28700 (Mm), Q05343 (Rn) |
| Wikipedia | RXRA (Hs) |
Selected 3D Structures  |
|||||||||||||
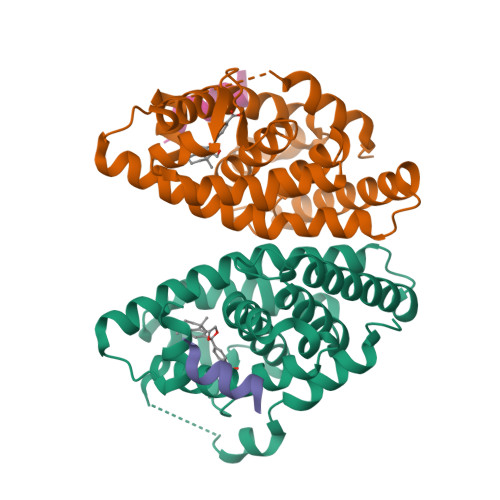
|
|
||||||||||||
Natural/Endogenous Ligands  |
| alitretinoin |
| docosahexaenoic acid |
Download all structure-activity data for this target as a CSV file 
Agonists  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific agonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| It is unclear whether docosahexaenoic acid and phytanic acid are bona fide endogenous ligands for RXR. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Antagonists  |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Key to terms and symbols | View all chemical structures | Click column headers to sort | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| View species-specific antagonist tables | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antagonist Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NB: LG100754 is a RXR:RXR antagonist, a RXR:PPARalpha agonist but also functions as a RXR:PPARgamma agonist [11]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Immuno Process Associations | ||
|
Co-binding Partners  |
|||
| Name | Interaction | Effect | Reference |
| Pregnane X receptor | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 5-6,37,42 |
| Thyroid hormone receptor-α | Physical, Functional | DNA binding (this is also true for TRβ) | 9,27,44 |
| Vitamin D receptor | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 9,27 |
| Retinoic acid receptor-α | Physical, Functional | DNA binding (also all the other RARs) | 4,9,26-27,38,44,75 |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 38,67 |
| Liver X receptor-α | Physical, Functional | DNA binding (and also all other LXRs) | 23,65,72-73 |
| Farnesoid X receptor | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 61 |
| Constitutive androstane receptor | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 3,17 |
| Nuclear receptor related 1 | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 57 |
| Nerve Growth factor IB | Physical, Functional | DNA binding | 24,57 |
Main Co-regulators  |
||||||
| Name | Activity | Specific | Ligand dependent | AF-2 dependent | Comments | References |
| NCOA1 | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 52,56 | |
| NCOA2 | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 68-69 | |
| NCOA3 | Co-activator | No | Yes | - | 15,52 | |
| PPARGC1A | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 19 | |
| MED1 | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 52,74 | |
| TBP | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 39,52,60 | |
| TAF4 | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 39,52,60 | |
| TAF11 | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 51 | |
| CREBBP | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 12,33 | |
| EP300 | Co-activator | No | Yes | Yes | 12 | |
Tissue Distribution 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Tissue Distribution Comments | ||||||||||
| RXRa2, an isoform, is specifically expressed in testis. Similar expression patterns are also seen in rodents. | ||||||||||
Functional Assays 
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
Physiological Consequences of Altering Gene Expression 
|
||||||||||
|
Phenotypes, Alleles and Disease Models 
|
Mouse data from MGI | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General Comments |
| Through its heterodimeric interaction with many other nuclear receptors, RXRα may play a role in a wide variety of diseases as well as in the control of multiple target genes. |
References
1. Allenby G, Bocquel MT, Saunders M, Kazmer S, Speck J, Rosenberger M, Lovey A, Kastner P, Grippo JF, Chambon P. (1993) Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (1): 30-4. [PMID:8380496]
2. Almasan A, Mangelsdorf DJ, Ong ES, Wahl GM, Evans RM. (1994) Chromosomal localization of the human retinoid X receptors. Genomics, 20 (3): 397-403. [PMID:8034312]
3. Baes M, Gulick T, Choi HS, Martinoli MG, Simha D, Moore DD. (1994) A new orphan member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that interacts with a subset of retinoic acid response elements. Mol Cell Biol, 14 (3): 1544-52. [PMID:8114692]
4. Berrodin TJ, Marks MS, Ozato K, Linney E, Lazar MA. (1992) Heterodimerization among thyroid hormone receptor, retinoic acid receptor, retinoid X receptor, chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor, and an endogenous liver protein. Mol Endocrinol, 6 (9): 1468-78. [PMID:1331778]
5. Blumberg B, Kang H, Bolado J, Chen H, Craig AG, Moreno TA, Umesono K, Perlmann T, De Robertis EM, Evans RM. (1998) BXR, an embryonic orphan nuclear receptor activated by a novel class of endogenous benzoate metabolites. Genes Dev, 12 (9): 1269-77. [PMID:9573044]
6. Blumberg B, Sabbagh W, Juguilon H, Bolado J, van Meter CM, Ong ES, Evans RM. (1998) SXR, a novel steroid and xenobiotic-sensing nuclear receptor. Genes Dev, 12 (20): 3195-205. [PMID:9784494]
7. Boehm MF, McClurg MR, Pathirana C, Mangelsdorf D, White SK, Hebert J, Winn D, Goldman ME, Heyman RA. (1994) Synthesis of high specific activity [3H]-9-cis-retinoic acid and its application for identifying retinoids with unusual binding properties. J Med Chem, 37 (3): 408-14. [PMID:8308867]
8. Boehm MF, Zhang L, Badea BA, White SK, Mais DE, Berger E, Suto CM, Goldman ME, Heyman RA. (1994) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel retinoid X receptor-selective retinoids. J Med Chem, 37 (18): 2930-41. [PMID:8071941]
9. Bugge TH, Pohl J, Lonnoy O, Stunnenberg HG. (1992) RXR alpha, a promiscuous partner of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. EMBO J, 11 (4): 1409-18. [PMID:1314167]
10. Canan Koch SS, Dardashti LJ, Cesario RM, Croston GE, Boehm MF, Heyman RA, Nadzan AM. (1999) Synthesis of retinoid X receptor-specific ligands that are potent inducers of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Med Chem, 42 (4): 742-50. [PMID:10052980]
11. Cesario RM, Klausing K, Razzaghi H, Crombie D, Rungta D, Heyman RA, Lala DS. (2001) The rexinoid LG100754 is a novel RXR:PPARgamma agonist and decreases glucose levels in vivo. Mol Endocrinol, 15 (8): 1360-9. [PMID:11463859]
12. Chakravarti D, LaMorte VJ, Nelson MC, Nakajima T, Schulman IG, Juguilon H, Montminy M, Evans RM. (1996) Role of CBP/P300 in nuclear receptor signalling. Nature, 383 (6595): 99-103. [PMID:8779723]
13. Chawla A, Lazar MA. (1993) Induction of Rev-ErbA alpha, an orphan receptor encoded on the opposite strand of the alpha-thyroid hormone receptor gene, during adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem, 268 (22): 16265-9. [PMID:8344913]
14. Chawla A, Lazar MA. (1994) Peroxisome proliferator and retinoid signaling pathways co-regulate preadipocyte phenotype and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 91 (5): 1786-90. [PMID:8127882]
15. Chen H, Lin RJ, Schiltz RL, Chakravarti D, Nash A, Nagy L, Privalsky ML, Nakatani Y, Evans RM. (1997) Nuclear receptor coactivator ACTR is a novel histone acetyltransferase and forms a multimeric activation complex with P/CAF and CBP/p300. Cell, 90 (3): 569-80. [PMID:9267036]
16. Chiba H, Clifford J, Metzger D, Chambon P. (1997) Distinct retinoid X receptor-retinoic acid receptor heterodimers are differentially involved in the control of expression of retinoid target genes in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol, 17 (6): 3013-20. [PMID:9154799]
17. Choi HS, Chung M, Tzameli I, Simha D, Lee YK, Seol W, Moore DD. (1997) Differential transactivation by two isoforms of the orphan nuclear hormone receptor CAR. J Biol Chem, 272 (38): 23565-71. [PMID:9295294]
18. Clifford J, Chiba H, Sobieszczuk D, Metzger D, Chambon P. (1996) RXRalpha-null F9 embryonal carcinoma cells are resistant to the differentiation, anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of retinoids. EMBO J, 15 (16): 4142-55. [PMID:8861943]
19. Delerive P, Wu Y, Burris TP, Chin WW, Suen CS. (2002) PGC-1 functions as a transcriptional coactivator for the retinoid X receptors. J Biol Chem, 277 (6): 3913-7. [PMID:11714715]
20. Desvergne B, Wahli W. (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev, 20 (5): 649-88. [PMID:10529898]
21. Dollé P, Fraulob V, Kastner P, Chambon P. (1994) Developmental expression of murine retinoid X receptor (RXR) genes. Mech Dev, 45 (2): 91-104. [PMID:8199055]
22. Egea PF, Mitschler A, Moras D. (2002) Molecular recognition of agonist ligands by RXRs. Mol Endocrinol, 16 (5): 987-97. [PMID:11981034]
23. Feltkamp D, Wiebel FF, Alberti S, Gustafsson JA. (1999) Identification of a novel DNA binding site for nuclear orphan receptor OR1. J Biol Chem, 274 (15): 10421-9. [PMID:10187832]
24. Forman BM, Umesono K, Chen J, Evans RM. (1995) Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors. Cell, 81 (4): 541-50. [PMID:7758108]
25. Gearing KL, Göttlicher M, Teboul M, Widmark E, Gustafsson JA. (1993) Interaction of the peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor and retinoid X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 90 (4): 1440-4. [PMID:8381967]
26. Germain P, Iyer J, Zechel C, Gronemeyer H. (2002) Co-regulator recruitment and the mechanism of retinoic acid receptor synergy. Nature, 415 (6868): 187-92. [PMID:11805839]
27. Glass CK. (1994) Differential recognition of target genes by nuclear receptor monomers, dimers, and heterodimers. Endocr Rev, 15 (3): 391-407. [PMID:8076589]
28. Harmon MA, Boehm MF, Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ. (1995) Activation of mammalian retinoid X receptors by the insect growth regulator methoprene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (13): 6157-60. [PMID:7597096]
29. Heitel P, Gellrich L, Kalinowsky L, Heering J, Kaiser A, Ohrndorf J, Proschak E, Merk D. (2019) Computer-Assisted Discovery and Structural Optimization of a Novel Retinoid X Receptor Agonist Chemotype. ACS Med Chem Lett, 10 (2): 203-208. DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.8b00551 [PMID:30783504]
30. Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Dyck JA, Stein RB, Eichele G, Evans RM, Thaller C. (1992) 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell, 68 (2): 397-406. [PMID:1310260]
31. Hoopes CW, Taketo M, Ozato K, Liu Q, Howard TA, Linney E, Seldin MF. (1992) Mapping of the mouse Rxr loci encoding nuclear retinoid X receptors RXR alpha, RXR beta, and RXR gamma. Genomics, 14 (3): 611-7. [PMID:1358808]
32. Jones KA, Fitzgibbon J, Woodward KJ, Goudie D, Ferguson-Smith MA, Povey S, Wolfe J, Solomon E. (1993) Localization of the retinoid X receptor alpha gene (RXRA) to chromosome 9q34. Ann Hum Genet, 57 (Pt 3): 195-201. [PMID:8257089]
33. Kamei Y, Xu L, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Kurokawa R, Gloss B, Lin SC, Heyman RA, Rose DW, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG. (1996) A CBP integrator complex mediates transcriptional activation and AP-1 inhibition by nuclear receptors. Cell, 85 (3): 403-14. [PMID:8616895]
34. Kastner P, Grondona JM, Mark M, Gansmuller A, LeMeur M, Decimo D, Vonesch JL, Dollé P, Chambon P. (1994) Genetic analysis of RXR alpha developmental function: convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell, 78 (6): 987-1003. [PMID:7923367]
35. Kastner P, Mark M, Chambon P. (1995) Nonsteroid nuclear receptors: what are genetic studies telling us about their role in real life?. Cell, 83 (6): 859-69. [PMID:8521510]
36. Kastner P, Messaddeq N, Mark M, Wendling O, Grondona JM, Ward S, Ghyselinck N, Chambon P. (1997) Vitamin A deficiency and mutations of RXRalpha, RXRbeta and RARalpha lead to early differentiation of embryonic ventricular cardiomyocytes. Development, 124 (23): 4749-58. [PMID:9428411]
37. Kliewer SA, Moore JT, Wade L, Staudinger JL, Watson MA, Jones SA, McKee DD, Oliver BB, Willson TM, Zetterström RH, Perlmann T, Lehmann JM. (1998) An orphan nuclear receptor activated by pregnanes defines a novel steroid signaling pathway. Cell, 92 (1): 73-82. [PMID:9489701]
38. Kliewer SA, Umesono K, Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. (1992) Retinoid X receptor interacts with nuclear receptors in retinoic acid, thyroid hormone and vitamin D3 signalling. Nature, 355 (6359): 446-9. [PMID:1310351]
39. Lala DS, Mukherjee R, Schulman IG, Koch SS, Dardashti LJ, Nadzan AM, Croston GE, Evans RM, Heyman RA. (1996) Activation of specific RXR heterodimers by an antagonist of RXR homodimers. Nature, 383 (6599): 450-3. [PMID:8837780]
40. Lampen A, Meyer S, Nau H. (2001) Phytanic acid and docosahexaenoic acid increase the metabolism of all-trans-retinoic acid and CYP26 gene expression in intestinal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1521 (1-3): 97-106. [PMID:11690641]
41. Lehmann JM, Jong L, Fanjul A, Cameron JF, Lu XP, Haefner P, Dawson MI, Pfahl M. (1992) Retinoids selective for retinoid X receptor response pathways. Science, 258 (5090): 1944-6. [PMID:1335166]
42. Lehmann JM, McKee DD, Watson MA, Willson TM, Moore JT, Kliewer SA. (1998) The human orphan nuclear receptor PXR is activated by compounds that regulate CYP3A4 gene expression and cause drug interactions. J Clin Invest, 102 (5): 1016-23. [PMID:9727070]
43. Leid M, Kastner P, Chambon P. (1992) Multiplicity generates diversity in the retinoic acid signalling pathways. Trends Biochem Sci, 17 (10): 427-33. [PMID:1333659]
44. Leid M, Kastner P, Lyons R, Nakshatri H, Saunders M, Zacharewski T, Chen JY, Staub A, Garnier JM, Mader S. (1992) Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell, 68 (2): 377-95. [PMID:1310259]
45. Lemotte PK, Keidel S, Apfel CM. (1996) Phytanic acid is a retinoid X receptor ligand. Eur J Biochem, 236 (1): 328-33. [PMID:8617282]
46. Levin AA, Sturzenbecker LJ, Kazmer S, Bosakowski T, Huselton C, Allenby G, Speck J, Kratzeisen C, Rosenberger M, Lovey A. (1992) 9-cis retinoic acid stereoisomer binds and activates the nuclear receptor RXR alpha. Nature, 355 (6358): 359-61. [PMID:1309942]
47. Mangelsdorf DJ, Borgmeyer U, Heyman RA, Zhou JY, Ong ES, Oro AE, Kakizuka A, Evans RM. (1992) Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev, 6 (3): 329-44. [PMID:1312497]
48. Mangelsdorf DJ, Ong ES, Dyck JA, Evans RM. (1990) Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature, 345 (6272): 224-9. [PMID:2159111]
49. Mark M, Chambon P. (2003) Functions of RARs and RXRs in vivo: genetic dissection of the retinoid signaling pathway. Pure Appl Chem, 75: 1709-1732.
50. Mark M, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P. (2006) Function of retinoid nuclear receptors: lessons from genetic and pharmacological dissections of the retinoic acid signaling pathway during mouse embryogenesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 46: 451-80. [PMID:16402912]
51. May M, Mengus G, Lavigne AC, Chambon P, Davidson I. (1996) Human TAF(II28) promotes transcriptional stimulation by activation function 2 of the retinoid X receptors. EMBO J, 15 (12): 3093-104. [PMID:8670810]
52. McKenna NJ, Lanz RB, O'Malley BW. (1999) Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr Rev, 20 (3): 321-44. [PMID:10368774]
53. Monczak Y, Trudel M, Lamph WW, Miller WH. (1997) Induction of apoptosis without differentiation by retinoic acid in PLB-985 cells requires the activation of both RAR and RXR. Blood, 90 (9): 3345-55. [PMID:9345016]
54. Nagy L, Thomázy VA, Shipley GL, Fésüs L, Lamph W, Heyman RA, Chandraratna RA, Davies PJ. (1995) Activation of retinoid X receptors induces apoptosis in HL-60 cell lines. Mol Cell Biol, 15 (7): 3540-51. [PMID:7791761]
55. Nakayama M, Yamada S, Ohsawa F, Ohta Y, Kawata K, Makishima M, Kakuta H. (2011) Discovery of a Potent Retinoid X Receptor Antagonist Structurally Closely Related to RXR Agonist NEt-3IB. ACS Med Chem Lett, 2 (12): 896-900. [PMID:24900278]
56. Oñate SA, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW. (1995) Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science, 270 (5240): 1354-7. [PMID:7481822]
57. Perlmann T, Jansson L. (1995) A novel pathway for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with NGFI-B and NURR1. Genes Dev, 9 (7): 769-82. [PMID:7705655]
58. Pogenberg V, Guichou JF, Vivat-Hannah V, Kammerer S, Pérez E, Germain P, de Lera AR, Gronemeyer H, Royer CA, Bourguet W. (2005) Characterization of the interaction between retinoic acid receptor/retinoid X receptor (RAR/RXR) heterodimers and transcriptional coactivators through structural and fluorescence anisotropy studies. J Biol Chem, 280 (2): 1625-33. [PMID:15528208]
59. Sakaki J, Konishi K, Kishida M, Gunji H, Kanazawa T, Uchiyama H, Fukaya H, Mitani H, Kimura M. (2007) Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of RXR antagonists based on the diazepinylbenzoic acid structure. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 17 (17): 4808-11. [PMID:17651969]
60. Schulman IG, Chakravarti D, Juguilon H, Romo A, Evans RM. (1995) Interactions between the retinoid X receptor and a conserved region of the TATA-binding protein mediate hormone-dependent transactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (18): 8288-92. [PMID:7667283]
61. Seol W, Choi HS, Moore DD. (1995) Isolation of proteins that interact specifically with the retinoid X receptor: two novel orphan receptors. Mol Endocrinol, 9 (1): 72-85. [PMID:7760852]
62. Sucov HM, Dyson E, Gumeringer CL, Price J, Chien KR, Evans RM. (1994) RXR alpha mutant mice establish a genetic basis for vitamin A signaling in heart morphogenesis. Genes Dev, 8 (9): 1007-18. [PMID:7926783]
63. Sucov HM, Izpisúa-Belmonte JC, Gañan Y, Evans RM. (1995) Mouse embryos lacking RXR alpha are resistant to retinoic-acid-induced limb defects. Development, 121 (12): 3997-4003. [PMID:8575300]
64. Takahashi B, Ohta K, Kawachi E, Fukasawa H, Hashimoto Y, Kagechika H. (2002) Novel retinoid X receptor antagonists: specific inhibition of retinoid synergism in RXR-RAR heterodimer actions. J Med Chem, 45 (16): 3327-30. [PMID:12139443]
65. Teboul M, Enmark E, Li Q, Wikström AC, Pelto-Huikko M, Gustafsson JA. (1995) OR-1, a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily that interacts with the 9-cis-retinoic acid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 92 (6): 2096-100. [PMID:7892230]
66. Thacher SM, Vasudevan J, Chandraratna RA. (2000) Therapeutic applications for ligands of retinoid receptors. Curr Pharm Des, 6 (1): 25-58. [PMID:10637371]
67. Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Spiegelman BM. (1994) mPPAR gamma 2: tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev, 8 (10): 1224-34. [PMID:7926726]
68. Voegel JJ, Heine MJ, Tini M, Vivat V, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H. (1998) The coactivator TIF2 contains three nuclear receptor-binding motifs and mediates transactivation through CBP binding-dependent and -independent pathways. EMBO J, 17 (2): 507-19. [PMID:9430642]
69. Voegel JJ, Heine MJ, Zechel C, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H. (1996) TIF2, a 160 kDa transcriptional mediator for the ligand-dependent activation function AF-2 of nuclear receptors. EMBO J, 15 (14): 3667-75. [PMID:8670870]
70. Vuligonda V, Thacher SM, Chandraratna RA. (2001) Enantioselective syntheses of potent retinoid X receptor ligands: differential biological activities of individual antipodes. J Med Chem, 44 (14): 2298-303. [PMID:11428923]
71. Wagner CE, Jurutka PW, Marshall PA, Groy TL, van der Vaart A, Ziller JW, Furmick JK, Graeber ME, Matro E, Miguel BV et al.. (2009) Modeling, synthesis and biological evaluation of potential retinoid X receptor (RXR) selective agonists: novel analogues of 4-[1-(3,5,5,8,8-pentamethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-naphthyl)ethynyl]benzoic acid (bexarotene). J Med Chem, 52 (19): 5950-66. [PMID:19791803]
72. Wiebel FF, Gustafsson JA. (1997) Heterodimeric interaction between retinoid X receptor alpha and orphan nuclear receptor OR1 reveals dimerization-induced activation as a novel mechanism of nuclear receptor activation. Mol Cell Biol, 17 (7): 3977-86. [PMID:9199332]
73. Willy PJ, Mangelsdorf DJ. (1997) Unique requirements for retinoid-dependent transcriptional activation by the orphan receptor LXR. Genes Dev, 11 (3): 289-98. [PMID:9030682]
74. Yuan CX, Ito M, Fondell JD, Fu ZY, Roeder RG. (1998) The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor- associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95 (14): 7939-44. [PMID:9653119]
75. Zhang XK, Lehmann J, Hoffmann B, Dawson MI, Cameron J, Graupner G, Hermann T, Tran P, Pfahl M. (1992) Homodimer formation of retinoid X receptor induced by 9-cis retinoic acid. Nature, 358 (6387): 587-91. [PMID:1323763]
76. Zhou H, Liu W, Su Y, Wei Z, Liu J, Kolluri SK, Wu H, Cao Y, Chen J, Wu Y et al.. (2010) NSAID sulindac and its analog bind RXRalpha and inhibit RXRalpha-dependent AKT signaling. Cancer Cell, 17 (6): 560-73. [PMID:20541701]
How to cite this page
2B. Retinoid X receptors: Retinoid X receptor-α. Last modified on 28/03/2019. Accessed on 01/11/2024. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY, https://www.guidetomalariapharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=610.