GtoPdb is requesting financial support from commercial users. Please see our sustainability page for more information.
|
Synonyms: HepFlush®
heparin is an approved drug (FDA (1939))
Compound class:
Metabolite
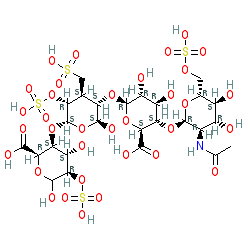
Comment: Heparin is an endogenous secretory glycosaminoglycan (GAG) that is released predominantly from connective tissue mast cells. Isolated heparin is used clinically as an anti-coagulant. Structurally, heparins (generally known as unfractionated heparin) are a heterogeneous group of anionic, sulfated GAGs. Commercial preparations usually vary in size from 12-15 kDa, while a low molecular weight (fractionated) versions are also available. Database entries may specify the sodium salt forms.
SARS-CoV-2: There is strong experimental evidence which shows that heparin interacts directly with GAG-binding motifs on the Spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 [3], and that inhibiting this interaction can reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection of host cells [6,8]. These findings suggest that heparin may offer repurposing potential as a prophylactic COVID-19 therapeutic [2], in addition to its benefit as a treatment for COVID-19-related thrombotic complications. Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Heparin is used clinically as an anti-coagulant. In response to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic plans are underway to evaluate haparin in COVID-19 patients, as part of the UK's Accelerating COVID-19 Research and Development (ACCORD) initiative (June 2020). ACCORD aims to fast-track potential treatments for COVID-19 through early-stage clinical trials [9]. In this setting heparin will primarily be acting classically as an anti-coagulant to reduce mortality caused by COVID-associated thromboembolic events [5,7]. It may also have non-anticoagulant activities that are beneficial in this disease [4]. |