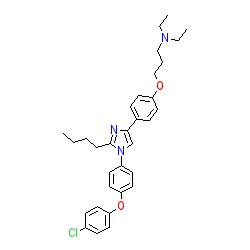
|
Synonyms: TTP488
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Azeliragon is an orally bioavailable small molecule that inhibits the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) [4-5].
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖ |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| Azeliragon is being assessed in Phase 2I clinical trial as a potential treatment for mild Alzheimer's disease (AD). The US FDA has granted azeliragon fast track designation, to expedite its route to approval, based on positive clinical outcomes from a Phase 2 trial [1]. |
Mechanism Of Action and Pharmacodynamic Effects  |
| Amyloid β (Aβ) uptake into the brain is dependent on RAGE [2]. Prolonged Aβ interaction with RAGE causes a chronic inflammation which is a crucial driver of amyloid plaque formation and chronic neuronal dysfunction. Thus RAGE is intimately linked to the pathogenesis of AD. Azeliragon antagonises the Aβ interaction with RAGE and is predicted to reduce Aβ accumulation in the brain, and has the potential to delay the formation of Aβ plaques. |