|
Synonyms: Bumex® | Burinex® | PF 1593 | Ro 10-6338
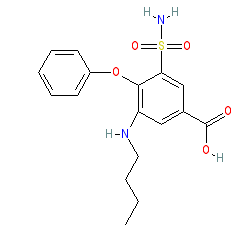
bumetanide is an approved drug (FDA (1983))
Compound class:
Synthetic organic
Comment: Bumetanide is a loop diuretic drug. It inhibits NKCC1 (SLC12A2) tranporters in the brain and kidney-specific NKCC2 (SLC12A1) transporters in the thick ascending limb of Henle's loop. The latter action modulates water and electrolyte homeostasis and is reponsible for the drug's diuretic effects.
Ligand Activity Visualisation ChartsThese are box plot that provide a unique visualisation, summarising all the activity data for a ligand taken from ChEMBL and GtoPdb across multiple targets and species. Click on a plot to see the median, interquartile range, low and high data points. A value of zero indicates that no data are available. A separate chart is created for each target, and where possible the algorithm tries to merge ChEMBL and GtoPdb targets by matching them on name and UniProt accession, for each available species. However, please note that inconsistency in naming of targets may lead to data for the same target being reported across multiple charts. ✖
View more information in the IUPHAR Pharmacology Education Project: bumetanide |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| No information available. |
Summary of Clinical Use  |
| A loop diuretic use to treat edema associated with heart failure, hepatic and renal disease. Diuretics and autism spectrum disorder (ASD) Treatment of autistic children and adolescents with bumetanide (Phase 3 trial NCT01078714) improves core ASD symptoms [2-3]. The mechanism is proposed (at least in part) to reflect the effect that bumetanide exerts on intracellular neuronal chloride levels and the consequences of this on GABAergic networks. In preclinical models bumetanide decreases interacellular chloride levels and promotes GABAergic mediated hyperpolarisation (inhibition). |